Tuesday, November 25, 2014
నేనుసైతం
Sunday, November 23, 2014
NEWS FOR UNEMPLOYEES
3.DEPT..BSNL
POST : JAO ,BASIC PAY:16400-40500
NO OF POSTS:962
LAST DATE TO APPLY : 1-12-2014 TO 31-12-2014
exam date :22-02-2015
WEB SITE :
DSC/TET CUM TRT
NO OF POSTS:10313
LAST DATE TO APPLY :
exam date : 9,10,11 OF MAY 2015
WEB SITE :
2.BANKS
NO OF POSTS:6425
LAST DATE TO APPLY : 09-12-2014
exam date : jan/feb 2015
WEB SITE : www.sbi.co.in and www.statebank ofindia.com
Wednesday, January 30, 2013
ముఖ చిత్రాలు
- Avantsa SomaSundar.jpg
180 KB - Damerla Rama Rao.jpg
2.71 MB - Durgabai Deshmukh.jpg
2.9 MB - Gurajada Venkata Apparao.jpg
3.08 MB - Gurram Jashua.jpg
2.92 MB - HaritaKata Rajahmundry.JPG
2.61 MB - Kandukuri Viresalingam.jpg
2.78 MB - Kshetrayya.jpg
1,006 KB - Madapati Hanumantha Rao.jpg
2.73 MB - Mutnuri Krishna Rao.jpg
2.79 MB - Portrait of Annamayya.JPG
4.23 MB - Portrait of Errana.JPG
4.36 MB - Portrait of Nannayya.JPG
4.36 MB - Portrait of Pothana.JPG
4.29 MB - Portrait of Tyagayya.JPG
3.74 MB - Portrait of Vemana.JPG
4.42 MB - Raghupati Venkataratnam.jpg
3.03 MB - Raghupati Venkayya.jpg
2.96 MB - Srirangam Srinivasa Rao.jpg
3.03 MB - Suravaram Pratapa Reddi.jpg
2.83 MB - Tanguturi Prakasam.jpg
2.99 MB - Vanga Pandu Prasad.JPG
5.01 MB - Yallapragada Subba Rao.jpg
3.14 MB
Monday, January 28, 2013
కవిత్రయం
ఆదికవి నన్నయ్య

మిళిత సుగంధ బంధుర సమీరణుఁడన్ సఖుఁ డూచుచుండఁగా
తిక్కన
.jpg)
Sunday, January 27, 2013
విప్లవ దార్శనికుడు

‘చాటండి గళమెత్తి విప్లవదార్శనికుడు చారుమజుందార్ చచ్చిపోలేదని- కామ్రేడ్ చారుమజుందార్ చంపబడ్డాడని’ అంటూ చెరబండరాజు తన కవితా సంకలనం ‘గమ్యం’ అంకితమిస్తూ చారుమజుందార్పై ఈ చరణాలు రాశాడు. చారుమజుందార్ అమరుడై నిండా నలభైఏళ్లు. ఆయన నక్సల్బరీ నిర్మాతగా పీడిత ప్రజల ప్రియతమ నాయకుడయ్యారు. నక్సల్బరీలో 1967 మే 23-25 తేదీలలోవూపజావూపతిఘటన వెల్లువ తర్వాత 22 ఏప్రిల్ 1969న సీపీఐ మార్క్సిస్ట్-పూనినిస్ట్ ఏర్పడి ఆయన దానికి కార్యదర్శిగా ఎన్నికైనట్లుగా కలకత్తాలో షహీద్ మినార్ మైదానంలో వేలాదిమంది ప్రజలు పాల్గొన్న బహిరంగసభలో ఎర్రజెండాల మధ్యన కానుసన్యాల్ ప్రకటించాడు. నక్సల్బరీ నాటి నుంచి అజ్ఞాతంలో గడుపుతూ పార్టీ ఏర్పాటు తర్వాత పూర్తి అజ్ఞాత నిర్మాణంలోని రాజకీయ విశ్వాసంతో 1972 జూలై 20న అరెస్టు అయ్యేదాక కూడా చారుమజుందార్ అజ్ఞాత జీవితంలోనే ఉన్నాడు. ఆయనది చాలా బలహీనమైన ఆరోగ్యం. మధుమేహం, రక్తపో టు, ఆస్తమా వ్యాధులతో బాధపడుతూ.. తన బక్క పలుచటి శరీరాన్ని విప్లవ సంకల్పం కోసమే అజ్ఞాత జీవితమంతా మందులతో కాపాడుకున్నాడు. ఆయనకు ఆశ్రయం ఇచ్చినవాళ్లు, శ్రేణులు, ప్రజలు ఆయనను కంటికి రెప్పలా కాపాడుకున్నారు. చారుమజుందార్ స్వభావ రీత్యా ఎంత భావావేశపరుడో అంత విప్లవ స్వాప్నికుడు కూడా అని, ఆయన రచనలు చదివిన ఎవరికైనా ఇట్టే అర్థమవుతుంది. 1972 జూలై 20న ఒక ద్రోహి ఇచ్చిన సమాచారంతో పోలీసులు అతన్ని కలకత్తా నగరంలోనే అరెస్టు చేసి చిత్రహింసలకు ప్రఖ్యాతి గాంచిన లాల్బజార్ పోలీస్ స్టేషన్లో గోప్యంగా నిర్బంధించారు. భౌతిక చిత్రహింసల కన్నా ఆయన పలురకాల వ్యాధులకు తీసుకుంటున్న మందులన్నీ స్వాధీనం చేసుకుని, వాటిని వాడకుండా చేసి ఆ వారం రోజులు ఆయనను చికిత్స లేకుండా మరణించేలా చేశారు. చిలీ అధ్యక్షుడు అలెండి హత్య తరువాత అమెరికన్ సామ్రాజ్యవాదం మిలాకత్తో పినోచెట్ నియంతృత్వం క్యాన్సర్తో బాధపడుతున్న పాబ్లో నెరుడాను ఎట్లా చనిపోయేలా చేసిందో, సరిగ్గా అట్లాగే చారుమజుందార్ విషయంలోనూ మన పాలకులు చేశారు. మనుషులు, డాక్టర్లు కలవకుండా చికిత్స అందకుండా చేసి చారుమజుందార్ను చంపారు.
కానీ.. నలభై ఏళ్లుగా చారుమజుందార్ విప్లవ, పీడిత ప్రజల హృదయాల్లో ఒక నిప్పు రవ్వ. ‘జానకి తాడు’కు అంటిన మంటలా దేశమంతటా విస్తరిస్తూనే ఉన్నాడు. ఇవ్వాళ.. దండకారణ్యంలో ప్రజాయుద్ధమై ప్రజలపై ప్రభుత్వయుద్ధాన్ని ప్రతిఘటిస్తున్నాడు. అయన తెరాయి దస్తావేజుల్లో(1965నుంచి 67 వరకు రాసిన 8 వ్యాసాలను తెరాయి దస్తావేజులు, ‘ఎనిమిది డాక్యుమెంట్లు’ అనే పేరు తో పిలుస్తారు.) ప్రతిపాదించిన అన్ని అధికారాలు ప్రజల కే (ALL POWER TO PEOPLE) ఇవ్వాళ దండకారణ్యంలో ముఖ్యంగా బస్తర్లో క్రాంతికారీ జనతన సర్కార్లో ప్రయోగంగా ఆచరణకు వచ్చింది. ఆయన ప్రతిపాదించిన గెరిల్లా యుద్ధం ఇవాళ దండకారణ్యంలో చలనయుద్ధం స్థాయికి చేరుకున్నది. చారుమజుందార్ ప్రతిపాదించిన దున్నేవానికి భూమి దండకారణ్యంలో ప్రతి ఆదివాసీ అనుభవంలోకి వచ్చింది. తమ శ్రమతో, సహకారంతో భూమిని స్వాధీనంచేసుకొని, చదును చేసుకుని, గ్రీన్హంట్ పేరిట భారత ప్రభుత్వం ప్రకటించిన యుద్ధ సమయంలోనూ వాళ్లు ఉత్పత్తిలో పాల్గొంటున్నారు. భూస్వామ్య పెట్టుబడిదారీ సామ్రాజ్యవాద దళారీ నిరంకుశ పాలకులకు నక్సల్బరీలో చారుమజుందార్ వేసిన దారి అత్యంత ప్రమాదరకరమైన అంతర్గత శత్రువుగా భయపెడుతున్నది. ఒకప్పుడు యూరప్ను వెంటాడి భయపెడుతుందని మార్క్స్ కమ్యూనిస్టు మేనిఫెస్టోలో చెప్పిన కమ్యూనిస్టు భూతం, ఇవ్వాళ బుంకాల్ మిలిషియా రూపంలో అదేవిధంగా భారత పాలకులను భయపెడుతున్నది. ఎందుకంటే.. ఇది భూత, వర్తమానాల్లో స్పష్టంగా ఆవిష్కరించపడుతున్న భవిష్యత్తు. అందుకే చారుమజుందార్ 40 ఏళ్ల క్రితం కన్నా ఇప్పుడు ఆజానుబావుడై అజరామరంగా మన మధ్య నిత్య సమరశీలిగా మసలుకుంటున్నాడు.
1967 నక్సల్బరీ నాటికి చారుమజుందార్ సీపీఎం డార్జిలింగ్ జిల్లా సిలిగురి డివిజన్ కార్యదర్శి. 1967లో సీపీఐ చీలి సీపీఎం ఏర్పడ్డప్పుడు పార్టీలోనూ, ప్రజల్లోనూ చాలామంది ఆశించినట్లుగానే ఆయన కూడా సీపీఎం వర్గపోరాట పంథా తీసుకుంటుందని భావించాడు. అందుకే 65నుంచి ‘తెరాయి దస్తావేజు లు’ రాయడం ప్రారంభించాడు. తెరాయి ఇండియా-టిబెట్ చైనాకు మధ్యన ఉన్న ఒక కీలకమైన భూభాగం. సంతాల్ తెగలు ఉండే ఆదివాసీ ప్రాంతం. ‘దస్తావేజులు’ రచిస్తున్న కాలంలోనే.. 1956-65 దాకా కృశ్చెవ్ సిద్ధాంతంపై (శాంతియుత పరివర్తన, శాంతియుత పోటీ, శాంతియుత సహజీవనం) మావో నాయకత్వంలో గ్రేట్ డిబేట్ ముగిసి చైనాలో శ్రామిక వర్గ సాంస్కృతిక విప్లవం ప్రారంభమైంది. బోల్షివిక్ విప్లవం, చైనా విప్లవం తరువాత చారుమజుందార్ ఇది మూడో విప్లవం అన్నాడు. తెరాయి దస్తావేజుల్లో ఆయన ప్రజల ముందు కార్మిక వర్గపార్టీ నాయకత్వంలో ఆచరించాల్సిన మూడు కర్తవ్యాలను ఉంచాడు. అవి-భూమిలేని నిరుపేదలు భూమిని స్వాధీనం చేసుకోవడమనే ఆర్థిక పోరాటం. భూస్వాముల చేతుల్లో ఉన్న మిగులు భూములు, భూస్వాముల ఆక్రమణలో ఉన్నవి కావచ్చు, ప్రభుత్వ భూములు కావచ్చు. అది సాఫిగా సాగే పనికాదు కాబ ట్టి అవి స్వాధీనం చేసుకోవడానికి, నిలుపుకోవడానికి గెరిల్లా పోరాటమనే సైనిక పోరాట ప్రతిపాదన చేశాడు. ఇది మొదట భూ ఆక్రమణదారుల గూండాల నుంచి, మాఫియాల నుంచి, ఆ తరువాత వాళ్లకు అండగా ఉండే పోలీసు, ప్రభుత్వాల నుంచి ప్రజలను రక్షించడానికి ప్రజలకు అండగా ఉంటుంది. ఈ క్రమమంతా గెరిల్లా పోరాటం ద్వారా శత్రువు బలహీనంగా ఉండే గ్రామాలను విము క్తం చేయడంగా ఉండాలి. ఒకసారి విముక్తం అయిన గ్రామం ఎల్లకాలం విముక్తం అయి ఉంటుందని గ్యారంటీ లేదు. ఒకసారి గెలుచుకున్న కోట ఎప్పుడూ మన వశంలోనే ఉంటుందనీ లేదు. ఇది సరళ రేఖగా సాగే పోరాటం కాదు. అందుకే ప్రజలకు రాజ్యాధికారం ఇచ్చే రాజకీయ పోరాటంగా రాజకీయ లక్ష్యంగా కొనసాగాలి. అన్ని అధికారాలు ప్రజలకు అన్నప్పుడు అందులో ఇమిడి ఉన్నది రాజకీయ లక్ష్యమే. అదే ఇప్పటి దండకారణ్యంలోని క్రాంతికారీ జనతన సర్కార్. ‘తెరాయి దస్తావేజు’ల రచన చేసే నాటికే దేశంలో (1967) సాధారణ ఎన్నిక లు వచ్చాయి. నెహ్రూ, ఇందిర కుటుంబ పాలనతో ప్రజలు విసిగి పోవడంతో దేశంలోని వివిధ రాష్ట్రాల్లో కాంగ్రేసేతర ప్రభుత్వాలుగా బూర్జువాపార్టీలు అధికారంలోకి వచ్చాయి. బెంగాల్లో కాంగ్రెస్ నుంచి బయటకి వచ్చిన అజయ్ముఖర్జీ బంగ్లా కాంగ్రెస్ పెట్టాడు. సీపీఎం నాయకత్వంలో లెఫ్ట్ ఫ్రంట్ ఆయనకు ఎన్ని స్థానాలు వచ్చినా ఆయనకే ముఖ్యమంత్రి పదవి ఇస్తామనే ఒప్పందంతో ఆ పార్టీతో పొత్తు పెట్టుకున్నది. రాష్ట్రంలో ఉన్న మిగులు భూములను ప్రజలకు పంచుతామని లెఫ్ట్ ఫ్రంట్ వాగ్దానం చేసింది. బెంగాల్లో ఆరు లక్షల హెక్టార్ల భూమి జోతేదారుల (భూస్వాముల) ఆక్రమణలో ఉందని, తాము అధికారంలోకి రాగానే ఆ భూమిని భూమిలేని నిరుపేదలకు పంపిణీ చేస్తామని ఎన్నికల వాగ్దానం చేశారు.
ఎన్నికల్లో ఈ పొత్తు విజయం సాధించి బంగ్లా కాంగ్రె స్కు 5 సీట్లు, లెఫ్ట్ ఫ్రంట్కు 80 సీట్లు వచ్చాయి. జ్యోతిబసు ఉప ముఖ్యమంత్రి, హోంమంత్రి కూడా అయ్యారు. కనుక సీపీఎం సిలిగురి డివిజన్ కార్యదర్శిగా చారుమజుందార్ చేసిందల్లా ఈ వాగ్దానాన్ని ఆచరణలో పెట్టడమే. కాకపోతే బూర్జువాపార్టీలు వాగ్దానాలు చేస్తాయి. కార్మికవర్గ పార్టీలు ప్రాణాలకు తెగించి వాటిని ఆచరణలోకి తెస్తాయి. వాగ్దాన భంగాలను ప్రజలకు బట్టబయలు చేస్తాయి. అయితే దున్నేవానికే భూమి భూస్వామ్య వ్యతిరేక ఆర్థిక పోరాటమే. చారుమజుందార్ దృష్టిలో చాలా స్పష్టంగా నూతన ప్రజాస్వామిక విప్లవం ఉన్నది. వ్యవసాయ విప్ల వం ఇరుసుగా సాగేది దీర్ఘకాలిక సాయుధ పోరాటం. నక్సల్బరీ గ్రామస్తుడే అయిన కానుసన్యాల్, బంగత్ సంతాల్ నాయకత్వంలో మే 23వ తేదీ నుంచి 25 వరకు 10వేల మందికి పైగా సంతాల్ ఆదివాసీలు నక్సల్బరీ, కేలిబరీ గ్రామాల్లో విశాలంగా పరుచుకొని ఉన్న నేల మీద నిలబడి ఇది మా భూమి అని ప్రకటించారు. వాళ్లం తా విల్లంబులు, గొడ్డళ్లవంటి సంప్రదాయక ఆయుధాలతో ప్రతిఘటనకు సిద్ధమై వచ్చారు. వారిపై మే 25న భూమి వాగ్దానం చేసిన లెఫ్ట్ ఫ్రంట్ ప్రభుత్వం నక్సల్బరీ రైల్వేస్టేషన్ నుంచి బుల్లెట్ల వర్షం కురిపించింది. కేవలం లెఫ్ట్ ఫ్రంట్ పోలీసులే కాదు, ఇందిరాగాంధీ సీఆర్పీఎఫ్ బలగాలు కూడా తోడయ్యాయి. ఆ కాల్పుల్లో ఏడుగురు స్త్రీలు, నలుగురు పిల్లలు అక్కడికక్కడే అమరులయ్యారు. రేపటి చరిత్ర ఆధునిక స్త్రీ రచిస్తుందని గురజాడ అప్పారావు చెప్పినట్లుగా ఈ నక్సల్బరీ మహిళలు నలభై ఏళ్లుగా చరివూతను తిరగరాస్తున్నారు. ఈ చరిత్ర నిర్మాణా న్ని, రచనను శ్రీకాకుళం, వైనాడు మొదలు ఇవ్వాళ.. జంగల్మహల్, దండకారణ్యం, నారాయణపట్నం దాకా ప్రజలకు అందించారు. ఈ చరిత్ర నిర్మాణాన్ని, ప్రజలు రచించే ఈ చరివూతను కలగన్న విప్లవ దార్శనికుడు చార్మజుందార్. అందుకే ‘ఆయనకు మరణం లేదు. అప్పుడే అతడు ఒళ్లు విరుచుకొని సమాధి నుంచి లేచి, ఆయుధం చేతబట్టి తిరిగి రణరంగంలో చేరినాడు.’ అని శివసాగర్ ‘అమ్మా’ అనే కవితలో జూలై 1972లో రాశాడు. రణరంగానికి కేంద్ర బిందువు, ఇవ్వాళ దండకారణ్యపు పోరాటంగా చారుమజుందారే కాదు (ఆయన పోరాటంలో ఒరిగిన మొదటివాడు, చివరివాడూ కాదు.) ఈ జూలైలో దక్షిణ బస్తర్లో అమరుడైన విప్లవోద్యమ నాయకుడు విజయ్ మడ్కం కూడా లేచి ఆయుధం చేతబట్టి తిరిగి రణరంగంలో చేరినాడు. మనం కళ్లు తుడుచుకొని ఆ పోరాటానికి బాసటగా నిలుద్దాం. అడుగుల్లో అడుగులేద్దాం. ప్రజలు తమ స్వప్నంగా ఆవిష్కరించుకుంటున్న జనతన సర్కార్కు అండగా నిలుద్దాం. ప్రజల ఆశలను చిదిమేస్తున్న భూస్వామ్య, దళారీ భారత ప్రభుత్వ దాడిని వ్యతిరేకిద్దాం. భారత విప్లవోద్యమ నిర్మాత చారుమజుందార్ ఆశలు, ఆకాంక్షలు నెరవేరుద్దాం.
(నేడు నక్సల్బరీ ఉద్యమ నిర్మాత చారుమజుందార్ 40 వ వర్ధంతి )
Wednesday, January 16, 2013
శ్రీ కృష్ణదేవరాయలు 1509-1530 (ఈ సామ్రాజ్యం 1336 నుండి 1660 వరకు వర్ధిల్లింది. )
- హరిహర I (దేవ రాయ) 1336-1343
- బుక్క I 1343-1379
- హరిహర II 1379-1399
- రెండవ బుక్క రాయలు 1399-1406
- మొదటి దేవ రాయలు 1406-1412
- వీర విజయ 1412-1419
- రెండవ దేవ రాయలు 1419-1444
- (తెలియదు) 1444-1449
- మల్లికార్జున రాయలు 1452-1465 (తేదీలు సందేహాస్పదం)
- రాజశేఖర రాయలు 1468-1469 (తేదీలు సందేహాస్పదం)
- మొదటి విరూపాక్ష రాయలు 1470-1471 (తేదీలు సందేహాస్పదం)
- ప్రౌఢదేవ రాయలు 1476-? (తేదీలు సందేహాస్పదం)
- రాజశేఖర 1479-1480 (తేదీలు సందేహాస్పదం)
- రెండవ విరూపాక్ష రాయలు 1483-1484 (తేదీలు సందేహాస్పదం)
- రాజశేఖర 1486-1487 (తేదీలు సందేహాస్పదం)
- నరసింహ 1490-?
- నరస (వీర నరసింహ) ?-1509
- శ్రీ కృష్ణదేవరాయలు 1509-1530
- అచ్యుత దేవరాయలు 1530-1542
- సదాశివరాయలు (నామమాత్రపు రాజు) 1542-1567
- రామరాయలు (పట్టాభిషిక్తుడు కాదు) 1542-1565
- తిరుమల రాయలు (పట్టాభిషిక్తుడు కాదు) 1565-1567
- తిరుమల (పట్టాభిషిక్తుడు) 1567-1575
- రెండవ రంగరాయలు 1575-1586
- మొదటి వెంకటాపతి రాయలు 1586-1614
- రంగ దేవరాయ II 1614-1615
- రామ దేవరాయ 1615-1633
- వెంకట దేవరాయ III 1633-1646
- రంగ దేవరాయ III 1614-1615
- ఈ సామ్రాజ్యం 1336 నుండి 1660 వరకు వర్ధిల్లింది.
Friday, December 7, 2012
FDI చర్చ

ఎఫ్డిఐల రాకతో రాష్ట్రంలోని యువత సేల్స్ బాయ్స్గా సెల్స్ గర్ల్స్గా మారాల్సి వస్తుందని విపక్షాలు ధ్వజమెత్తుతున్నాయి. చిన్న దుకాణాల వారు విదేశీ సంస్థలను ఎదుర్కోలేక ఇబ్బందులు పడతారని చెబుతున్నాయి.
వినియోగదారులచే బలవంతంగా అదే ధరలకు కొనుగోలు చేయడమే వీటి ఉద్దేశ్యమన్నారు. దేశీయ మార్కె ట్లో వస్తువ్ఞలు కొనరాదనే వీరి సిద్ధాంతమన్నారు. దీనివల్ల దేశీయ మార్కెట్ పూర్తిగా దెబ్బ తింటుందన్నారు.
విదేశీ కంపెనీలు రైతులవద్ద నుండి అతి తక్కువ ధరకు ఉత్పత్తులను కొనుగోలు చేసి అధిక ధర లకు విక్రయిస్తారని, అదే విధంగా ఆయా సంస్థలలో పని చేసే వారికి అతి తక్కువ వేతనాలు ఇస్తారని . ప్రపంచంలో ఉన్న అన్ని సూపర్ మార్కెట్ సంస్థలు చేస్తున్నది ఇదే. మెక్డోనాల్డ్స్ కంపెనీ టమోటాలను అసలు కొనుగోలు చేయదన్నారు. విదేశీ కంపెనీలు 90 శాతం చైనా నుండి కొనుగోలు చేసి చైనా వారినే ఎక్కువగా ఉద్యోగాలలో పెట్టుకుంటున్నాయన్నారు.
We have boycotted this debate. It was decided by the party...this was the best decision that the SP could come up with...FDI will destroy farmers, Mulayam says.
MM Joshi says we do not want any foreign dictatorship.
FDI will bring much-needed investment in the country, says Lalu
Thursday, November 22, 2012
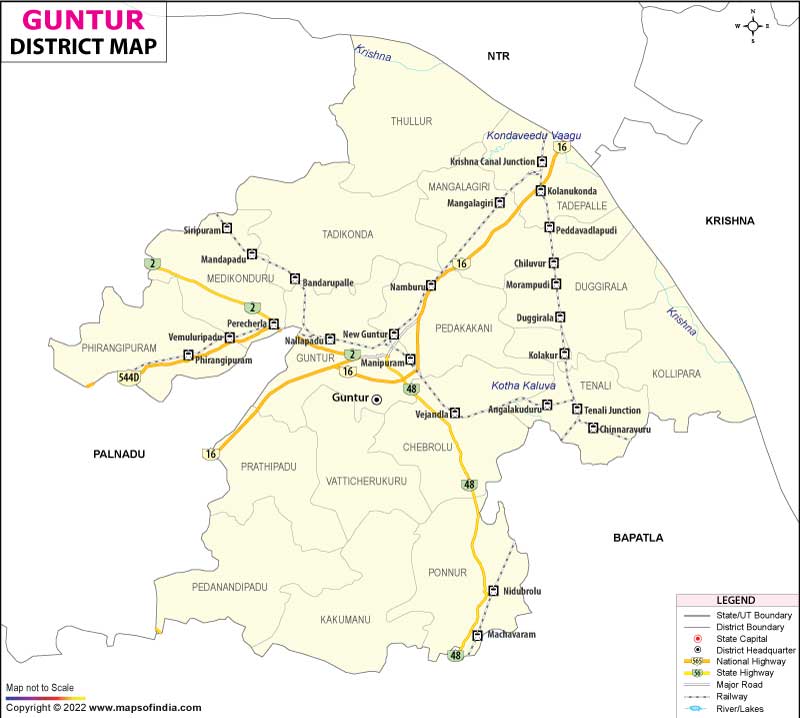
STAES IN INDIA
| YEAR | Author | Work |
| 1955 | Suravaram Pratap Reddy | Andhrula Sanghike Charitamu (Social History) |
| 1956 | Bulusu Venkateswarulu | Bharatiya Tatva Sastramu (Translation of Dr. Radhakrishnan's History of Indian Philosophy) |
| 1957 | Chariantanananda Swami | Sri Ramakrishnuni Jivita Charitra(Biography) |
| 1958 | No Award | |
| 1959 | No Award | |
| 1960 | Ponangi Srirama Apparavu | Natyasastramu (A History of Bharata's Natyasastra) |
| 1961 | Balantrapu Rajanikanta Rao | Andhra Vaggeyakara Chritramu (A History of Telugu composers and song writers) |
| 1962 | Vishwanatha Satyanarayana | Viswanadha Madhyakkarulu (Poetry) |
| 1963 | T. Gopichand | Panditha Parameshwara Sastry Veelunama(Novel) |
| 1964 | Gurram Joshua | Kreestu Charitra (Poetry) |
| 1965 | Acharya Rayaprolu Subbarao | Misra Manjari (Poetry) |
| 1966 | No Award | |
| 1967 | No Award | |
| 1968 | No Award | |
| 1969 | Thummala Seetharamamurthy | Mahatma Katha (Poetry) |
| 1970 | D. Balagangadhar Tilak | Amrutham Kurisina Rathri (Poetry) |
| 1971 | Thapi Dharma Rao | Vijayavilasamu: Hridayollasavyakhya(Commentary) |
| 1972 | Srirangam Srinivasarao | Sri Sri Sahityamu (Poetry) |
| 1973 | C. Narayana Reddy | Mantalu Manavudu (Poetry) |
| 1974 | Dasaradhi | Thimiram Tho Samaram (Poetry) |
| 1975 | Boyi Bhimanna | Gudiselu Kalipotunnai (Poetry) |
| 1976 | No Award | |
| 1977 | Kundurti Anjaneyulu | Kundurti Kritulu (Poetry) |
| 1978 | Devulapalli Venkata Krishna Sastry | Collected Works of Krishna Sastri (6 vols.) |
| 1979 | P. Narayanacharya | Janapriya Ramayana (Poetry) |
| 1980 | No Award | |
| 1981 | V. R. Narla | Seeta Josyam (Play) |
| 1982 | I. Saraswati Devi | Swarna Kamalaalu (Short stories) |
| 1983 | Ravuri Bharadwaja | Jeevana Samaram (Sketches) |
| 1984 | Aluri Bairagi | Aagama Geeti (Poetry) |
| 1985 | Palagummi Padmaraju | Gaalivana (Short stories) |
| 1986 | G.V. Subramanyam | Andhra Sahitya Vimarsa Angla Prabhavam(Literary criticism) |
| 1987 | Arudra | Gurazada Gurupeetham (Essays) |
| 1988 | Rachamallu Ramachandra Reddi | Anuvaada Samasyalu (Criticism) |
| 1989 | S. V. Joga Rao | Mani Pravalamu (Essays) |
| 1990 | K. Siva Reddy | Mohana-o-Mohana (Poetry) |
| 1991 | Bhamidipati Ramagopalam | Itlu, Mee Vidheyudu (Short stories) |
| 1992 | Malati Chandur | Hrudaya Netri (Novel) |
| 1993 | Madhuranthakam Rajaram | Madhuranthakam Rajaram Kathalu (Short stories) |
| 1994 | Gunturu Seshendra Sharma | Kala Rekha (Criticism) |
| 1995 | Kalipatnam Rama Rao | Yajnam To Tommidi (Short stories) |
| 1996 | Ketu Viswanatha Reddy | Kethu Vishwanatha Reddy Kathalu (Short stories) |
| 1997 | Penumarthi Viswanatha Sastri(Ajanta) | Swapna Lipi (Poetry) |
| 1998 | Balivada Kantha Rao | Balivada Kantha Rao Kathalu (Short stories) |
| 1999 | Vallampati Venkata Subbaiah | Katha Silpam (Essays) |
| 2000 | N. Gopi | Kalanni Nidra Ponivvanu (Poetry) |
| 2001 | Tirumala Ramachandra | Hampi Nunchi Harappa Daka(Autobiography) |
| 2002 | Chekuri Ramarao | Smrti Kinankam (Essays) |
| 2003 | Utpala Satyanarayanacharya | Sri Krishna Chandrodayamu (Poetry) |
| 2004 | Ampasayya Naveen | Kala Rekhalu (Novel) |
| 2005 | Abburi Chayadevi | Tana Margam (Short Stories) |
| 2006 | Munipalle Raju | Ashtitvanadam Aavali Teerana (Short Stories) |
| 2007 | Gadiyaram Ramakrishna Sarma | Satapatramu (Autobiography) |
| 2008 | ||
| 2009 | Yarlagadda Laxmi Prasad | Draupadi (Novel) |
| 2010 | Sayed Saleem | Kaluthunna Poolathota (Novel) |
| 2011 | M. Bhoopal Reddy | Uggupaalu (Children short stories) |
| Current Population of India in 2012 | 1,220,200,000 (1.22 billion) |
| Total Male Population in India | 628,800,000 (628.8 million) |
| Total Female Population in India | 591,400,000 (591.4 million) |
| Sex Ratio | 940 females per 1,000 males |
| Age structure | |
| 0 to 25 years | 50% of India's current population |
| Currently, there are about 51 births in India in a minute. | |
| India's Population in 2011 | 1.21 billion |
| India's Population in 2001 | 1.02 billion |
| Population of India in 1947 | 350 million |
POPULATION OF INDIA | |
| Population Density of India | 324 persons per square kilometre |
| Age structure | |
| 0 to 14 years | 31.7% (male 173,869,856; female 164,003,915) |
| 15 to 64 years | 63.5% (male 349,785,804; female 326,289,402) |
| 65 years and over | 4.8% (male 25,885,725; female 25,235,905) (2004 estimate) |
| Median age | |
| Total | 24.4 years |
| Male | 24.4 years |
| female | 24.4 years (2004 est.) |
| Population growth rate | 1.44% (2004 est.) |
| Birth rate | 22.8 births/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
| Death rate | 8.38 deaths/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
| Net migration rate | -0.07 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2004 est.) |
| Infant mortality rate | |
| Total | 57.92 deaths/1,000 live births |
| Female | 57.29 deaths/1,000 live births (2004 est.) |
| Male | 58.52 deaths/1,000 live births |
| Life expectancy at birth | |
| Total population | 63.99 years |
| Male | 63.25 years |
| Female | 64.77 years (2004 est.) |
| Total fertility rate | 2.85 children born/woman (2004 est.) |
| Nationality | |
| Noun | Indian(s) |
| Adjective | Indian |
| Ethnic groups | |
| Indo-Aryan | 72% |
| Dravidian | 25% |
| Mongoloid and other's | 3% (2000) |
| Religions | |
| Hindu | 80.5% |
| Muslim | 12% |
| Christian | 2.3% |
| Sikh | 1.9% |
| Other groups including Buddhist, Jain, Parsi | 2.5% (2000) |
| Languages | English is a widely spoken language in national, political, and commercial communication. Hindi is the official language of India and is spoken by more than 30% of the population. Part from these, 14 other official languages like Bengali, Telugu, Marathi, Tamil, Urdu, Gujarati, Malayalam, Kannada, Oriya, Punjabi, Assamese, Kashmiri, Sindhi, and Sanskrit are also used widely throughout the country. |
| Literacy Rate (Definition: Age 15 and over that can read and write) | |
| Total Population | 59.5% |
| Male | 70.2% |
| Female | 48.3% (2003 est.) |
LDCE BSNL
I.Fill in the blanks
The signals which operate throughout the duration of a call is known as _____________ signals.( Line Signals)
If the speech channel and the corresponding signaling channel are rigidly in association with each other,the signaling system is ______(CAS)
If the signaling link and the speech circuit group run along different routes, that mode of CCS is known as ____________(Quasi associated)
In a CCS#7 network, the actual signaling information pertaining to a call is sent through ______________________________signal unit.(MSU)
The bit pattern for flag in CCS#7 is _________(01111110)
The two types of Inter exchange digital signaling are _____________ & _____________(CCS#7 ,CAS)
The bottommost three layers of CCS No7 node is known as -------------------------------- (MTP)
In CCS7 signalling, the source and destination of signalling traffic are called ---------------- .(Signaling Point)
The length indicator(LI) for FISU is _____________ (0)
The length indicator(LI) for LSSU is _____________ (1or 2)
The length indicator(LI) for FISU is _____________ (3 to 63)
Choose the correct Answer
The signals exchanged between two different nodes mainly for sending the address information during the phase of setting up are
(a. Register signals b. PTS signals c. Line signals d. All the above)
The signal unit which carries information for the operation of signaling links is
(a. MSU b. LSSU c. FISU)
The specific field in the CCS#7 packet which is used to differentiate
between the three signal units is
(a. SIF b. LI c. CK)
The Signal unit which contains the address of the destination exchange to which the C7 message is to be transferred (routing label) is
(a. MSU b. LSSU c. FISU d. MTP)
State True/False
CSMF is a digital signaling system(F)
Quasi-associated mode of signaling is preferable in routes with heavy traffic conditions.(F)
CCS#7 is having a fixed length frame format.(T)
Expand the following: -
MTP- Message Transfer part
PSTN- Public switched telephone network
CSMF – Compelled sequence multi frequency
FISU-Fill in signal units
DPC- Destination point code
STP – Signal transfer point
MSU – Message signal unit
LSSU – Link status signal unit
IN
1.The service logic in IN is concentrated in a central node called -----------( SPC)
2.The most popular service in IN is ----------------(ITC)
3.The mass calling IN platform is located at --------------(HYDRABAD)-
4. A call to the IN is detected by (SCP, SSP, SMP)
5. Announcements to subscriber is generated by (ROI, IP, SCP)
6. IN traffic analysis is carried out by (SCP, STP, SMP)
7. Subscriber and Network data base is available in (SCP, SSP, SMP)
8. Billing center is located in (SCP, SMP, IP)
9. What are the three different categories of charging for IN services
1. No charging 2. unit charging 3. higher rate charging
IN Service key
1800 - FPH (Free phone service)
1801 - VPN (Virtual private network)
1802 – ITC/ VCC
1803 – Televoting no charge
1804 – (ACC)Account card calling
1805 – FLPP direct
1806 – FLPP remote
1807 - (UAN)Universal Access number(mgmt)
1808 – (UPN)Universal Personnel number (mgmt)
1860 – (UAN)Universal Access number(local &distant)
1869– (UAN)Universal Access number(Revenue sharing)
1867 – PRM (Premium rate call)
1861- Televoting unit charge rate
1862- Televoting 2unit charge rate
1863 - Televoting different charge rates
IN SCP CODE( ALCATEL )
Bangalore -425
Calcutta - 345
Hydrabad -424
Lucknow - 180
Ahammedabad - 233
Alcatel IN system SCP capacity of 4 lakhs BHCA Which can grow up to 12 lakhs
50 lakhs VCC data storage capacity
ISDN
1.The interface between NT & ISDN exchange is called -------------------(U)
2.The two rates of access in ISDN are __________ & __________
( BRA(144 Kbps) ,PRA(2Mbps)
3.The Interface between NT1 & NT2 ( T)
4.__________is used to carry data on ISDN B-channels(LAP-B (Link Access Protocol B)
5. BRI D-channel service operates at ____________Kbps(16 kbps )
6. ISDN BRA offers ____________(two B channels and one D channel (2B+D))
7. BRI B-channel service operates at _________ kbps (64)
8.ISDN PRA offers ____(30 B channels and 1 D channel )a total bit rate of 2.048Mbps
10. BRA D-channel service operates at ____________Kbps(64)
11. Interface between non ISDN terminal and TA ( R)
12. Interface between ISDN terminal and NT2 (S)
13. Interface between NT1 and NT2(T)
14. non ISDN terminal is connected to ISDN via _____________ (TA)
15. T/S is a physical interface of ___________ wires (4)
16. U is a physical interface of ___________ wires (2)
E-10B
I. Fill in the blanks.
Subscribers are connected to ___________________ rack(URA or CSE)
2MB digital streams are connected to ________________rack(URM)
One XEJ16 card can accommodate __________ number of subscribers(16)
Frequency Receivers are equipped in _____________________rack (ETA)
Maximum number of MR racks in E-10B Exchange is _____________(6)
There are ________number of call processing registers available in one MR (256)
Subscribers/ Trunk /Analysis Data are stored in ________________unit(TR)
Load and traffic observations are performed by ________________unit(TX)
All the units in E-10B are connected to the unit OC by __________link(LC)
During the failure of data link the detailed billing data is stored in _____
(DSF)
LU links connect all Connection units to ___________________rack(MQ)
Recorded announcement machine is equipped in _______________rack(BDA)
In the Time Base ________MHz oscillator is used for signal generation
One switch module can connect _______________ number of LRs(16)
Detailed billing data are stored in a _______________in the OMC(Magnetic tape)
Choose the correct answer
1. Maximum number of LR connectivity in the Switch is ____________
( 192, 384, 512, 1024)
2. Traffic handling capacity of E-10B is____________________Erlangs
( 1024, 2048, 4000, 5120 )
3. Switching principle used in E-10B is ____________
( Analogue switch, TST switch , single T switch, single Space switch)
4. One GUR contains ____________________URs
(12, 16, 18, 24)
5. In an E-10B Exge. the maximum number of UR is _____________
(192, 384, 1024, 2028)
6. CSED is connected to URM by means of maximum _______PCMs
( 2, 4, 8, 16)
7. UR number of BDA is _____________
(32, 16, 8, 1 )
8. MQ racks are installed in _____________ suit
( K, L, M, C )
9. UGCX is associated with ___________________ rack
( OC, TR, MR, MQ)
10. Capacity of one module in the MATR of TR rack is ______K Words
( 64, 128, 256, 512)
11. Subscribers meter accounts are stored in _______________ file in TX
( FIHTX, FITAX, FITTX, FICLX)
12. Terminals like TTY, CV are connected to ________________
( BDA, OC, DSF, OMC )
13. LM link is used to interconnect ______________________________
( MR to UGCX, TX to UGCX, MQ to UR, All control units)
14. UR 48 will be always a ______________
( URM, CSE, ETA, BDA)
15. The hard disk in the OMC is __________________
( UD-80, ETM, MAE, LP55)
III. Answer the following
Name the functional blocks of CSE(Subscriber terminal I/F ,Concentration network , Control network)
What is the significance of URM-48(Data link is connected from PMC)
Write down the functions of BDA( Announcements and Alarm transmission module)
What is ELS-48 ?(Control logic – 48 bit dataprocessor logic)
What is the maximum number of TR files ?(523)
List the basic signal generated by BT
List the peripherals of OMC (TTY,IR,MAE ,CV,Hard disk ,MTU)
write down the phases of call processing (Pre selection ( Dial tone),Sellection (Ringing)and Call connection)
IV. Match the following
Column A Column B Aà B
1.
BT
a.
Magnetic Tape
4
2.
URM
b.
Tone generator
3
3.
ETA
c.
2MB PCM
2
4.
DSF
d.
Sub’s meter account
5
5.
TX
e.
6.144 Mhz.
1
OCB-283
I.The Switching Matrix of OCB-283 is a ____________switch.(T)
In OCB-283 ,external PCMs are terminated in ---------------- unit.(SMT)
The CCS7 protocol handler is---------& CCS7 protocol controller is------------------- in OCB System(PUPE , PC)
4.____________ multiplex carries out interchange of information between SMM and SMC.(MIS)
5._____________________ is the alarm multiplex.(MAL)
6. Subscriber in OCB is getting dial tone from ____________ station(SMA)
7. ____________ unit is providing synchronisation pulses in OCB(STS)
8. The subscriber connection unit in OCB is ____________(CSN)
9. In one SMT2G ____________nos. of LRs can be terminated(128)
10. The central control of OCB system is ____________(SMC)
11 .____________ multiplex carries out interchange of information between Functional units of SMC.(MIS)
Fill in the Blanks:
The Switching Matrix of OCB-283 is a ______________ switch.(T)
OCB-283 Switching Network can carry a maximum traffic of ______________ Erlangs.(25000)
Type of redundancy employed in SMC is ______________________.(N+1)
Redundancy of PC is ________________.(Active standby)
The operating system loaded in OCB-283 is _________________.(RTOS – Hypavisor and supervisor) )
The software implementation of a function unit is called ______________________.(ML)
Maximum number of MRs possible in the OCB-283 system is ______________.(7)
Interface controlling SCSI peripheral device is ______________. ACBSG
Console is connected to _____________________ Board.ACFTD
AL 01 and AL 09 are normally used for connecting ____________ terminal.(PCWAM)
The main alarm coupler is ._____________________ .(ACRAL)
Each ACTUJ Board can connect maximum ________________ number of terminals.(8)
Switching network of an OCB-283 exchange is capable of terminating a maximum of ________________ LRs.(2048)
RCMT board consists of ______________ number of 64X64 matrices.(4)
SMX works in ____________________ mode.(Active –Active)
The maximum number of PCM terminations in SMT2G is __________________(128)
The time base generation board in STS is ______________.(RCHOR)
From STS the synchronization cable is terminated in ________________ station.(SMX)
The clock from SDH ring for external synchronization of the Switch is terminated in _________________ coupler in STS.(RCHIS)
The board, which is triplicated in STS is ________________.(RCHOR)
The type of redundancy employed in PUPE is _______________.(N+1)
The PUPE functionality is implemented using the hardware entity __________________ in SMA.
The clock board of SMA is _____________________.(ICHOR)
Tones are generated in SMA by ___________________.(ICTSS)
The two levels of concentration in the CSN are in the _________________ and _____________________.(CN level and RCX level)
A maximum of _______ LRIs (Internal Matrix links )are used to connect a CNL to the RCX.(4)
The UCX breaks down into two parts namely ________________ and ________________.(UC and RCX)
The ICNE allows connection of a maximum of ______ PCM links.(42)
The _________ board selects the Pilot/Reserve logic and generates the P/R signal.(TSUC)
CSN communicates with OCB Switch in _______________ signaling mode.(CCS7)
The converter board in CSNL sub racks is ___________.(TCRMT)
The _________ board allows the connection of 16 analog subscribers with remote metering application.
GTA is always created as CN__________.(CN20)
In the new version of subscriber connection unit CSN MM, MM
stands for __________________.(Multimedia Multi service)
In a TCTRS board , _________ number of PCMs can be terminated.(16)
Answer the following
The SMCs’ communicate each other over which Ring?(MIS)
The type of redundancy employed in Token ring operation?
Which station acts as the Primary Ring Manager?
Which is the only station in OCB that terminates MIS and MAS token rings?(SMC)
Secondary storage devices are available in which station?(SMM)
II.Draw a neat schematic of Hardware configuration of OCB-283 System, showing all the interconnection links between units.
II. Say TRUE or FALSE
1. Digital subscribers can be connected to the CSN of OCB (T)
2. In large configurations, number of MIS rings can go up to 4.(F ,Only one)
3. SMX follows a T-S-T architecture.(F,T)
4. Time distribution in OCB is triplicate(T)
5. The system terminals are connected to SMC. F (SMM)
CDOT
1. CDOT MBM system employs -------------------------- switching configuration.(TST)
2. CDOT SBM system employs -------------------------- switching configuration.(T)
3. --------------------------- is the basic growth module in CDOT DSS.(BM)
4. Clock and synchronization is provided on a centralized basis by ------------------------------------.(CM)
5. -------------------------- provides control message communication within a base module.(BMS)
6. CDOT MAX-XL provides connectivity to ---------------- BMs.(32)
7. Maximum --------------PCMs can be provided between RSU and main exchange.(16)
8. One multiframe has ----------------- frames.(32)
9. Only --------------------- numbered BMs can be configured as RSU.(even)
10. In DTU, one set of --------------------- and ---------------- provide one E1 interface.DTC and DTS)
11. Ideally traffic handling capacity of MAX-XL is -------------------- Erlangs.(8000)
12. The concentration ratio between TU and time switch is ----------------(1:4)
13. IOP to IOP link speed is --------------------------------.
14. The cards used to generate clock in CM-L and CM-XL are ---------------------- and ----------------------- respectively.(FCK,CCK)
15. RESBC stands for ---------------.(Respiration utility for base cartridge)
16. The command for creating the new exchange code is -----------------(MOD-XCOD)
16. ------------------ processes are created at the time of system initialization and remain alive throughout the life of the system.(ETERNAL)
17. A line module can terminate ------------------- analog subscribers.(768)
18. A space switch card in CM takes care of switching of ------------ number of BMs and handles switching of ---------------- timeslots.(4, 2048)
19. The CMS that interface with AP are --------------and --------------.(1, 2)
20. To get a free subscriber directory number ----------------------------
command is used.(DSPL – DIRN)
State true or false. If false correct the underlined word.
a. Provision of special circuits like announcement is done in AM.
b. ATU/DTU can be used in concentration with ISTU.
c. Network synchronization is done by AM.
d. With one ISTU a maximum of 128 bearer channels can be provided.
e. BPU is implemented as a duplicated controller.
f. Hunt group is used for both PSTN and ISDN sub but DDI is used only for ISDN subscribers
g. CDOT DSS MAX cannot be configured as TAX.
h. BHCA handling capacity of BP can be enhanced by upgrading the processor card.
i. PSM card is used for connecting BMs in MAX-XL.
j. PSS cards are used for space switching.
k. SCIC and TIC are of the same hardware.
l. HDLC link is used between BPU and BMS.
m. BME has a capacity of 8 MB.
n. PSU II is used inTSU frame.
o. It should be ensured that operator is added in both the IOPs at the same time.
p. The maximum value of PSWD-TAMP-THRS is 10.
q. Hotline is a terminating facility.
r. The directory numbers should have been created and its status should be OOS-OPR before they become member of the hunt group
q. The priority assigned for CCB is 8.
r. NSC card forms interface between DTS & CCK.
Expand the following:-
1. RSU-
2. FAW-
3. ATU
4. ASIO
5. HDLC
6. SCIC
7. BMDC
8. ISUP
9. MSN
10. DTS
II.
1) Level ‘1’ routes ----------------type of calls.
2) CCM card provides home metering frequency of ------ for -------number of subscribers.
3) Maintenance Panel (MP) interacts with --------- card in the 256 RAX .
4) The line test card used in 256P RAX is -------.
5) ADP & IOP are connected to------------------- in MBM switch.
6) Inter-BM calls are switched by ------------------- in MBM system.
7) BPC has got -----------------------HDLC links.
8) The signalling protocol used between LE & AN RAX is -------------
9) The maximum concentration possible in the case of AN RAX with LE is-----
10) The PCM links from the LE will be terminated in-------------card in AN RAX.
11) The feature that allows automatic selection of a free line from a group of serving lines is called ……….
12) Conference card can be equipped in the ………. slot of master frame in 256p RAX switch.
VI STATE TRUE OR FALSE
1) LCC depends on SPC for Voice Switching.
2) HDB3 interface circuits are available in RDC .
3) Control message is available in the 2nd TS of MUX stream towards TSU in a BM.
4) Prefixing of digits is an O/G parameter for Trunk administration.
5) CCB cards can be used in place of Line cards.
6) The Ring cadence timings are 0.2s ON 0.4s OFF 0.2s ON and 0.2s OFF.
7) The CDOT MAX L switch can accommodate maximum 8 RSUs.
8) AN RAX will provide third level of remoting.
9) The AN RAX will support 248 subscribers.
10) Only odd numbered BMs can be configured as RSU.
11) The maximum number of RDTs that can be put in a 256p RAX is limited to 8
12) In 256p RAX the MF/DTMF tones are generated by RMF card
EXPAND THE FOLLOWING
HDLC -
RAP-
ADP –
RSU-
RAT-
DTU-
KEY II.
Special service
16 KHZ,2
RAP
RTC
AM
CM
6
V 5.2
8:1
ANC
Line Hunting (Hunting)
7th
False
False
False
False
True
False
True
False
True
Fasle
True
True
HDLC-High level data link control
RAP-RAX administrative processor
ADP-Alarm display panel
RSU-Remote Switch Unit
RAT-RAX Announcement & Tones
DTU- Digital Trunk Unit
III
I. Fill in the blanks:-
1. To get a free subscriber directory number -------------- command is used.
2. Any subscriber data modification is possible only when the status of the
subscriber is --------------------------.
3. The parameter values of LIN-TYP as PTM & PTP are used for ---------------
subscribers.
4. Maximum number of SHM cards in a SUM is -------------------------.
5. Sig-inf parameter in TGP for CCS7 Data creation is ----------------------
6. A system implemented between the local exchange and user replacing
part or whole of the local line distribution network is called ----------------
7. CDOT MAX-L exchange supports a maximum of --------------- V5.2
interfaces per BM.
8. A trunk group is identified by a number between ------------- to ----------in MAX-L.
9. The position in the received digit sequence from which digits are to be outpulsed
on an OG trunk is called --------------------------------.
10. --------------------------- command displays all active traffic reports.
12. The command to be executed before taking printout of meter readings is -----------
13. Subscriber individual charge counters are stored in --------------------------- in a BM and
dumped to -------------------------- at a regular periodicity.
14. In CDOT, there is provision for -------- different day types.
15. In exchanges which support CCS7 signalling, for charging ------------------------is
received from TAX.
16. A device is connected to 4th ASIO port of IOP. The terminal name for this device
is ------------------------------------.
17. The two types of detailed billing records generated in CDOT are -------------------
and -------------------------.
18. CDOT AN RAX will provide the ------------------------- level of remoting.
19. ARC and ARI cards are connected by ------------------- cable.
21. There are ------------ number of calling and called subscriber categories in CDOT.
22. The maximum number of entries possible in a command file is --------------.
23. The priority assigned for CCB is --------------------.
II) State True or False.
It is not possible to change the TEN keeping the same directory number.
Hunt group is used for both PSTN and ISDN sub but DDI is used only for ISDN sub.
The directory numbers should have been created and its status should be OOS-OPR before they become member of the hunt group.
Hardware of VU is same as that of SU.
SUB-TRFINF counters are getting reset at 00:00 hours daily.
To interrogate the tariff zone for a day type Displ-Day-Typ command is used.
It should be ensured that operator is added in both the IOPs at the same time.
While displaying the traffic observation reports, TO-DATE should be greater than or equal to FRM-DATE.
The maximum length of route code is 10 digits.
Charge rate numbers have 127 possible values.
11. For displaying entries made in the calendar on specific date, key- in command "DISPL-CAL-LOG"
Hotline is a terminating facility.
4 counters are associated with a subscriber at the time of creation.
A trunk group cannot be put under billing observation.
Command file can execute a set of commands at one stretch.
SU and VU can be concentrated together.
III. Expand the following:-
MSN-
LSB-
STP-
RGEN-
ARC-
Answer the following:-
1. Mention any 3 advantages of MSN facilities for ISDN subscribers.
2. Calculate the internal threshold and No.7 threshold for the following parameters.
a) BPC card with 4 SHM cards.
b) One Home BM and 3 other Trunk BMs having CCS7 trunk
circuits.
3 .Write the commands in order for CCS7 data creation.
4. Write the No.7 ten format
5. What are the two types of supervisions with respect to traffic measurement?
6.Write any 4 operations by which a commercial billing record is generated?
7. Differentiate the commands MOD-OPR-PWD and SET-PWD.
8. A CDOT SBM is connected to TAX through Digital trunks. DTK 1 provided
in TU21 is used. Write down the TENs of the first fifteen circuits used as O/G.
9. Explain briefly with example
a) Special route
b) DID route
An O/G trunk group is to created from CDOT to OCB exchange with route code as 512. Taking the charge rate number as 18,tgp-cat as 1 and tgp number as 21, what values will you give for the following parameters in cre-rout command.
Route code:
Route flag :
Charge rate number:
Digit length:
Trunk group choice:
In the above question, if the trunk group is created as CAS , using the 3rd digital trunk circuit in the DTU frame available in BM1 in 1st frame, what values you will give for the following parameters.
TGP-STA:
LIN-SIG :
REG-SIG:
TGP-TYP:
TGP-CAT:
RNK-DGT:
DGT-SZFD:
TEN:
Explain the architecture of VU frame in CDOT.
13. List out any four different types of traffic reports that can be taken in
CDOT exchange.
14. Briefly explain the architecture of AN RAX.
15. The local calls between main exchange and RSU are to be restricted as the RSU is located
in an area of different code. How this is possible?
EWSD
1.The DLUs are connected to the Switching Network via-------------( LTG(B-function)
2. the local DLUs are connected to the ________________ by____________
(LTG(B) by 4 Mbps carriers.)
3. The remote DLUs are connected to the ______________ by __________(LTG(B) , 2 Mbps carriers.)
4.____________ is used for signaling between a DLU and the Group Processor (GP) in the two LTGs.( CCS#7)
5.________________serve to connect analog subscribers to the system. (subscriber line modules, analog (SLMA)
6.Digital subscribers are connected via___________( subscriber line modules, digital
(SLMD))
7. . ___________ is used in each DLU of a remote control unit (SASCE)
8. The remote control unit, (RCU ) consist of up to ___________ DLUs.(6)
9. DLU no. : 10 to 2550 (in steps of 10)
10. LTG no. : tsg-ltg
where tsg = 0 to 7 (Time Stage Group on which the associated LTG is terminated)
ltg = 1 to 63
11. DLU creation CR DLU : DLU= dlu no.,
Shelf=A,
DLUC0 = tsg-ltg-diu0 <-diu 1>
DLUC1 = tsg-ltg-diu2 <-diu 3>;
12.The transfer rate on the secondary digital carrier (SDC) from the LTG to the SN and
vice versa is ______________Mbps. ( 8)
13.Each of the SDCs has 128 time slots of 64 kbit/s each, out of which _________
time-slots are used for user information and _____ time slot for messages. ( 127 , 1 )
14.The CP, sends __________to the GP. (commands)
15. The GP sends___________s to the CP. (message)
16. A GP exchanges with other GPs,( reports)
17. With the common channel signaling network control (CCNC), the GP uses ___________________ (orders. )
18. A can be installed to connect an Access Network AN via V5.2 interface(PHMA card)
19.The CP113 comprises the following hardware functional units
· base processors (BAP)
· call processors (CAP)
· input/output controls (IOC)
· bus for common memory (BCMY)
· common memory (CMY)
input/output processors (IOP):
20. The ________________connects all processors (BAP, CAP), including the input/output controls (IOC), with each other and with the common memory .( bus for common memory (BCMY)
21. The unit functions as the Message Transfer Part (MTP) of CCS#7is ___________________( Common Channel Signaling Network Control (CCNC) Unit)
22. The User Part (UP) is incorporated in ______________( LTG)
23. ______________controls the functional units of the LTG(Group Processor (GP))
24.Tthe EWSD switching network has _____________and _____________ to connect
504 LTGs and has a traffic - handling capacity of 25,200 erlang ( 8 TSGs ,4 SSGs)
II
The two main components of DLU system are DLUC & DIUD
The DLUC 0 & 1 works on LOAD SHARING basis.
SLMA & SLMD cards are connected to 4096 network bus & control network bus
During emergency operation SASCE/SASC card in remote DLU controls the call processing function
The DLUC & CP communicate on time slot TS 16 of PDC for message exchanging where as GP sends information to CP on timeslot TS0 of SDC.
The metering information during speech phase is stored in GP
In maximum configuration 504 number of LTGs can be connected to SN.
6 CAP’s are provided in the basic configuration of CP.
The functions of CCS7 level 2 are implemented in the SILTG of CCNC.
MB-0 & MB-1 works on Load Sharing basis.
LEN
DLU NO – SHELF NO – CARD NO – PORT NO
10<2550 - 0<3 – 0<15 – 0<31
II. Answer the following
Name the functional units of CP 113.
1) BAP 2) CAP 3) iop:- I/P O/P CONTROLLER & PROCESSOR 4) CMY 5)BCMY
The CCG contains three modules:
1) CCUXXA 2) CCUB 3) CCUD
Mention the functional unit of SN
TSU:- LIL, TSM, LIS, LIM
SSU:- LIS, SSM 15/8, SSM 16/16, LIM
SUC
Explain Cross Office (COC) condition.
Explain RM:CTC function:
III. Draw the block diagram of EWSD exchange. Mention the names of each functional units and mark the links.
1. The main components of DLU System are …………… & ……
(DIUD and DLUC)
2. The SLMA & SLMD Cards are connected to
(The control bus andThe 4096 kbps bus )
3. DLUC0 & DLUC1 work on ----------------------------------------------basis.
( load sharing )
5. The CCS messages sent on PDC0 are duplicated over --------------------
( PDC2)
6. When PDC2 fails, the signaling for PDC3 will be carried in -----------
( PDC0)
7. List out the additional modules required for RDLU.(SASCE,ALEX)
8. What is the EMSP module used for? (Frequency receiver)
9. (True/ False)
In an R-DLU, under normal operation the intra-DLU calls ( Calls within
the DLU) will be handled by SASC (Stand-alone service controller).(F)
10. How many DTMF receivers are available in one EMSP module?(8)
11. How many external alarms can be terminated in R- DLU? In which
card?
1. If DLUC0 fails DLUC1 will process the information for DIU D0 also
True
2. During SA operaticn , DTMF subs can’t make outgoing call ( false)
3. What is the difference between DIUD and DIU: LDID modules
(Remote DLU interface and local DLU interface)
4. In R-DLU on which card, alarm are external .(ALEX)
5ESS
I. Fill up the blanks:
1. The COMDAC operates Active-Active mode.
2. FACLTP will accommodate SIX number of AIUs
3. The designated two time slots for carrying control messages in the NCT link is TS0 & TS1
4. The PIDB carries 32 time slots.
5. During call processing space time slots are allotted by AM
6. For fast transfer of control messages the overlay network called QLPS is used.
7. The most important HMI terminal in 5 ESS is MCC.
8. OS of 5ESS software is called UNIX RTR
9. The DBM software subsystem in 5 ESS consists of Relational & Dynamic.
10. The capacity of the Hard Disk in 5 ESS is 1GB X4
II. MATCH THE FOLLOWING:
A
B
1
TMS
a
AP
2
DLI
b
QGP
3
MMP
c
SM 2000
4
TLWS
d
Space switch
5
MH
e
Time switch
6
3B21D
f
SM classis
g
HMJ drive
h
MAIL BOX
1-d 2—f 3—h 4---g 5---c 6---a
III. Draw the hardware architecture of 5ESS switching system marking clearly the (i) modules (ii) UNITS in each module (iii) the links interconnecting the modules.
ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS:
1) What are the 4 fields required for finding out LEN?
aaabbbccdd
aaa-SM No(1<192) bbb-AIU No(1<104) cc-Circuite pack No (0<19)
dd-Port No(0<31)
2) What are the PCBs used for terminating the ordinary Analog subscriber STD PTs and ISDN BRA subscriber in the AIU?
LPZ 122B(32 connections) , LPP 100 (24 connections,LPU112( 12 connections)
3.What is the latest generic version of 5 ESS switch ---16(1)
(For Main Paper)
3) What is the function of FPC in the MSGS of CM?
4) What is the maximum number of SM 2000 that could be connected to a full fledged CM3? (23)
5) What is meant by ‘Q-Pipe’ ion a QLPS network?
6) What is the function of TG and TD in the DSU during call processing?
7) What are the important functions of SMP?
8) What are the three stages in call processing and what is the cut off point for each stage?
9) What are the two minimum parameters required for subscriber creation?
10) What are the different cirucuits/subscriber terminations in the DLTU of peripheral unit in SM 2000?
11) What is meant by FAST PUMP FEATURE in 5 ESS?
12)What is the latest generic version of 5 ESS switch? What are the 2 features
additionally available in this version?
Switching
1. An exchange which can switch pairs of trunks towards different exchanges is called a ------------ exchange. (Ans:Transit)
2. BORSHT functions are done by --------------- ( Ans:Line interface/ine circuits )
3. The two types of switching systems are -------------------&----------------- (space division & time division)
4. ------------------ is a high speed data processing unit which controls the operation of the switching network. (Central control)
5. The information in the ----------------store changes continuously with origination and termination of each call. (Data Store)
6. ------------------- detects and informs CC of all significant events/signals on subscriber lines and trunks.
7. The physical setup and release of paths through the switching network is performed by ------------------ under the control of CC.(Marker)
1) Which of the following is an electronic exchange
a) AXE b) C DOT c) EWSD d) All the above
2) Which of the following facility enable a subscriber to setup connection to more than one subscriber.
a) Call waiting b) Hot line c) Conference call d) Call forwarding
3) The telephone traffic is measured in
a) Erlangs b) Busy hour c) Holding time d) Hertz
4) The maximum termination capacity of C DOT SBM exchange is
a) 256 b) 128 c) 2K d) 8
5) Which of the following is the basic module in C DOT MAX
a) Base module b) Central module c) Input output module d) All the above
6) A subscriber line card in C DOT RAX interfaces ___________ number of subscriber lines.
a) 1 b) 8 c) 128 d) 256
GSM
I
I. Fill in the Blanks
1. Cellular systems employ ………………….. to compensate for the
limited frequency spectrum.
2. Cells using the same frequencies are called …………….
3. A group of cells in which the same frequencies are not reused is called …..
4. ………………… works as an incoming transit exchange for GSM PLMN.
5. …………………. is a part of MSC/VLR area where the mobile can move freely without location updation.
6. …………………. Is the access method used in GSM N/w .
7. ……………………. is the ITU vision for the third generation mobile systems.
8. The switching functions of the GSM network are carried
out by ……………….
9. The theoretical maximum speed supported by GPRS network is …..
10. ……………… acts as the MSC of the GPRS network.
11. In …………. Class of GPRS mobile , the GSM &GPRS can be simultaneously activated.
12. …………….. is implemented to support data on Abis interface in the GPRS Network.
13. In EDGE network ………………………….. type of modulation is used.
14. 3G System is capable of providing data rate upto ………….
15. The core band of IMT 2000 is …………………
II.Match the Following:
1 IMT2000 a. Reference database for sub parameters[ ]
2. Burst Period b. Rate Adapatation from 13kb/s to 64 kb/s[ ]
3. IMSI c. packet data technology [ ]
4. TRAU d. future standard for 3G services. [ ]
5. GPRS e. 577 microsec [ ]
6. HLR f. Absolute identity of the subscriber[ ]
III.Expand the Following
a. GPRS
b. GMSC
c. WCDMA
d. SMS
e. RACH
f. PDTCH
g. MSRN
h. IMSI
i. SIM
j. EDGE
V. Answer the following:
1. Define a cell? What do you mean by sectorisation of cells?
2.Mention any 3 advantages of third generation systems?
3. Mention the following with respect to GSM:
a. Duration of burst period:………….
b. No: of RF Carriers inGSM 900:……….
c. Frequency Bands for uplink & downlink:…….
d. TDMA Frame duration:……………
e Modulation Method:
f. No: of timeslots per RF Carrier:…………
4.Mention any four functions of CSR ?
5. List the different stages in the network attachment process of a Mobile
Station?
6 .Draw the schematic of migration of GSM network in BSNL towards 3G?
7.Define GPRS? What are the network elements of GPRS?
Answer keys
I. Fill in the Blanks
1. Frequency Reuse
2. Cochannel Cells
3. Cluster
4. GMSC
5. Location Area
6. FDMA/TDMA
7. IMT2000
8. MSC
9. 171.2KB/S
10. SGSN
11. Class A
12. PCU
13. 8PSK
14. 384Kb/s (slow moving) or 2Mb/s (stationary)
15. 1885-2025MHz , 2110-2200MHz
II. Match The Following:
16. d
17. e
18. f
19. b
20. c
21. a
III. Expand the Following
a.GPRS General Packet Radio Service
b. GMSC Gateway Mobile Switching Centre
c. WCDMA Wideband Code Division Multiple Access
d. SMS Short Message Service
e.RACH Random Access Channel
f. PDTCH Packet Data Traffic Channel
g.MSRN Mobile Subscriber Roaming Number
h.IMSI International Mobile Subscriber Identity
i. SIM Subscriber Identity Module
j EDGE Enhanced Data for GSM Evolution
VI. Answer the following:
1. A cell is the basic geographical unit of a cellular system. A cell
represents the coverage area of BTS. Cells are represented in
the shape of hexagons.
Sectorisation of cells: Cells are further divided into smaller units called
sectors. Each sector behaves as an independent cell. Directional
antennas are made use of in sectored cells
2.
a.More Bandwidth ,security and reliability/Fixed & Variable data
rates./Backward compatibility of devices with existing networks
b.New radio spectrum to relieve overcrowding in existing systems./
c.Rich Multimedia services/Asymmetric Data rates
3
b. Duration of burst period: 577 microseconds
b. No: of RF Carriers inGSM 900: 124
g. Frequency Bands for uplink & downlink: 890-915 MHz(U/L)
935-960 MHz(D/L)
h. TDMA Frame duration: 4.615millisec
i. Modulation Method : GMSK
j. No: of timeslots per RF Carrier: 8
4. 1.Customer Care Activities:Receipt of order forms and feeding
them,/ Handling customer queries for services/ sale of prepaid
cards/issuance of duplicate bills/Trouble ticketing.
2. Facility Provisioning and counseling on tariff plans.
3. Billing
4 Service provisioning aspects,Activation
5. Network Attachment process is the process of selecting an
appropriate cell by the MS to provide available servicesand make it’s
location known to the network.
The different stages in the network attachment process are:
1.Cell Identification
2 PLMN Selection
3. Cell Selection
6.
GSM GPRS EDGE WCDMA
7. GPRS is a packet data technology which provides mobile data service to
users of GSM mobile phones.
GPRS system consists of additional network elements as mentioned below added to an existing GSM Network
1.PCU
2.SGSN
3.GGSN
4.BG
5.CG
6.DNS
7.Firewalls
II
1.The maximum data rate of ___________ could be achieved with GPRS network
a) 115kbps b) 171.2kbps c) 384kbps d) 2mbps
2.The GPRS user related data to perform routing is stored in _____________.
a) SGSN b) GGSN c) HLR d)PCU
3.In GPRS _____________ provides the subscriber management and mobility management.
a) OMC-G b)SGSN c)GGSN d) VLR
4.The translation between IP and IMSI is carried out by ___________ in GPRS network
a) GGSN b) PDN c)GMSC d) PCU
5.Remote PCU means, the PCU implemented in _____________.
a) BTS b)SGSN c)MSC d)BSC
6.The _____________ interface is introduced to provide packet data transport between BSS and GPRS backbone.
a) Gb b)Abis c)Gn d)Gi
7.Call related CDRs are produced at some interval during the call, if ___________ feature is used.
a)Call hold b)CLIP c) LDC d)MOSMS
1.What are the 3 basic categories of CDR supported by MSC
2.Draw the network architecture of GPRS
Key:
1.b, 2.c, 3.b, 4.a, 5.d, 6.a, 7.c
Write 3 features of 3G mobile communication.
EDGE uses ___________ modulation.
ITU vision of 3G standard is called ________________.
Answers:
1•IMT-2000 is the ITU’s vision for 3G mobile system.
•Efficient use of the radio spectrum.
•Single Unified Standard.
•Anywhere Anytime Communication
•High speed packet data access. (144Kb/s, 384Kb/s& 2Mbps)
•Global Seamless Roaming.
•Integration of Terrestrial & Satellite components.
•Wide Range of Telecommunication Services.( Voice, Data, Multi-media, Internet ).
•Increased network efficiency and capacity.
•Backward compatibility with second generation(2G) systems.
2. 8PSK
IMT 2000.
III
1. GSM belongs to ______________________ generation of mobile systems.
2. The logical channel which acts as beacon is ____________________
3. The interface between BSC and BTS is called _______________________
4. In GSM, each RF carrier carries _____________________ timeslots.
5. An example of bearer service in GSM is ____________________________
6. The modulation scheme used in EDGE is ___________________________
7. The database that stores IMEI numbers of all registered mobile subscribers is called __________________________
8. In WCDMA _______________________________________ feature is used to avoid system overload
9. The permanent identity of the user stored in the SIM and HLR is ___________________________
10. WCDMA uses radio carrier having bandwidth of _____________________
State True/False
1. TMSI reallocation procedure is used to protect the user identity in the air interface.
2. The traffic handling capacity of a cellular system is large if the cluster size is large.
3. UMTS network uses only packet switching technology.
4. The logical channel RACH in GSM operates in the Downlink.
5. RNC is connected to the core network using Iur interface.
6. The provisioning of services is the function of Basic Level CSR.
7. When MS moves from one location area to another a periodic location procedure is invoked by the system.
8. RF Band allocated for GSM downlink is 890 MHz –915 MHz
9. In softer handover a mobile station communicates with two or more base stations
10. Frequency Hopping is used in GSM to increase transmission quality and spectral efficiency
Match the Following:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1. TDMA Frame a. packet data technology
2. Location Area b. 577 micro sec
3. TRAU c. Reference database
4. Burst Period d. 4.615 milli sec
5. HLR e. Single unified standard
6. IMT 2000 f. Rate Adaptation from
13 kbps to 64 kbps
7. SCH g. Consists of many cells
8. GPRS h. Used for synchronization
Expand the Following
1. GPRS
2. IMEI
3. EDGE
4. WCDMA
5. BCCH
1. The channel bandwidth in GSM is
(a) 25 KHz (b) 50 KHz (c) 100 KHz (d) 200 KHz
2. A group of cells where the available frequency spectrum is consumed is called
(a) BTS site (b) Cluster (c) Location area (d) MSC area
3. The modulation technique used in GSM is
(a) GMSK (b) QPSK (c) QAM (d) BPSK
4. The interface between MS and BTS is
(a) A (b) A bis (c) Um (d) B
5. The identity which guarantees the integrity of a mobile on radio interface is
(a) LMSI (b) TMSI (c) IMSI (d) MSRN
6. The access technique used in GSM is
(a) TDMA (b) FDMA (c) CDMA (d) FDMA/TDMA
7. MSRN is allocated by
(a) MSC/VLR (b) HLR (c) EIR (d) AuC
Answer Key
1. d
2. b
3. a
4. c
5. b
6. d
7. a
Write full form of following.
1. TRAU :
2. TMSI :
3. MSISDN :
4. EIR :
5. MSRN :
6. UMTS :
7. SGSN :
8. CDR :
9. EDGE :
10. SDCCH :
Fill in the Blank
1. UP link frequencies band in GSM-1800……………MHz ( 890-915/1805-1880/1710-1785 )
2. Speech encoding $ decoding is performed in…………………….( MS/BTS/BSC)
3. UMTS will support the data rate upto………….Mbps ( 2/8/16)
4. Modulation Technique in GSM is ……………………………( BPSK/GMSK/QPSK)
5. HLR contains the ……………………Data base of subscriber ( Permanent/Temporary/None)
6. …………level CSR generates the duplicate bills ( 1st /2nd / None)
7. GPRS is……………………………based switching ( Circuit/ Packet)
8. Duplex spacing in GSM 1800 is…………MHz ( 20/ 45/75 )
9. EIR is connected to……………………( HLR/ VLR/MSC)
10. GSM works on …………………………………………..( TDMA+FDMA/ TDMA/ CDMA/ FDMA)
Match the following
1. AGCH a) BSS
2. GMSK b) RPE-LTP
3. UMTS c) Method of Modulation
4. Speech coder d) 3G
5. OMC-R e) is used in down link direction
Tick the correct Answer
1. Down link frequency in GSM is
a) 935-960 MHz
b) 890-915 MHz
c) 824-849 MHz
d) 860-894 MHz
2. Up link is between
a) BTS to MS
b) BSC to MSC
c) MS to BTS
d) MSC to HLR
3. Total number of RF channels per carries available in GSM
a) 124
b) 50
c) 8
d) None of the above
4. BSS consists of
a) MS & BTS
b) BTS & BSC
c) BSC & MSC
d) None of the above
5. Location information of a subscriber is available in
a) VLR
b) HLR
c) HLR & Visited VLR
d) MSC
6. Echo cancel equipment is used between
a) MSC-MSC
b) MSC-PSTN
c) MSC-BSC
d) None of the above
7. In one burst of GSM the number of information data bits are
a) 57
b) 2
c) 114
d) 8
8. The duration of a burst is
a) 4.165 ms
b) 0.577 ms
c) 3.9 ns
d) 125 ms
9. Maximum data rate achieved in GPRS is
a) 144 kbps
b) 171.2 kbps
c) 384 kbps
d) 2 Mbps
10. The Maximum allowed output power of GSM portable terminal
a) 0.2 Watt
b) 2 Watt
c) 8 Watt
d) 20 Watt
ANSWER.
Write full form of following.
1. TRAU- Transcoder Rate Adapter Unit
2. TMSI- Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity
3. MSISDN- Mobile Station International subscriber directory Number
4. EIR- Equipment Identity Register
5. MSRN- Mobile Subscriber Roaming Number
6. UMTS- Universal Mobile Telecommunication System
7. SGSN- Service / serving GPRS Support Node
8. CDR- Call Detailed Record
9. EDGE- Enhanced Data rate for GSM Evolution
10. SDCCH- Standalone Dedicated Control channel
Fill in the Blank.
1. 1710-1785
2. MS
3. 2
4. GMSK
5. Permanent
6. 2nd
7. Packet
8. 75
9. MSC
10. FDMA+TDMA
Match the following
1- e
2- c
3- d
4- b
5- a
Tick the following
1. a
2. c
3. c
4. b
5. c
6. b
7. c
8. b
9. b
10. c
Questions
Write full form of following.
1. ISDN :
2. GMSC :
3. PSTN :
4. OMC :
5. IMSI :
6. SIM :
7. AUC :
8. UMTS :
9. CDR :
10. GGSN
QB. Fill in the Blank
1. BSC and BTS are connected with…………………link ( E1,X.25, Abis)
2. SIM card is protected by a ………digit PIN ( 2,4,6 )
3. A…………… is the area served by network operator ( CGI, L.A.I, PLMN)
4. Frequency BW in GSM 900 is ………MHz ( 25, 30, 25 )
5. Down link is from ……………….to………………( MS to BTS, BTS to MS )
6. Down link in GSM 900 is ……………to……………..MHz ( 824/849, 935/960, 890/915 )
7. Number of Time slots per carrier is ………….( 8, 12, 42 )
8. The CCS 7 protocol stack comprises of ………layers ( 4,9,3)
9. Types of Modulation in GSM…………( QPSK, PSK, GMSK)
10. UMTS is …………Generation ( 2, 2.5 , 3 )
QC. Write True or False ( 10 Marks)
11. Trans power in GSM-BTS is 20 W
12. Interface between BSC & OMC is X.25
13. Handover of cells within BSC is controlled by the same BSC
14. BSC is a main switching center of GSM
15. Adjacent cells use the same frequency in GSM
16. Maximum cell Radius is 25 KMs in GSM
17. The AUC is used for security purposes
18. Wireless billing information is available in CDR
19. Up link is from BTS to MS
20. Spacing between two adjacent RF is 0.2 MHz
QD Answer all the questions
1. Write types of cells
2. Write different types of interfaces
3. Write different types of Handover in GSM
4.Write BW, UL, DL and no. of carriers in GSM 900 and GSM 1800
5. Write different types of frames in GSM
6. What are the different types of services in GSM
7. Write different types of Protocols in GSM
8.Write two entities of GPRS
9. What is the difference between CAS & CCS?
10.Write the different types of signaling units
11.what is the advantages of LI ?
QE Match the following
1. GSM a. 2.5 G
2. Co Channel interference b. 75 MHz
3. UMTS c. MS to BTS
4. MCC d. GMSK
5. GPRS e. AUC
6. Cluster f. 3 digital code
7. UL g. 0.577 msec
8. Ki h. D/R
9. GSM 1800 i. 7 cells
10. Duration of Timeslot j. 2 Mbps
Tick the correct Answer
1. GSM uses the following Technique
a. CDMA
b. FDMA
c. TDMA
d. FDMA & TDMA
2. Down link frequency in GSM is
a. 935-960 MHz
b. 890-915 MHz
c. 824-849 MHz
d. 860-894 MHz
3. Channel Bandwidth in GSM is
a. 1.25 MHZ
b. 0.2 MHz
c. 200 GHz
d. 800 MHz
4. Up link is between
a. BTS to MS
b. BSC to BSC
c. MS to BTS
d. MSC to HLR
5. Total number of RF Channels per Carrier available in GSM
a. 124
b. 50
c. 8
d. None of the above
6. BSS consists of
a. MS & BTS
b. BTS & BSC
c. BSC & MSC
d. None of the above
7. Location information of a subscriber is available in
a. VLR
b. HLR
c. HLR & Visited VLR
d. MSC
8. Type of Modulation used in GSM
a. QPSK
b. BPSK
c. GMSK
d. GFSK
9. Echo cancel equipment is used between
a. MSC-MSC
b. MSC-PSTN
c. MSC-BSC
d. None of the above
10. The typical cluster contains
a. 13 cells
b. 7 cells
c. 8 cells
d. 9 cells
11. In one burst of GSM the number of information bits are
a. 57
b. 2
c. 114
d. 8
12. The duration of a burst is
a. 4.165 ms
b. 0.577 ms
c. 3.9 us
d. 125 ms
13. Frequency hopping in GSM system
a. Increases the effect of co- channel interface
b. Reduces the effect of co- channel interface
c. Neutralize the effect of co- channel interface
d. None of the above
14. In GSM system, OMC-R is the
a. Centralized maintenance and diagnostic heart of the MSC
b. Centralized maintenance and diagnostic heart of the NSS
c. Centralized maintenance and diagnostic heart of the BSS
d. Centralized maintenance and diagnostic heart of the BTS
15. Maximum data rate achieved in GPRS is
a. 144 Kbps
b. 171.2 Kbps
c. 384 Kbps
d. 2 Mbps
16. CCS systems transfer signals at the rate of
a. 64 Kbps
b. 144 Kbps
c. 171.2 Kbps
d. 384 Kbps
17. In CCS 7 protocol stack comprises of
a. 4 layers
b. 5 layers
c. 6 layers
d. 3 layers
18. Area served by one network operator
a. PLMN
b. LAI
c. CGI
d. MSC Area
. Write full form of the following
1) I S D N : Integrated Services Digital Network
2) G M S C : Gateway Mobile services Switching Center
3) P S T N : Public switched Telephone Network
4) OMC : Operation and Maintenance Centre
5) IMSI : International Mobile Subscriber Identity
6) SIM : Subscriber Identity Module
7) AUC : Authentication Center:
8) UMTS : Universal Mobile Telecommunications System
9) CDR : Call Detail Record
10) GGSN : Gateway GPRS Support Node
Fill in the Blank
1. Abis
2. 4
3. PLMN
4. 25
5. BTS to MS
6. 935 to 960
7. 8
8. 4
9. GMSK
10. 3
Write True or False
1. T
2. T
3. T
4. F
5. F
6. F
7. T
8. T
9. F
10. T
Answer all the questions
1.Micro, selective ,umbralla , large,small,pico
2.Um, Abis, M ,A, B, C , D , E ,F,G, X.25
3. a. Handover of channels in the same cell
b. Handover of cells in the same BSC
c. Handover of BSC in the same MSC
d.Handover of MSC
4. GSM 900 GSM1800
BW 25MHz 75MHz
UL 890-915MHz 1710-1785MHz
DL 935-960MHz 1805-1880MHz
No.of Carriers 124 374
5. a.TDMA frame
b. Multiframe
c. Superframe
d. Hyperframe
6. a.Tele services
b.Bearer Services
c. Supplementary services
7. LAPDm,LAPD & DTAP and MAP
8. 1) SGSN 2) GGSN
9. In CAS speech and signaling follows the same path whereas in CCS, Speech and signaling follows
in different paths.
10. MSU,FISU,LSSU.
11. To identify MSU,FISU & LSSU
Match the following
1.d
2.h
3.j
4.f
5.a
6.i
7.c
8.e
9.b
10.g
Tick the correct Answer
1. D
2. A
3. B
4. C
5. C
6. B
7. C
8. C
9. B
10. B
11. C
12. B
13. B
14. C
15. B
16. A
17. A
18. A
CDMA WLL
I
A) FILL UP THE BLANKS WITH SUITABLE WORDS:
1. The spread spectrum signal rate is __________________ Mbps.(1.2288)
2. Maximum data rate in IS 95A network is ______________ Kbps.(14.4)
3. The digital modulation method used in CDMA system is _______________.(QPSK)
4. Non CDMA calls are routed through _______________________.(MSC)
5. Voice coding rate used in Cor Dect system __32_____________ Kbps.
6. Maximum number of CBS connected to one BSD is _________4__________.
7. LG system will function as a Access Network when the BSC is connected to PSTN using ___V5.2 signaling.
8. Fixed wireless stations whose mast / tower height does not exceed _____________ meters comes undermost height category.
9. OMC used for the mtce of MSS is _____________________.(OMC-S)
10. Forward Link traffic channels ----(Walsh code)
11. Cell sector identification -----(PN short code)
12. Sub identification ------(PN long code)
13. Reverse Link traffic channels ------( PN long code)
B) STATE TRUE OR FALSE IF FALSE CORRRECT THE UNDERMENTIONED PORTION:
CDMA 2000 IX supports Voice and Data.(T)
The value of S./N required for CDMA system is low.(T)
In reverse link the channels are separated by long codes. .(T)
The down link frequency range in 800 MHZ is 869-894 Mhz.(T)
DIU will function as a local exchange using R2MF signaling.(T)
C) Give the expansion for the following:
IWF (Interworking function)
RBF
SACFA
DJU
ESN(Electronic serial number)
D) Answer the following questions:
What are the informations provided by HLR ?
Sub parameters like MDN,MIN,IMSI,ESA,LAI,services offered.
Draw the schematic route connection for a fixed subscriber when calls to mobile subscriber.
Telephone à LE à TAX à MSC à BSC à BTS à MS
Mention the codes used in CDMA system and their use.
Walsh code, PN short code, PN long code
E. Draw the schematic diagram CDMA cellular mobile communications system.
II
1. Forward link power control command bits are punctured in the _______.
a. F-FCH b. F-PCH c. R-FCH d. R-PICH
2. Application form for full siting category stations is done in _______.
a. WPC S-1 b. WPC S-4 c. WPC S-2 d. None of these
3. Fundamental Channel F-FCH can support data, voice or signaling multiplexed with one another at any rate from ___________ to ___________.
a. 750 bps to 14.4 kbps b. 750 bps to 9.6 kbps
c. 14.4 kbps to 153.6 kbps d. 14.4 kbps to 307.2 kbps
4. Which of the following is not an enhanced feature of CDMA2000 1X ?
a. Quick Paging channel
b. Synchronisation of base station to Universal Coordinated Time
c. Reverse link gated transmission
d. Forward Pilot channel
5. Which is the method adopted for assigning a Supplemental Channel for a very large duration to users that need to download a large amount of data and release that SCH as soon as the user becomes idle?
a. Infinite duration b. Pseudo infinite assignment
c. Pseudo finite assignment d. Fixed assignment
Fill up the blanks:
1. The number used to identify a WLL Handset is _____________.
2. If the antenna height is less than 20 meters and distance from Air port is more than 7 km, No Objection is to be obtained from __________________ ________________________________
3. In CDMA, channel bandwidth is ___________________________
4. The power on reverse link is controlled by ________________________ and ________________________mechanisms.
5. A single SCH provides a data rate of upto ___________ FCH in CDMA2000 Release 0 and upto _____________ FCH in CDMA2000 Release A.
6. The database used for storing the data of all the subscribers who are entering the coverage area is ______________________.
7. The Downlink Frequency band in CDMA _____________________.
8. The validity of a WLL subscriber is checked by _____________________.
9. The common time reference due to synchronization of _________________ in a network has improved the acquisition of channels and hand off procedures.
10. The OMC terminal connected to the switch is called ___________________ and that connected to BSS is called _____________________
Write full form of following.
1. I W F
2. M S C
3. P S P D N
4. B T S
5. B S M
6. PN
7. FEC
8. HO
9. IMSI
10. EVDO
Fill up the blanks with correct Answer
1. BSC and BTS are connected with ……………………Link ( E1, FATM, X.25 )
2. BSC works on……………… volt DC ( -12, -48, -64 )
3. Number of Active Channels between BTS to MS are ……….to…….. per sector per RF carrier(12to24, 20to40)
4. Traffic channels are separated by …………………code ( Walsh, Short, Long )
5. CDMA IS-95 can support Maximum………….BTS ( 12/20/48)
Write True or False
1. One BSC can control max. 48 BTS in cdma-IS-95.
2. Interface between BSC & OMC is X.25.
3. Softer hand off is between the BTSs.
4. BSC may be a switching center in IS-95.
5. Adjacent cells are in forward link
6. Walsh codes are Traffic Channel codes
7. Access channels are in Forward CDMA channel
8. Short code is known as users address mask
9. Up link is from BTS to MS
10. Spacing between adjacent RF is 0.2 MHz
Match the following
1. Walsh Code a) Short Code
2. Spacing in RF b) China Made
3. ZTE c) BTS
4. Identity of Cell & Sector d) 1.25 MHz
5. HPA e) Forward Channel
Answer the following
1. Write types of Codes in CDMA?
2. Write different types of interfaces in CDMA 2000 ?
3. Write different variants ( flavor ) of CDMA?
4. Write the Advantages of CDMA?
5. Write services provided in CDMA 2000?
cor-DECT WLL
Write the full form of following
1. WS
2. DIU
3. RBS
4. RAS
5. BSD
Tick the correct Answer.
1. Cor- DECT System works on
a. 16 Kbps
b. 32 Kbps
c. 64 Kbps
d. 128 Kbps
2. One CBS can handle Maximum
a. 10 simultaneous voice calls
b. 11 simultaneous voice calls
c. 12 simultaneous voice calls
d. 15 simultaneous voice calls
3. Maximum Data Rate possible for a subscriber is
a. 35 Kbps
b. 70 Kbps
c. 144 Kbps
d. 171.2 Kbps
4. Frequency Band for cor-DECT in BSNL is
a. 1800 to 1820 MHz
b. 1840 to 1860 MHz
c. 1880 to 1900 MHz
d. 1940 to 1960 MHz
5. Distance between a CBS & RBS is
a. 4 Kms
b. 10 Kms
c. 25 Kms
d. 50 Kms
Fill in the Blanks
1. Maximum number of ………….OMC in one DIU ( 1/2/5)
2. Transmit power of CBS is………………………..( 250mW/ 20 W/ 40 W )
3. In cor-DECT WLL…………………….. Modulation is used ( GFSK/ GMSK/ QPSK)
4. Maximum number of ……………………..subscribers in one DIU ( 10/ 100/ 1000 )
5. Internet Access is supported at ………………….Kbps in cor-DECT ( 35/ 70/ Both )
Write full form of the following
1. IWF: Inter Working Function
2. MSC: Mobile Switching Centre
3. PSPDN: Packet Switched Public Data Network
4. BTS: Base Transceiver Subsystem
5. BSM: Base Station Manager
6. PN: Pseudo random Noise
7. FEC: Forward Error Correction
8. HO: Hand off/ Handover
9. IMSI: International Mobile Subscriber Identity
10. EVDO: Evolution for Data Only
Fill up the blanks with correct Answer
1. E1 2. -48 3. 20 to 40 4. Walsh 5. 48
True or False
1.T 2.T 3.F 4.T 5.T 6.T 7.F 8. F 9.F 10.F
Match the following
1-e 2-d 3- b 4- a 5-c
Answer the Following
1. A. Walsh . B. Long. C. Short. D. PN
2. Abis, A, B, C, D, E, F, N, X 25, CCS#7, Um
3. A. CDMA IS-95A, IS-95B B. CDMA 20001X:EVDO,EVDV C.CDMA 2000 D. W CDMA
4. Large Capacity, Vocoder & Variable data rate, Less power per cell, Seamless Handoff, High Tolerance to interference, No frequency planning, Multiple diversity.
5. Provide wire line voice quality, FAX, SMS, VMS, Internet at 144 Kbps.
Cor-DECT WLL ( Answer)
Write the full form of following
1. WS: Wall Set
2. DIU: DECT Interface Unit
3. RBS: Relay Base Station
4. RAS: Remote Access Switch
5. BDS: Base Station Distributor
Tick the correct Answer.
1.b, 2.c , 3.b, 4.c, 5.c
Fill in the blanks.
1. 2 , 2. 250mW, 3. GFSK, 4. 1000, 5. Both
11. State True or False
1. The basic frame length of 20 ms is divided into 16 equal power control groups.
2. The reverse link power control command bits are punctured into R-FCH or R-DCCH.
3. When a mobile terminal is traveling in a network, if the pilot strength from a BTS falls below the Drop Threshold, it is added to the Active set.
4. In the CDMA transmission system, soft handoff technology refers to the inter-cell handoff using “connecting to the new cell after disconnecting the original one”.
5. Long PN Codes differentiate base stations.
Expand the following: -
TADD
EVDO
TLDN
MIN
NID
1. The bandwidth required for a single CDMA channel is
(a) 1.2288 MHZ
(b) 2.048 MHZ
(c) 5 MHZ
(d) 25 MHZ
2. The BSC will function as Local Exchange, when it is connected to PSTN using
(a) V 5.1 interface
(b) V 5.2 interface
(c) R2MF signalling
(d) Proprietary Signalling
3. The Multiple Access Method used in CDMA Technology is
(a) FDMA
(b) TDMA
(c) FDMA/TDMA
(d) CDMA
4. The bandwidth used for CDMA Technology is
(a) 864 – 868 MHZ
(b) 1427 – 1525 MHZ
(c) 824 – 849 MHZ & 869 – 894 MHZ
(d) 1880 – 1900 MHZ
5. The concentration facility is performed in
(a) BTS
(b) BSC
(c) MSC
(d) NMS
KEY:1-a,2-c,3-d,4-c,5-b.
1 BSC and OMC are connected with ……… ………. Link (E1, X.25, A)
2. BSC works on …………….. Volt DC. (–24,- 48, -64 )
3 .…… ……….Hand Off is between sectors in the same BTS. (Soft, Softer, Hard)
4. WLL can work on maximum ……. Degree Centigrade Temperature. (25, 30, 50)
5. R F spacing is …… MHz (0.2, 1.25, 45 MHz)
6. Forward Frequency … ...to ………MHz (824/849, 869/894, 890/915)
7. Number of Active channels between BTS & MS are,..to… (12/24, 20/40,40/60)
8. Modulation technique in CDMA is …… …. (GFSK, QPSK, GMSK)
9. Traffic channels are separated by ………… …… Code. ( Walsh, Long, Short)
10. Long code is based on ………….. characteristic polynomials. (15,42,64)
ANSWER
1. BSC and OMC are connected with ………X.25………. Link
2.BSC works on ……-48……….. Volt DC. (–24,- 48, -64 )
3.……Softer ……….Hand Off is between sectors in the same BTS. (Soft, Softer, Hard)
4.WLL can work on maximum …50…. Degree Centigrade Temperature. (25, 30, 50)
5.R F spacing is ………1.25…… MHz (0.2, 1.25, 45 MHz)
6.Forward Frequency …869 ...to …894……MHz (824/849, 869/894, 890/915)
7. Number of Active channels between BTS & MS are, 20..to…40 (12/24, 20/40,40/60)
8. Modulation technique in CDMA is ……QPSK…. (GFSK, QPSK, GMSK)
9.Traffic channels are separated by …………Walsh…… Code. (Walsh, Long, Short)
10.Long code is based on ……42…….. characteristic polynomials. (15,42,64)
(1) State True / False :- 5 Marks
a) One DIU’s can support 1000 subscribers.
b) Maximum 5 CBS can be connected to one BSD.
c) One Carrier can supports maximum 10 channels at a time.
d) Voice coding is 32 kbps ADPCM .
e) One DIU can support max. 20 CBS’s.
Q. (2) Write full form : 5 Marks
a) WS :
b) DIU :
c) RBS :
d) RAS :
e) BSD :
Q. (3) Fill up blanks :- 10 Marks
a) Frequency band is …………….. to………. ……..MHz
b) Transmit power during burst is …………mw
c) DECT works on ………………………. multiple access.
d) Number of time slots per carrier is ……………………
e) DECT can support more than ……………… data rates .
f) One BSD can support ……………..number CBS
g) Maximum distance between CBS & WS is ………………Km.
h) Maximum distance between BSD & CBS is ………….. Km
i) Maximum distance between CBS & RBS is ………………Km
j)A built –in-battery provides ……………hrs talk time for voice call.
a) One DIU’s can support 1000 subscribers. T
b) Maximum 5 CBS can be connected to one BSD. F
c) One Carrier can supports maximum 10 channels at a time. F
d) Voice coding is 32 kbps ADPCM . T
e) One DIU can support max. 20 CBS’s. T
write full form :
a) WS = Wall Set
b) DIU = DECT Inter face Unit
c) RBS= Relay Base Station
d) RAS = Remote Access Switch
e) BSD= Base Station Distributor
Fill up blank :-
a) Frequency band is …1880….. to……1900…. MHz
b) Transmit power during burst is …250………mw
c) DECT works on ………Time Division…… multiple access.
d) Number of time slots per carrier is …12…….
e) DECT can support more than ………32……… data rates .
f) One BSD can support ………4……..number CBS
g) Maximum distance between CBS & WS is ………10………Km.
h) Maximum distance between BSD & CBS is ………1…….. Km
i) Maximum distance between CBS & RBS is …………25……Km
j) A built –in-battery provides ………3……hrs talk time for voice call.
PCM
I. Fill in the Blanks
The process of translating individual speech circuits into preassigned frequency slots within the bandwidth of the medium is called …………………(FDM)
The sharing of transmission medium by a number of circuits in the time domain by making use of time slots is called ………………(TDM)
……………. is a measure of the amplitude of a signal evaluated over a small duration over which the value of the signal changes over a negligible amount.(Sampling)
The sampling frequency is …………. .> 2f max
The process of breaking down a continous amplitude into a number of discrete levels is called ……………………(Quantisation)
There are …………………….. number of quantising intervals in PCM.(256)
The two methods of quantisation are …………… and ………………(Linear and non linear)
The stepsize varies according to signal levels in ………………. type of quantisation.( non linear)
CCITT has recommended ………………….. law for companding for 30 channel PCM.(A)
There are ………………. Number of timeslots in s 30 channel PCM.(32)
The duration of one timeslot in PCM is ……………..3.9micro seconds
The bit duration is ……………….. and frame duration is ……………(488 nanoseconds ,125 microseconds)
……………timeslot is reserved for carrying signaling and …………. is reserved for carrying synchronization information.(TS16 , TS 0)
Duration of Multiframe is …………….(2 milliseconds)
In even frames TS0 carries ……………. and odd frames TS0 carries ………..(FAW and Alarm signal)
The frame FO carries ……………..in TS16.(MFAW)
The 30 channel system follows ………………….. interleaving method.(Bit)
Answer the following:
1.Mention the processing steps involved in the formation of a PCM signal from an
analog signal?
Filtering,Sampling,Quantising,Encoding,&Line coding
2. Answer the following with respect to a PCM frame?
a. Total number of bits per frame : 256
b. Total number of frames per second:8000
c. Total number of bits per second:2048 Kbps
d. Duration of a PCM Frame :125 micro seconds
e. Duration of one timeslot: 3.9 micro seconds
f. Duration of PCM multiframe:2 milli seconds
3. Mention the format of 8 bit en coded signal indicating the purpose of the bits?
P ABC WXYZ
P-Polarity bit ,ABC –Segment code , WXYZ – level in that segment
State true or false
1. The first bit of the encoded signal indicates the polarity of the signal.(T)
2. Timeslot zero of every frame carries the FAW.(F)
3. The duration of multiframe is 125 microseconds. .(F)
4. Linear quantization method is used to realize segmented quantization in PCM.(F)
5. Timeslot 16 is used to carry signaling information. .(T)
OFC & S
FILL IN THE BLANKS CHOOSING THE APPROPRIATE ANSWER FROM THE BRACKET
1) For optical fibre transmission the range of wavelength used is ___________ in the infrared region. (0.8 to 1.6µm, 0.5 to 1.3µm, 1.6 to 2µm)
2) Velocity of light in optical fibre is _________ compared to that in air. (more, less, same)
3) Refractive index of core is _________ that of cladding. (same as, greater than, less than)
4) ____________ fibre propagate light through a number of paths within the core.
(single mode, multimode)
5) Spreading of light pulse in fibre is caused by ____________(attenuation, dispersion)
6) Single mode fibre has ________ bandwidth. ( large, small)
7) For connections inside the equipment room __________ fibre is used.
(loose tube, tight tube)
8) In the OF cable used by BSNL, the diameter of the core is ________ and the diameter of the cladding is ______(50µm, 125µm, 8µm, 140µm)
9) Jelly is filled in the jacket to protect from _____________ (moisture, chemical action)
10) The standard depth of OF cable trench is ____________(1.4m, 1.5m, 1.65m)
I. MATCH ‘A’ SIDE WITH APPROPRIATE CHOICE FROM ‘B’ SIDE
a) Numerical aperture 1) Triangular profile
b) Modal dispersion 2) Light gathering ability
c) Dispersion shifted fibre 3) Multimode
d) Minimum attenuation 4) Source
e) Spectral width 5) Single mode fibre
f) Rayleigh scattering 6) Wavelength dependent
g) Wave guide dispersion 7) 1550nm
III Answer the following questions by putting a tick mark to the most appropriate answer.
1) When a LED or a LD is used as the optical source, it should be --------------.
a) Forward biased
b) Reverse biased
c) Either forward biased or reverse biased depending upon signal strength.
2) Concentration of radiation and improved coupling efficiency are provided by
a) Surface emitter LED
b) Edge emitter LED
c) Both are equally efficient
3) In PIN diodes
a) A lightly doped intrinsic layer separates the more heavily doped p-type and n-type materials
b) A heavily doped intrinsic layer separates a lightly doped p-type and n-type materials
c) None of the above
4) Pumping threshold is required for the operation of
a) LED
b) Laser Diode
c) Both LED and Laser Diode
5) Spectral width of Laser is
a) More than that of LED
b) Less than that of LED
c) Equal to that of LED
6) In PIN diode the absorption of photos takes place in
a) P region
b) I region
c) N region
7) In APD secondary carriers are carried in
a) High field region
b) Drift region
c) Diffusion region
8) Responsivity is expressed as
a) A/W
b) W/A
c) A simple ratio
9) To be adequately detected, the optical signal should be at least
a) Twice the noise current
b) Four times the noise current
10) Optical line code is
a) Unipolar
b) Bipolar
11) 5B 6B code should not contain more than
a) 5 identical bits
b) 6 identical bits
c) 11 identical bits
12) If the RDS = +2, the change of state is from
a) State 1 to state 2
b) State 2 to state 1
c) Continues to remain in state 1
13) When the decoder in the uncertain state receives the next word with RDS equal to zero
a) It continues to remain in the uncertain state
b) It goes to state 1
c) It goes to state 2
IV Say True or False. If False correct the underlined portion.(w.r.to 30 Chl PCM)
1) The duration of a frame is 125 micro sec
2) Sampling rate of VF channel is 8000 times/sec
3) Sampling rate of signaling information is 1000 times/sec
4) Line code used for 2.048 mb/s is HDB3
5) Frame alignment word is sent in TS0 of even frames
V. Answer the following questions with respect to 2nd order digital mux by
putting a tick mark against the most appropriate answer.
1) Time slot 161 in the frame always contain
a) Four justification bits per tributary
b) A justification control bit per tributary
c) Justification bit or information bit, one per tributary
2) The number of 11-bit elastic store per multiplexer unit is
a) 8
b) 1
c) 4
3) Perforated clock of 2112kb/s is used for
a) Writing the tributary data into the buffer memory of the multiplexer
b) Reading the data from the buffer memory in the demultiplexer unit
c) Writing the data into the buffer memory of the demultiplexer unit
4) In the 2nd order D-MUX frames
a) Bits from 4 primary PCM streams are interleaved
b) PCM words (8 bits) from primary PCM systems are interleaved.
c) Samples of speech from 120 channels are interleaved.
5) The alarm bit in bit position No:11 in the frame structure is detected in
a) Multiplexer unit
b) Demultiplexer unit
c) Alarm unit
d) Interface unit
VI. Fill in the blanks suitably by choosing most appropriate choice from the brackets
( w.r.to 140 Mb HFCL System)
1) HFCL 140 Mb/s uses _________ window on single mode fibre.
( 1st , 2nd , 3rd )
2) The interface line code used for the 2/34 muldex unit is ______
(HDB3, CMI, AMI)
3) In an HFCL cabinet, a maximum of _____ systems can be equipped.
(2,4,6)
4) The output of the power supply unit are _________ (+10v,+5v, -10v,-5v)
5) The signal code used for 140 Mb/s is _________ (HDB3, CMI, 5B 6B).
OFC & S (KEY)
I.
1. 0.8 TO 1.6 µm 6. large
2. Less 7. tight tube
3. Greater than 8. 8µm, 125 µm
4. Multimode 9. moisture
5. dispersion 10. 1.65 M
II.
a) 2 e) 4
b) 3 f) 6
c) 1 g) 5
d) 7
III
1 a 8. a
2 b 9. a
3 a 10. a
4 b 11. a
5 b 12. a
6 b 13. a
7 a
IV
1 True
2 True
3 False, 500
4 True
5 True
V
1 c
2 c
3 c
4 a
5 b
VI
1. 2nd
2. HDB3
3. 4
4. +5v & -5v
5. CMI
II
. 1 Fill in the Blanks and tick the correct answer
1. SDH stands for ……………………………………………………………….
2. No. of rows and columns in STM-1 frame are ………. and ………………….
a- 9 and 270 b- 10 and 270 c- 9 and 260 d- 8 and 280
3. Frame duration of STM-1 frame is…………microseconds
4. Multiplex section is the section between……….
a- Terminal and regenerator equipment b- Two Terminal equipment
c- Two regenerator equipment d- b and c
Bit rate of STM-16 is ………16 times of STM-1
a-more than b-less than c-exactly b-none of these
Pointer is an indicator whose value defines frame …….of a VC
C-3 container can not accommodate ………..mbps bit rate
a- 140 b- 34 c-45 d-none of these
K-1 & K-2 bytes in STM frame structure are used for ………….
a-frame alignment b-order wire c-parity check d-protection
E-1 & E-2 bytes in STM frame structure are used for ………….
a-frame alignment b-order wire c-parity check d-protection
GFP is a mechanism of mapping ………bit rate data into SDH
a-variable b-constant c-a and b both d-none of these
AU pointer bytes are available in …….row of STM frame structure
a-3rd b-4th c-5th d-6th
SNCP method is providing a………….
a-line protection b-path protection c-both line & path protection
Bit rate of STM-16 is about……………Gb/s
SDH can not accommodate ………mbps PDH signal
In BSNL only …….. fiber ring mechanism is being adopted
a- 1 b- 2 c- 3 d- 4
DWDM stands for………….
DWDM system operates in……….window
a- 1st b- 2nd c- 3rd d- none of these
Wavelength range of C-conventional band and L-long band is ………..and ……….. respectively
Wavelength used for supervisory channel is……….nm in DWDM system
a-1510 b-1530 c-1565 d-1625
Channel spacing of 32 channel DWDM system is …… Ghz
……….fibre is recommended for DWDM system by ITU-T
a- G.652 b- G.653 c- G.654 d- G.655
Most popular amplifier used in DWDM
a- CDFA b- DDFA c EDFA d- FDFA
A satellite link is similar to a terrestrial M/W link with two hops, the satellite playing role of ………….
The frequency used from satellite to earth station is known as………
The uplink freq. of C-band is ……...to…….GHz
The Geo-stationary satellite is at about……….Km from earth.
The center of a communication network is called……………
Hub station for Ku band services located at………………
Downlink frequency used in Sat. Com in C- band
a- 4 GHz b- 6 GHz c- 8 GHz d- 2 GHz
Hub station for DSPT located at………………
a. Bangalore b- Kolkata c- Hasan d- Sikandrabad
VSAT is not known as-
a-Micro E/S b- Mini E/S c-Roof Top Terminal d-Main E/S
DSPT stands for ………………………………..
The hub station for DSPT is located at ……………………
LNB is a part of ……………………….in Ku band VSAT
a- outdoor unit b- indoor unit c- none of these
Period of revolution of Geostationary satellite is………………….
Answer 1
1. Synchronous Digital Hierarchy
a
125
b
c
location
a
d
b
c
b
b
2.5
8
b
dense wavelength division multiplexing
c
1530-1565 and 1565-1625
a
100
d
c
repeater
down link
5.925 to 6.425
36000
hub
Bangalore
a
d
d
Digital Satellite Phone Terminal
Sikandrabad (UP)
a
24 hrs
Choose the correct answer
1.One PCM stream has _________ VF channels
1) 24
2) 32
3) 30
2.Output of the PCM line coder is ______________code.
1) HDB3
2) AMI
3) CMI
3.STM1 frame is represented by a matrix of _____________________________
1) 9 rows & 270 columns
2) 270 rows & 9 columns
3) 9 rows & 261 columns
4.When diffraction increases ,band width of fibre ________
1) decreases
2) increases
3) remains the same
5.Each byte in SDH payload represents a
1) 2Mbps
2) 64Kbps
3) 8bps
6.Bit rate of STM1 Signal is _________________________.
1) 155.52 Mbps
2) 155.52 Gbps
3) 155.52 Kbps
7.STM1 can accommodate _____________ number of 2 Mbps tributaries.
1) 64 2)63 3)21
8.Spectral width of LASER is _________________ than that of LED
1) same
2) more
3) less
9.Jelly filled in buffer tube is to protect from _________________
1) Rodents
2) Acidity
3) Moisture
10.The tool used to remove the primary coating of fibre
1) Cleaver
2) Stripper
3) Sheath remover
11.For connections inside equipment room _____________ cable is used
1) Tight buffered
2) Loose buffered
3) Unbuffered
12.Standard depth of OF Cable Trench is ______________
1) 1 m
2) 1.5 m
3) 1.65 m
13.OTDR uses the following principle for its working
1) back scattering
2) dispersion
3) diffraction
14.Part of optical connector used for alignment of fibre is
1) Ferrule
2) Adapter
3) Connector body
15.Light gathering capacity of fibre is expressed as
1) dispersion
2) attenuation
3) numerical aperture
II.Expand the following
HDB3
CMI
STM
DWDM
BROAD BAND
1.What are the elements in Broadband Multiplay aggregation network?
BNG (Broadband Network gateway)
RPR Tier1/Tier2 switch
OC LAN switch
2.What are the components of PMS?
Motive and Metasolv
3.Write any one multicasting protocol supported by BNG?
PIM (Protocol Independent Multicasting), IGMP (Internet group management protocol) and Multicast routing.
Choose the Correct answer
4.Which device is acting as the gateway of the Broadband traffic towards the MPLS core?
BNG, OCLAN Switch, DSLAM
5.The OC LAN switch is deployed as (Tier 2) network device in the BSNL Multi play
DSLAM, Tier 1, Tier 2, BNG
Fill in the Blanks
6.The application system responsible to present a web portal to the eligible subscribers to enable request for various Multi play services is Subscriber Service Selection System (SSSS).
7.The (RADIUS based server) server will authenticate subscriber credentials with the help of LDAP.
8.RPR technology is optimized for robust and efficient packet networking over (fiber ring) topology.
9.Provisioning of services on the network elements using the EMS is facilitated by ASAP(Automated Service Activation Program ) application.
Question Bank of NIB-II PROJECT SERVICES
1) All A2,A3 nodes of NIB-II Project-I are dual mesh to A1 using ……. ( STM-16)
2) All B1,B2 nodes of NIB-II Project-I are dual mesh to A using ……. ( STM-1)
3) NIB-II Project-1 is for…………(MPLS VPN or MPLS based IP infrastructure)
4) NIB-II Project-2.1 is for… (Access Gateway Platform for Narrowband internet)
5) NIB-II Project-2.2 is for……(Access Gateway Platform for Broadband internet)
6) NIB-II offers fully managed services to customers. (TRUE)
7) NIB-II offers Bandwidth on demand over the same network. (TRUE)
8) List out any four services offered by NIB-II project.
Internet access, VPN, VAS, Messaging, BB services through DSL and Direct Ethernet.
9) What are the services offered in NIB-II Project-3
Messaging and storage service
Provisioning, Billing and Customer care
Enterprise Management Systems
Security systems
10) What are the components of narrow band access network in NIB-II
Narrow band RAS
LAN switch
EMS Server (Element Management System)
NIB-ISP
1.NIB_II has been implemented in --- projects (3)
2.NIB1 is connected to NIBII under ---project ( Project2.1)
3.---------router is used in the core network( CISCO 12416)
4.Core A1 nodes are available ---- locations (5)
5.Data center of NIB_II is at ---------( Bangalore)
Write the expansion of the following
MPLS : Multi Protocol Label Switching
VPN :Virtual Private Network.
NAT : Network Address Translation.
NOC : Network Operation Center.
EMS : Enterprise Management System.
PMS : Provisioning Management System.
Answer the following
1.What are the NIB_II projects?
Project-1 , Project-2.1, Project-2.2 and Project-3
2.What are the services planned from NIB_II?
1) Narrow band and broad band internet services.
2) MPLS_VPN services
3) Value added services and
4) Messaging services.
3.What are the value added services from NIB_II?
1)Encryption services
2)Firewall services and
3) NAT services
DNS
1.What is DNS ?
2.Why DNS is needed ?
3. What are three types of TLDs ?
4.What are the components of DNS?
5.Name 4 commonly used top domain names?
6.Explain how DNS works?
True/False (1 each)
DNS servers, also called as name servers
DNS traces its origins to ARPANET
Network Security
1.Define what is network security ?
2.What is social engineering ?
3.What are the methods of social engineering ?
4.Name the three broad categories of attach ?
5.What is firewall?
6.What is tunneling?
7.Name the two categories of tunneling?
True/False
Virus can spread without human help (F)
Worms need a software port to act (F)
Trojens need a software port to act (T)
Expand the following
1.SSSS
2.SSSC
3.LDAP
4.AAA
Data communication & Networking
1. The OSI model consists of _______ layers.(7)
2. The error detection method involving polynomials is ___CRC_____
3. A router functions in the _______ layer of OSI model.(3)
4. The cell size of ATM is ______ bytes.(576)
5. The end-to-end delivery of the entire message is the responsibility of the _____________ layer(4)
II. Tick the correct answer from the given choices
1. ____ are rules that govern a communication exchange
(a) Media
(b) Criteria
(c) Protocols
(d) All of the above
2. Communication between a computer and a keyboard involves ________ transmission
(a) Simplex
(b) Half-duplex
(c) Full-duplex
(d) None of these
3. In the ____ layer, the data unit is called a frame
(a) Physical
(b) Data link
(c) Network
(d) Transport
4. Decryption and encryption of data are the responsibility of the ______ layer
(a) Presentation
(b) Data link
(c) Network
(d) Transport
5. Node-to-node delivery of the data unit is the responsibility of the _____ layer
(a) Physical
(b) Data link
(c) Transport
(d) Network
6. Error detection is usually done in the ____ layer of the OSI model
(e) Data link
(f) Network
(g) Physical
(h) Any of the above
7. Which error detection method uses one’s complement arithmetic?
(a) VRC
(b) LRC
(c) CRC
(d) Checksum
8. Which error detection method involves polynomials?
(a) VRC
(b) LRC
(c) CRC
(d) Checksum
9. In cyclic redundancy checking, the divisor is ___ the CRC
(a) The same size as
(b) One bit less than
(c) One bit more than
(d) Two bits more than
10. In CRC, there is no error if the remainder at the receiver is _____
(a) Equal to the remainder at the sender
(b) Zero
(c) Nonzero
(d) The quotient at the sender
11. In a ____ connection, more than two devices can share a single link.
(a) Point-to-point
(b) Multipoint
(c) Primary
(d) Secondary
12. Analog signals are characterized by
(a) Amplitude and signal
(b) Amplitude and frequency
(c) Frequency and phase
(d) Amplitude, frequency and phase
13. PCM is an example of _____ conversion
(a) Digital-to-digital
(b) Digital-to-analog
(c) Analog-to-analog
(d) Analog-to-digital
14. Which of the following is most affected by noise?
(a) PSK
(b) ASK
(c) FSK
(d) QAM
15. The standard modulation protocol(s) for high-speed modems
(a) V.32
(b) V.32bis
(c) V.21
(d) Both a and b
16. The maximum compression ratio for a V.42bis modem is
(a) 4:1
(b) 1:4
(c) 2:5
(d) None of these
17. In sliding window flow control, if the window size is 63, what is the range of sequence numbers?
(a) 0 to 63
(b) 0 to 64
(c) 1 to 63
(d) 1 to 64
18. When a primary device wants to send data to a secondary device, it needs to first send ____ frame.
(a) An ACK
(b) A poll
(c) A SEL
(d) An ENQ
19. An ACK3 in sliding window flow control (window size of 8)means that frame ___ is next expected by the receiver.
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 8
20. In stop-and wait ARQ, if data 1 has an error, the receiver sends a ______ frame.
(a) NAK 0
(b) NAK 1
(c) NAK 2
(d) NAK
21. When data and acknowledgment are sent on the same frame,this is called __________
(a) Piggybacking
(b) Backpacking
(c) Piggypacking
(d) A good idea
22. Which of the following uses the greatest number of layers in the OSI model?
(a) Bridge
(b) Repeater
(c) Router
(d) Gateway
23. Which topology requires a central controller or Hub?
(a) Mesh
(b) Star
(c) Bus
(d) Ring
24. Which LAN has the highest data rate?
(a) 10BASE5
(b) 10BASE-T
(c) twisted-pair token ring
(d) FDDI
25. The ____ register holds the amount of time a station has to send its synchronous data
(a) Synchronous allocation (SA)
(b) Target token rotation time (TTRT)
(c) Absolute maximum time (AMT)
(d) Token rotation time (TRT)
26. The X.25 operates in the _____ of the OSI model
(a) Physical layer
(b) Data link layer
(c) Network layer
(d) All the above
III. Say whether the following statements are True or False. If it is false correct the underlined word.
1. The node-node delivery of the data unit is the responsibility of the Physical Layer. (F) Data link layer
2. The retransmission of damaged frames in the data link layer is known as Flow control. (F) Error control
3. In go-back-n ARQ, if frames 4,5,6 are received successfully, the receiver may send an ACK- 6 to the sender.(F) ACK-7
4. A de-facto standard is one which has been legislated by an officially recognized body.
IV. Expand the following.
1. HDLC -High level data link control protocol
2. ISO - International Organisation for Standards
3. ATM - Asynchronous transmission mode
4. LAPB Link access Protocol Balanced
5. ITU - International Telecommunication Union
6. PPP - Point to Point Protocol
II
In which of the following LAN topologies the data flow is unidirectional
(a) Bus (b) Ring (c) Star (d) None of the above)
Which of the following LAN topologies requires more media.
(a) Bus (b) Ring (c) Star (d) None of the above)
Token Ring passing is not the Media Access method in which of the following topologies. ?
(a) Bus (b) Ring (c) Star (d) None of the above)
In which of the following topologies there is no sharing of media?
(a) Bus (b) Ring (c) Star (d) None of the above)
For implementing Ring topology the preferred media is
(a) Optical Fiber (b) Twisted pair cable (c) Coaxial (d) None of the above.
In the Token Ring frame format the block which is specifying that the frame is a data frame or a token frame is
(a) SA (b) FC (c) FCS (d) None of the above.
The Media Access method used in Star Topology is
(a) Distributed (b) Star Control (c) Centrally Controlled (d) None of the above.
In which if the following CSMA methods stations wait for a specific interval of time before checking the media.
(a)Non Persistent (b)P-Persistent (c) 1-Persistent (d) None of the above.
Register insertion is a Media Access control method in which topology
(a) Bus (b) Ring (c) Star (d) None of the above)
Which of the following is not a contention access method.
(a) Pure Aloha (b) Token Ring (c) 1- Persistent CSMA (d) CSMA
State True or False
In Bus Topology nodes need not be intelligent
For interconnecting 2 Bus topology LANs repeater is not required.
In token ring passing media access method all the stations are in broadcasting mode.
In P-Persistent not all the stations are allowed to transmit simultaneously.
In CSMA/CD stations do not listen to the channel while they are transmitting.
Fill in the Blanks
In Ring topology the interconnecting nodes are called ……………………
In Bus topology data flow is … directional.
CSMA/CD is a media access method for ……….. topology.
A …………… is used to by pass a failed node in Ring topology.
In ……………. CSMA stations starts transmitting the data immediately when the channel is found free.
Key II
1. b 6. b 11. F 16. Ring Interface Units (RIU)
2. c 7. c 12. F 17. Bi
3. c 8. a 13. T 18. Bus
4. c 9. b 14. T 19. Dead Man Relay
5. a 10. b 15. F 20. 1-Persistent
III
Error Detection Correction, Data Link Control and Protocol
CRC is based on parity checking. (T/F) F
In CRC, the divisor is the redundant bit. (T/F) F
Hamming Code is a Reverse Error Correction mechanism. (T/F).F
The number of disagreements between two code words is known as –Hamming Distance
Define: Code word, Data Word, Hamming Distance and Weight.
Distinguish between Content Error and Flow Integrity Error.
Explain any one Error Detection Method.
Mention three Error correction methods.
State the encoder representations of Convolutional Coding.
Regulation of the rate of transmission of data frames is known as ……
In sliding window of Modulo 128 working, if the frames are numbered from 0 to 127, the window size is 127
In go-back-n ARQ, if frames 5, 6, and 7 are received successfully, the receiver may send an ACK _8___ to the sender.
In go back nwhen a NAK is received, all frames sent since the last frame acknowledged are retransmitted
What are the three functions of the Data link control?
Mention the categories of Sliding Window Error Control.
Mention the methods of ARQ.
Mention the full name of any three data link layer protocol.
To ensure the uniqueness of flag Zero bit stuffing in HDLC protocol.
Explain the frame format of HDLC protocol.
Mention the types of frames used in HDLC protocol
21.If the HDLC Control Field looks like this, what would you infer?
0111P/F110.
1001P/F011
1011P/F011
1000P/F100
10100000P/F0001111
11xxP/Fxxx
01000011P/F0001100
Answers
False, Binary Division or Modulo 2 division.
False, Remainder.
False, Forward Error correction.
Hamming Distance.
Code Word: The bigger block containing redundant bits.(Data word+ Redundant bits)
Data Word: Block of data bits to which redundant bits are added.
Hamming Distance: The number of disagreements between two code words.
Weight : The number of 1s in a code word.
6. Content Error: Error in the content of a block of data. It can be bit error or burst error. Bit error is common in parallel transmission and burst error depends on data rate and noise duration.
Flow Integrity Error: Missing block of data due to reasons like delivery to a wrong destination.
7. Parity Check : In parity check, at the sending end, a single redundant bit is added by counting the number of 1s in the data word, to make the parity either odd or even including the parity bit and at the receiver, the checking function detects the parity bit accordingly and finds out errors if any.
CRC;Cyclic redundancy check : In CRC, for each protocol there is a pre-defined divisor in the form of a polynomial. The data to be sent is divided into manageable blocks and each block is divided by the pre-defined divisor. The remainder is appended to the data block and sent. At the receiver when the incoming codeword is divided by the same divisor, if no remainder is got, it is assumed that there is no error. CRC bits(Remainder) will be always one bit less than the divisor. Using XOR gate and Shift registers the circuit is implemented so that the division performed is Modulo 2. (shifting right, comparing)
Checksum: This is an error detection mechanism employed by upper layers. Here the data word is arranged in the form of a matrix, each row containing n bits and modulo 2 addition is performed so that the sum is also having n bits (Ignoring the carry) . The sum is then complemented. This is the checksum field. This is appended to the data unit and sent. At the receiver, again the data after arranging in the form of a matrix,(including checksum bits) modulo 2 addition is performed. If the sum is all 1s, it is assumed that data is intact.
8. Hamming Code, Block Parity, Convolutional Code.
9. State Transition Diagram, Trellis Diagram.
10. Flow Control.
11. 127.
12. ACK 8.
13. Go Back n ARQ.
14. Media Access Control (Line Discipline), Flow Control, Error Control.
15. Go back n and Selective Reject.
16. Stop and Wait and Sliding Window.
17. HDLC: High Level Data Link Control
SDLC: Synchronous Data Link Control
ADCCP: Advanced Data Communication Control Procedure.
BSC/Bisynch: Binary Synchronous Data Link Control
Ethernet, Token Ring.
PPP:Point to Point Protocol.
LAP B :Link Access Procedure Balanced.
18. Bit stuffing.
19.
FLAG
FCS
DATA
CONTROL
ADDRESS
FLAG
Flag: One byte 01111110, Used for synchronization. Bit stuffing guarantees the uniqueness of flag.
Address: one byte. Indicates the address of the secondary station.
Control: One byte or 2 bytes. Begins with 0 for Information frame, begins with 10 for Supervisory frame and begins with 11 for Unnumbered frame.
Data: Variable.
FCS: Frame Check Sequence. For Error detection. 2 byte CRC is used here.
Information frame (I ) : For data, piggy bcked acknowledgements.
Supervisory frame ( S ) :For Control (Flow/Error) information.
Unnumbered frame ( U ): For Link Mangement.
1.Information frame, frame 7 is sending, ACK 6.
2. Supervisory frame, NAK 3/ Rej 3. (Go back n error control)
3. Supervisory frame, NAK 3/ Rej 3. (Selective Reject error control)
4. Supervisory frame, Receiver Ready, ACK 4.
5. Supervisory frame, Receiver Not Ready Ack 15. (Flow Control)(Extended)
6. Unnumbered frame.
7.Information frame, frame 67 is sending, ACK 12 (Extended)
IV
1. The secondary device in a multipoint configuration sends data in [ ]
response to ______
(a) an ACK
(b) an ENQ
(c) a poll
(d) a SEL
2. In sliding window flow control, if the window size is 63, what is the range of sequence numbers? [ ]
(a) 0 to 63
(b) 0 to 64
(c) 1 to 63
(d) 1 to 64
3. In sliding window flow control, the frames to the left of the receiver window are frames _______ [ ]
(a) received but not acknowledged
(b) received and acknowledged
(c) not received
(d) not sent
4. Regulation of the rate of transmission of data frames is known as [ ]
(a) line discipline
(b) flow control
(c) data rate control
(d) switch control
5. ____ decides the role (sender or receiver) of a device on a network [ ]
(a) line connection
(b) link connection
(c) line discipline
(d) link decision
6. The retransmission of damaged or lost frames in the data link layer [ ]
is known as _______
(a) error control
(b) error conditioning
(c) line discipline
(d) flow control
7. When a primary device wants to send data to a secondary device, it [ ]
needs to first send ____ frame.
(a) an ACK
(b) a poll
(c) a SEL
(d) an ENQ
8. When a secondary device is ready to send data, it must wait for ____ [ ]
frame.
(a) an ACK
(b) a poll
(c) a SEL
(d) an ENQ
9. In a peer-to-peer system, when one device wants to send data to [ ]
another device, it first sends _____ frame.
(a) an ACK
(b) a poll
(c) a SEL
(d) an ENQ
10. Flow control is needed to prevent_____ [ ]
(a) bit errors
(b) overflow of the sender buffer
(c) overflow of the receiver buffer
(d) collision between sender and receiver.
11. In go-back-n ARQ, if frames 4, 5, and 6 are received successfully, [ ]
the receiver may send an ACK _____ to the sender.
(a) 5
(b) 6
(c) 7
(d) any of the above
12. For a sliding window of buffer size n, there can be a maximum of [ ]
___ frames sent but acknowledged.
(a) 0
(b) n-1
(c) n
(d) n+1
13. An ACK3 in sliding window flow control (window size of 8) [ ]
means that frame ___ is next expected by the receiver.
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 8
14. In stop-and wait ARQ, if data 1 has an error, the receiver sends a ___ [ ]
frame.
(a) NAK 0
(b) NAK 1
(c) NAK 2
(d) NAK
15. In ____ ARQ, when a NAK is received, all frames sent since the last [ ]
frame acknowledged are retransmitted.
(a) stop-and-wait
(b) go-back-n
(c) selective-reject
(d) a and b
16. In ___ ARQ, if a NAK is received, only the specific damaged or lost [ ]
frame is retransmitted.
(a) stop-and-wait
(b) go-back-n
(c) selective-reject
(d) a and b
17. ARQ stands for _____ [ ]
(a) automatic repeat quantization
(b) automatic repeat request
(c) automatic retransmission request
(d) acknowledge repeat request.
18.Which of the following is not a Layer 2 function
a.error control
b.Encription
c.line discipline
d.flow control
Key IV
1. c 2. a 3. b 4. b 5. c 6. a 7. c 8. b 9. d 10. c 11. c 12. c 13. b 14. d15. d 16. c 17. b 18.b
Choose the correct answer
1. Which of the following is most affected by noise?
a) Amplitude Shift Keying
b) Frequency Shift Keying
c) Phase Shift Keying
d) None of the above
2. Modulation of an analog signal can be accomplished through changing the
___________ of the carrier signal.
a) Amplitude
b) Frequency
c) phase
d) all of the given
3. In_____________ transmission, bits are transmitted simultaneously, each across its dedicated wire.
a) Asynchronous serial
b) Synchronous serial
c) Parallel
d) Asynchronous & Synchronous serial
4. In_____________ transmission, bits are transmitted over a single wire, one at a time.
a) Asynchronous serial
b) Synchronous serial
c) Parallel
d) Asynchronous & Synchronous serial
5. As per Shannon’s capacity theorem, every transmission medium has a _______________ data rate.
a) Minimum
b) Maximum
c) Zero
d) Infinite
FILL UP THE BLANKS
1. For error detection , an extra bit called the _____________ is added to each word in a data transmission.
2. In ____________ transmission, we have to synchronize the source and destination for each character.
3. The _________________of a composite signal is the difference between the highest and the lowest frequencies contained in that signal.
4. The most widely used data code ASCII consists of 8 bits of which 7 are ______________bits and one ______________ bit.
True/False
1. Half Duplex Transmission is two way Simultaneous Communication
2. The problem of synchronization is solved in NRZ codes which ensure sufficient transitions in the data signal.
3. In the analog transmission of digital data, the baud rate is less than or equal to the bit rate.
4. The Nyquist theorem states that a signal must be sampled at a rate greater than twice the lowest frequency component of the signal to accurately reconstruct the waveform.
5. Multiplexing technique allows multiple users to share total capacity of a transmission medium.Short questions
1. An analog signal carries 4 bits per signal element. If 1000 signal elements are sent per second, find the bit rate and baud rate.
2. Calculate the maximum data rate permissible for transmission if the B.W. of a channel is 300-3400 Hz and S/N ratio is 127.
3. Calculate the number of levels required for transmission if the B.W. of a channel is 300-3300 Hz and data rate is 24kbps.
I. Answer the following questions.
1.What is “ARQ”? (Automatic repeat request)
2. Name a routing protocol.(RIP)
3. What is DHCP?(Dynamic host configuration pr0t0col)
4. Write a class C private IP address.(200.12.22.123)
5. Expand CSMA / CD
II. Fill up the blanks
1. Decryption and encryption of data are the responsibility of the ………………. layer.(Presentation)
2. Maximum segment length in case of 10base5 LAN will be……………………….(500m)
3. When a secondary device is ready to send data, it must wait for …………………frame.(Poll)
4. Router works in …………………………. layer of OSI model.(3)
5. In go-back-n ARQ, if frames 4, 5, and 6 are received successfully, the receiver may send an ACK …………………… to the sender.(7)
6. IP address 01101100.10001111.11100110.00100011 belongs to ----------(A)
7. If a carrier signal has 4 levels then the Bit rate will be --------------that of Baud rate.
8. IPv6 address consists of ---------- bits.(128)
III. Answer the following questions briefly
What do you understand by the term protocol?
Write the specific responsibilities of Network layer
What is differential Manchester coding
Distinguish between TCP and UDP.
5. Compare between Go-Back-n and Selective-Reject.
6.For the IP address 201.222.5.121/28 , find the following
a. Subnet address
b. Host addresses
I. Fill in the blanks
1. The minimum Bandwidth offered for a normal subscriber through Broadband is ----------------------.
2. In broadband network of BSNL DSLAM is placed between ………………..and ……………………………
3. Type II CPE provided under Multiplay project is having ---------------Ethernet ports.
4. The technology used in the T2-T1 switch traffic aggregation in Multiplay network is ________________.
5. The customer premises equipment in project 2.2 is also known as ………….
6. The protocol used in NIB II for routing the packets is …………………..
7. BRAS in conjunction with -------------------- authenticates the customer.
8. The NAT function in ADSL modem is for ----------------------
9. Tier I and Tier II switches are doing -------------- layer functions of OSI
10. In Router mode of configuration, the BRAS will be allotting IP address to ----------------------
II. Expand the following
PMS -
BNG-
SSSS-
OSS-
VRF-
f. DMT-
III. Answer the questions briefly
Name any two network elements required for implementing Wi-Fi.
Explain the technology behind ADSL .
3. Give any two functions of the following networking elements of Broadband.
(a) BRAS (b)DSLAM
4. Draw the architecture of MPLS VPN network and mark all elements involved.
5. Is it possible for two MPLS VPN customers to use the same IP address for connecting to the MPLS network ?. Explain
6. Draw the network archtecture of NIB II project 2.2 in A cities and mark the various network elements .
MPLS Questions
List the 2 broad classifications of VPN implementations.
List the main components of MPLS VPN architecture
Expansion of VRF?
Expansion of MP-BGP ?
Length of VPNv4 address ?
---- in the customer network interfaces with the service provider.
---- exists in the core of the provider network in MPLS VPN architecture.
Key
Overlay model & Peer to Peer model
Customer n/w, CE Routers, Provider network, PE Routers, P Routers
Virtual Routing and Forwarding Table
multiprotocol BGP
96 bits
Customer Edge Router (CE Router)
Provider Router (P Router)
Internet Account Tariff, Dial Up networking, Modems Proxy server.
The access no: of CLI based internet service is ………….
(a). 172233 (b) 172225 (c) 172227 (d) 172222
Modem standard which is used now a days is
(a). V 95 (b) V 91 (c) V 99 (d) V 90
Internal modems can be installed on which of the following slots
(a). COM (b) USB (c) PCI (d) PCMCIA
Which of the following port numbers can be used for a Proxy server.
(a). 80 (b) 21 (c) 3128 (d) None of the above
Which of the following is an advantage of using Proxy servers
(a). B/Wenhancement (b) B/W Conserving (c) QOS reduction (d) All the above
State True or False
Proxy is secure from data theft.
Request filtering is possible in Proxy servers.
Home 250 is a leased line package
Surfing pattern of users is a concern in determining the QOS of proxy servers.
Modem can act both as an A/D converter and D/A converter.
Key
1. d
2. d
3. c
4. c
5. b
6. F
7. T
8. F
9. T
10. T
Expand
1. URL
2. RADSL.
3. DIAS.
Answer the following:
1. Mention any 3 browser software.
2. Give any 3 options for providing user connectivity to the Internet.
KEY
Expand
1. Uniform Resource Locator.
2. Rate Adaptive Digital Subscriber Line.
3. Direct Internet Access System.
Answer the following:
1. Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, Opera, Safari, Lynx, Netscape Navigator.
Dial-up connections, DIAS, Broadband, Using Cable Modem, Leased Line.
Worksheet for TCP/IP
1. First 24 bits of MAC address represents ---------------( Identity of manufacture)
2.TCP is in the --- layer of TCP/IP suit (4)
3.IP is in the --- layer of the TCP/IP suit (3)
4.Name two application layer protocols
http and ftp
5.MAC address is used in --- layer (2)
6.MAC address is of --- bits length (48 bits)
7.what are the IP address versions? (IPV4 and IPV6)
8.what is the data speed of fast Ethernet (100 mbps)
9.Application port number is to identify -------(different applications in application layer)
10.Diat up modem belongs to which layer of TCP/IP suit (L-1)
Write the expansion of the following
http: Hypertext Transfer Protocol
ftp: File Transfer Protocol
TCP: Transmission Control Protocol
IP: Internet Protocol
UDP: User Datagram Protocol
ARP: Address Resolution Protocol
ICMP: Internet Control Message Protocol
DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration protocol
RARP: Reverse Address resolution Protocol
FDDI: Fiber distributed data interface
State True or false
1.ARP is used to resolve physical address (T)
2.RARP is used to resole logical address (T)
3.UDP is an application layer protocol (F)
4.IPV4 is 128 bits address (F)
5.Sourse and Destination IP address is added by a computer (T)
6.TCP is a connection-oriented protocol (T)
7.IP is a connection – less protocol (T)
Write the name of all the 5 layers of TCP/IP suit
Application
Transport
Network
Datalink
Physical
Resilient Packet Ring
Choose the correct answer
Give the IEE standard for RPR
802.11
802.16
802.17
802.13
Ans. 802.17
The recovery time of RPR to achieve protection against fibre cut is
Less than 50ms.
Less than 60 ms.
Less than 125μs
None of these
Ans. Less than 50ms
Maximum number of RPR stations supported in an RPR ring..
164
16
255
200
Ans. 255
The mandatory protection scheme employed in RPR
Wrapping
Topology discovery
Steering
Multicasting
Ans. Steering
Answer the following:
1. Give the three packet handling activities of a RPR node?
Insertion(Adding a packet into the ring)
Forwarding (Sending packet onward for transit traffic)
Stripping or dropping(taking out the packet off the ring.
2. Give the two packet delivery modes of RPR
Stict mode & Relaxed mode
3. Give the classification based on traffic priority
1) - Class A or premium quality (low latency, low jitter) sub-class A0(reserved) & A1(opportunistic ie if not used given class B &C )
2) - Class B or medium quality (predictable latency & jitter), B-CIR (committed information rate-non fe but used if free) & B-EIR (Excess information rate-fe)
3) - Class C or low priority traffic (“best effort” class)
Introduction to DWDM
I. Choose the correct answer:-
The Long band of Optical spectrum ranges from ________________________________.
(1450 to 1550nm, 1565 to 1620 nm , 1310 to 1550 nm).
Ans-1565 to 1620 nm
The losses caused by various effects on the signal limits the usable wavelength in the range ____________________________.
(1200 to 1550 nm, 1310 to 1550 nm, 1280 to 1650 nm).
Ans-1280 to 1650 nm
A Transponder is basically a _____________________converter.
(O-E-O, O-E, E-O)
Ans-O-E-O
In DWDM routes for boosting up the signals for long distance transmission, ___________________________ is used.
(Transponder, OADM, Optical Amplifier)
Ans- Optical Amplifier
In BSNL _______________spacing ITU Grid is used for DWDM channel selection.
(50GHz, 100GHz, 200GHz)
Ans-100GHz
In DWDM, adding and dropping of signals at any point along the span of
transmission is possible using __________________.
(Optical Amplifier, OADM, Transponder)
Ans- OADM
An Optical Amplifier does __________ regeneration.
(1R, 2R, 3R)
In the Conventional band DWDM operation __________is used as a supervisory channel.
(1565nm,1510 nm, 1560 nm)
II. Answer the following: -
a. What is a Transponder? Mention its Advantages.
b. Name the optical network elements used in DWDM?
c. Give the advantages of DWDM?
d. Mention some methods for Optical Multiplexing?
e. Mention the different ways by which WDM can act as a Multi Service Provisioning platform?
Answers:-
a. A Transponder is a device that adapts to the arbitrary bit rate of the incoming optical signal and maps its wavelength to the chosen WDM channel. Its main function is OEO. It converts wavelength coming from user equipment to electrical signal and then the electrical signal is converted into optical signal of a specific wavelength, which forms an optical channel for particular user.
Advantages
1. Greatly enhanced transmission capacity.
2. New services offered
3. Transmission of restructured signals.
4. Use of devices and interfaces form other vendors.
b. Optical Multiplexer
Optical Demultiplexer
Optical Amplifiers
Transponders
Regenerators
OADM
Optical cross connects
c. Multiple use of fibers.
Extremely high transport capacity at lost.
Format and bit rate independency.
d. Using Prism, Using Diffraction Grating
e. SDH over WDM
IP over WDM
Lambda services
CHL DWDM Systems .
1. The Working wavelength range of ZTE 32Chl DWDM System _____nm to ________ .
(Ans : 1529nm to 1565nm )
2. The channel interval of ZTE 32Chl DWDM System?
a) 50 GHz b)100 GHz. C)150GHz d) 25 GHz (Ans: b)
3. What are 3 configurations of ZXWM M900 ( ZTE DWDM system)?
Ans :- 1)OTM 2) OADM 3) OLA
4. The wavelength of the optical signal which carries supervisory channel of ZXWM M900 ( ZTE DWDM system) ?
a) 1500nm b)1490 nm c) 1510nm d) 1520nm (Ans: c )
5. The main control processor card of ZXWM M900 ( ZTE DWDM system) is known as __________ (Ans : NCP)
6. The main control processor card of ZXWM M900 ( ZTE DWDM system) is located in __________ Subrack (Ans : OA)
a) OTU b) OA c) Power Alarm d) None of these
7. The Optical Supervisory channel board of ZXWM M900 ( ZTE DWDM system) is located in __________ Subrack (Ans : OA)
a) OTU b) OA c) Power Alarm d) None of these
8. The Optical Multiplexer and demultiplexer of ZXWM M900 ( ZTE DWDM system) is located in __________ Subrack (Ans : OTU)
a) OTU b) OA c) Power Alarm d) None of these
9. A maximum of _________ fibres can be connected to an ODF board of ZXWM M900 ( ZTE DWDM system). (Ans :- 42)
a) 34 b) 40 c) 28 d) 42
10. ________ Board performs the processing of order wire in a supervisory channel.
a) OP b) OA c) OHP 5) OSC (Ans : c)
11. One NCP of ZXWM M900 ( ZTE DWDM system) manages _______ Racks at most.
a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 (Ans : d)
EXTERNAL PLANT
FILL UP THE BLANKS:-
1. The depth of the trench for laying local cable should be 1.2 METER.
2. The inner zone limit for a Telephone exchange is 500 METER.
3. In an LCU customer pair to network pair is 96/16.
4. Pillars are given two digit numbering scheme from 21 to 99.
5. The V/2 value for PIJF cable in APLAB fault locator is 88
6. Parallelism exceeding 800 METER with 11KV and above should be referred to PTCC
7. The color of 375th pair of a 400 pair PIJF cable is 2ND LAYER-LAST SUPER UNIT (BLACK COLOR BINDER)- 3RD UNIT (GREEN COLOUR BINDER) – ‘A’ WIRE –WHITE & ‘B’ WIRE-SLATE
8. The marking 200/0.5/248 over the sheath of a cable indicates 200 PAIR/0.5 MM DIAMETER/ MEASURED AT 248TH METER LENGTH.
9. The PTCC recommends THREE ELECTRODE type of GD Tubes.
10. In ducted cable system UNARMOURED type cables are used for reducing cost
IV) Decode:-
DP 4802/07 : TERMINAL NO.7 OF DP NO.2 CONTROLLED BY PILLAR NO.48
MDF 176/29 : TERMINAL NO.29 OF FUSE STRIP 6 ON VERTICAL 17
V) Draw the symbols
a) Pillar
b) Straight Joint
VI) ANSWER THE QUESTIONS
a) Write Four advantages of Computerised FRS.
ANY 4 ADVANTAGES AS GIVEN IN PAGE 133 OF HANDOUT VOLUME 2.
b) What are the advantages of Optical Fibre cables over PIJF cables ?
AS GIVEN IN PAGE 15 OF HANDOUT VOLUME 2
c) What are the different types of cards, kept as cable records?
1) PLAN OR MAPS: EXGE AREA LAYOUT MAP, CABINET/PILLAR AREA LAY OUT MAP.
2) LINE DIAGRAM: PRIMARY, SECONDARY, DISTRIBUTION, JUNCTION, PRESSURISATION
CARDS: DP, CABINET, PILLAR, MDF, SUBSCRIBER INDEX
I. Fill up the blanks:
1. The overprovision of distribution cable is ______________.
2. A telephone exchange is to be ideally situated at the ______________.
3. Pillars are given two digit numbers from ____ to ____
4. A 200 pair cable of 500m length (Skm) is equivalent to __________ckm.
5. The software that is used for customer relationship management in BSNL are_____________ and ___________.
6. The software that deals with the management of redressal of public complaints is---------
7. Project estimates can be prepared and sanctioned using the software called __________.
8. The three parts of the resource management software are ________, and ____________.
9. _______________ Software deals with the service records of the staff.
10. Management decisions on the free phone services, IN cards are taken on the basis of data maintained by _________ software.
11. Vehicle management is done using _________ software in BSNL.
12. ATOMS is the acronym for_______________.
13. Minimum download speed of Broadband in India---------------------
14. Wi-Fi is the technology used for -----------------------------------
15. Usually a PSTN (b-Fone) line is working at -------------------bps.
16. Aggregation point at service providers end from various customers’ ADSL line is-----------------------
17. Maximum distance between DSLAM and TIER –2 Switch, if connected by means of dark fibres------------------------.
18. ADSL stands for------(Asymmetrical digital subscriber line)
20. Technology used in the backbone core Network of Broadband is------(MPLS)
Fill up the following with reference to the survey results on customer response
1. _____________% of customers change the business relation due to indifferent attitude.
2. _______________ Number of the positive responses are required to compensate for one negative response of the operator.
3. ____________ % of dissatisfied customers won’t give the feedback to the organisation.
4. A satisfied customer would bring __________more new customers.
II. Choose the correct answer
1. Works in progress expenditure transferred to fixed assets in respect of A&P
a. When exge is commissioned b. When it is received
c. When Payment is made d. From the date of bill/invoice.
2. Security guards can be engaged in BSNL units through
a. Open tender b. Limited tender
c. DGR NewDelhi c. DGR NewDelhi or state ESM Corp
3. Penal interest is charged for the delayed submission (beyond 30 days) of ACE-2 accounts for Temporary advance is
a. 10% per day b. 2% per month
c. 10% per year d. 12% per year.
4. As per GFR 2005 , Limited tender procedure may be followed for purchase of good.
a. Up to Rs 50000 b. UP to Rs 2 lakhs.
c. Up to Rs 10 lakhs c. Up to Rs 25 lakhs.
5. To avid CST, for the goods transferred from other states by BSNL units (T.F/CGMTS) the form to be issued by the receiving unit is
a. Form.D b. Form C
c. Form F d. None of these
Match the following.
A. Abbreviated Dialing 1. Dial 124 xxxx 4
B. Call Transfer 2. Dial 124 xxxx 3
C. On line Meter reading 3. Dial 124 xxxx 2
D. Bar calls to up to 95 level 4. Dial 114 / 115
E. Bar ISD Calls alone 5. Dial 110 / 111
6. 1501
IV. Match the following.
A. ISDN 1.Digital Sub unit (DSU)
B. DIAS 2. 144 kbps
C. PRI 3. NTU-STU 160/CTU.S
D. MLLN 4.Terminal Adapter
E. BRI 5. 2048 Kbps
FILL UP THE BLANKS
1) 30 % 2) Load Centre 3) 21 to 99
4) 200 ckm 5) SSA NET and DOT SOFT 6) PGRMS 7) Inventory Management
8) Cash, Works Account, Asset, Inventory 9) HR Management
10) MIS on IN 11) Fleet Management
12) AT Offering Management System 13) 256 KBPS
14) WIRELESS LAN 15) 64 K 16) DSLAM
17) 10 km 18) Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line 19) MPLS
II FILL UP THE BLANKS:
1) 70% 68% 2) 12 25 3) 96% 4) 5 10
III CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER
1) a 2) d 3) b 4) d 5) c
IV MATCH THE FOLLOWING
A—5 B—4 C—6 D—1 E—2
V MATCH THE FOLLOWING
A—4 B—1 C—5 D—3 E—2
POWER PLANT
Fill up the blanks:
1- The capacity of Large Exchange Power Plant is greater than 50 A.
2- In the conventional 3 piece power plant the FR output is regulated with in the
range of -51.5 ± 0.5 V irrespective of input voltage variations of ± 12 %.
3- The Psophometric noise of Exchange power supply with a battery of appropriate capacity connected across the output is within 2 mv
4- Minimum Insulation resistance of components w.r.t. earth in power plant is
5 MEGHA OHMS
5- In the conventional 3 piece power plant, to limit the charging current variations BALLAST CHOKES are provided in the Battery charger
6- The FR current is shared by EXCHANGE LOAD & BATTERY SET
7- The two power converters in SMPS module are BOOST CONVERTER & DC-DC CONVERTER
8- Output voltage of SMPS module in float mode is -54 ± 0.5 V and in charge mode is -55.2 ± 0.5 V
9- In SMPS modules, to reduce the switching losses of the semiconductors due to non-zero switching times SNUBBER CIRCUIT is provided
10- In SMPS, the current signals are monitored continuously to ensure equal sharing of current is performed by POWER SYSTEM CONTROLLER (PSC) card in MAIN rack
11- The capacity of the battery increases with INCREASE in temperature
12- In parallel battery float scheme of working, the end point for the discharge of the cells has to be limited to 1.92 volt per cell
13- The type of charger suitable for charging VRLA battery is CONSTANT VOLTAGE CURRENT LIMITING CHARGER OR CONSTANT VOLTATE CHARGER.
14- VRLA battery works on OXYGEN RECOMBINATION Principle and the recommended float voltage of VRLA battery is 2.25 VPC at 27o C
Answer the following:
1- What are the points to be considered for deciding the capacity of power plant needed for an exchange?
1. BATTERY CHARGING CURRENT (BATTERY CAPACITY AT THE RATE OF 6 HR BACKUP)
2. BUSY HOUR LOAD (HOW LONG BATTERY IS REQUIRED TO SUPPLY DURING MAINS FAILURE.
2- Mention important four alarms displayed in Switching Cubicle.
MAINS FAIL, PHASE FAIL, OUTPUT FUSE FAIL, RECTIFIER ELEMENT FUSE FAIL, SMOOTHERING FILTER FUSE FAIL, CIRCUIT BREAKER TRIP, HIGH/LOW VOLTAGE ALARM, OVER LOAD ALARM
3.What is meant by efficiency of a power plant?
RATIO OF DC OUTPUT WATTS TO AC INPUT WATTS AT THE NORMAL INPUT VOLTAGE (NOT LESS THAN 75% IN LARGE EXCHANGE FRs UPTO 200 AMPS AND 80% IN CASE OF HIGHER OUTPUT CAPACITIES)
Match the following:
1- Knife switches a) Corrosion
2- Weak cell b) Battery charging
3- DC shunt c) Low S.G & p.d
4- Current transformer d)Measuring DC current
e) monitoring the input current
f) SCR firing circuit
g) Error Amplifier
Answer: 1- [ b], 2- [ c ], 3- [ d ], 4- [e]
Choose the correct answer from among the choices
1. What is the auto charge level in the SMPS system?
a) 54.0 V b) 55.2 V c) 65.0 V d) None of these.
2. The positive electrode in the VRLA battery is made of:
a) PbO2 b) Pb c) H2SO4 d) AGM
3. Which advantage is not applicable to SMPS?
a) Higher efficiency b) No noise
c) Reduced transformer size d) None of these.
PSC card is connected to module using:
a) 8 pin flat cable b) 4 pin flat cable
c) bunch of wires d) None of these.
Which indication represents a faulty condition?
a) Mains available b) FR/FC on float c) FR/FC on charge d) Load voltage low
The principle behind VRLA battery is:
a) Lead Sulphate deposition b) Oxygen recombination cycle
c) Osmosis d) None of these
In a thyristor controlled power plant when the O/P voltage goes higher, the firing pulse of thyristor is:
a) Retarded b) Neither advanced nor retarded
c) Advanced d) None of these.
The circuit element used in power plant to read the input current of RYB phases is:
a) Shunt b) Synchronisation transformer
c) Current transformer d) Photo coupler
Wave form across the capacitor in the emitter circuit of an UJT is:
a) Square wave b) Sine wave c) Triangular wave d) Saw tooth wave
PWM technique makes use of:
a) Constant pulse width b) Constant switching frequency
c) Variable frequency d) Variable cycle oscillator.
Boost converter works on the principle of:
a) Full bridge topoly b) Boost topology
c) Phase shift PWM d) Switching regulator
Isolation transformer in DC ~ DC converter stage is a must.
a) It is true b) It is false
c) It is partially correct d) Can work even without a transformer
The output voltage of a Basic Boost Cell is:
a) 400 volts AC b) 400 volts unregulated DC
c) 400 volts stabilized DC d) 450 volts stabilized DC
Which one of the following is not a function of PSC?
a)Equal current sharing b) Control the operation of the module
c) pulse width control d) Shutting of the faulty modules
15. In UPS, for fast change over of primary and secondary sources, the best choice is:
a) A sensitive relay b) A high speed relay c) A triac d) A thyristor
In on line UPS the inverter will be ON only during mains fail.
a) True b) False c) During system failure d) None of the above
17. The earth connection for the inveter is:
a) From the EB earth b) to be done separately for inverters
c) From the equipment earth d) none of these.
18. Stand alone inverters used in Exchanges provide AC voltage with a frequency of:
a) 65 Hz. b) 45 Hz. c) 50 Hz d) Can be anything
19. Which one of the following is not applicable to VRLA batteries?
a)No satisfaction b) Environment friendly c)Stackable nature d) Frequent topping up
20. As compared to conventional batteries, VRLA batteries have:
a) Greater self discharge b) No self discharge
c) Low self discharge d) Intermittent self discharge
21. The output stage of an SMPS module makes use of:
a) Power transistors b) SCRs c) Triacs d) Power MOSFETs
22. As the ambient temperature increase the recommended voltage for VRLA batteries:
a) Increases b) Neither increases nor decreases
c) Decreases d) None of the above
23. Which among the following wave forms is not applicable to UPS?
a) Sine wave b) Square wave c) Quasi sine wave d) Saw tooth wave.
24. Which among the following is not a protective device?
a) GD tube b) MOV c) Fuse d) Retrieval diode
25. If the float voltage is 53.35 at 27οC what will be the voltage at 30οC?
a) 53.13 V b) 53.0 V c) 52.9 V d) 53.2 V
AC PLANT & ENGINE ALTERNATORS
Fill in the blanks with suitable word/words.
1.Air conditioning is the simultaneous control of -TEMPERATURE ,HUMIDITY &--DUST.
2.The type of cooling resorted to, in the condensers of large air conditioning systems of capacity greater than 15 T is WATER COOLING
3. Alternator converts MACHANICAL ENERGY to ELECTRICAL energy.
Answer in two or three sentences:
a. Mention the different types of A/C systems used in our Department?
PACKAGE TYPE, SPLIT TYPE, WINDOW TYPE, CENTRALISED AC
b. What is the function of governor in a Diesel engine?
IT REGULATES THE AMOUNT OF FUEL SUPPLIED AT EACH STROKE AND THIS CONTROLS THE ENGINE SPEED AND POWER
EARTHING & MEASUREMENT / FIRE FIGHTING
1.What is the earth resistance of the earth electrode system for electronic exchanges ?
< 0.5 OHMS
2. What type of fire extinguisher is used to quench oil fires?
FOAM TYPE
3. Name the Three types of Earth Electrode systems.
SPIKE EARTH, PLATE EARTH, LEAD STRIP EARTH
POWERPLANT,AC PLANT & ENGINE ALTERNATORS
CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER:
Among the following which is not a function of float rectifier
a) Stepping up (b) Rectification (c) Regulation
2. What is the basic working principle of SMPs ?
(a)AC to DC conversion (b) Switching regulation (c) Rectification
3. In ITI 50 V –200 0A power plant (multi rack type) the voltage adjustment range on float mode is
(a) -40 to -60 v (b) –48 to –56v (c) -48 to –52v
4. If a 100AH battery is connected across a 50 A Exchange load, how long it can take the Exchange load?
(a) 2 hours (b) 24 hours (c) 50 hours
5. At 20 % depth of discharge what is the life expectancy of a VRLA battery
(a)5000 charge discharge cycle,
(b) 4000 charge discharge cycle
(c) 6000 charge discharge cycle.
6.The earth resistance earth electrode system for electronic exchanges should be
(a) < 0.5 Ω (b) < 1 Ω (c) < 2 Ω
7. In VRLA battery what should be the float voltage per cell?
(a) 2.15V (b) 2.25 V (c) 2.3 V
8. In a Power plant, if the Mains on battery discharge alarm glows them what is the
cause for the alarm?
(a) Battery failed and mains on
(b) Mains on
(c) Power plant voltage is less than the battery voltage
9.In SMPS which type of voltage conversion takes place in power converter stage?
(a) DC to DC conversion (b) AC to DC conversion (c) DC to AC conversion
10. During power stroke of a diesel engine which valve remains closed?
( a) Inlet valve (b) out let valve (c) Both the valves
Fill up the blanks :
1. Air conditioning is the simultaneous control of TEMPERATURE, HUMIDITY, DUST & FRESH AIR.
2. VRLA Battery should never discharged below 42 Volt.
3. In VRLA battery, MICROPORUS GLASS / ABSORTIVE GLASS MATRIX (AGM) is the separator used .
4. The EMI and RFI are suppressed in a SMPS by FILTERING circuit.
5. In a lead acid battery DILUTED SULPHURIC ACID (H2SO4) is used as electrolyte.
6. To quench fire on burning oil, FOAM TYPE fire extinguisher is used.
7. In a four stroke Diesel engine the first stroke is called SUCTION.
8. For expressing the capacity of an AC System TR is the unit used.
9. Once SCR starts conduction it can be switched off by bringing CURRENT below the thresh hold .
10. For a fully charged VRLA battery at 27 0 C, 2.15 V is the open circuit voltage.
ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS:-
1. What are the four processes involved in the refrigeration cycle?
EVAPORATION, COMPRESSION, CONDENSATION, EXPANSION
2. What are the different types of AC systems used in BSNL?
PACKAGE TYPE, SPLIT TYPE, WINDOW TYPE, CENTRALISED A/C
9. What is the function of governor in a Diesel engine?
IT REGULATES THE AMOUNT OF FUEL SUPPLIED AT EACH STROKE AND THIS CONTROLS THE ENGINE SPEED AND POWER
package used in BSNL
1. The package used in BSNL for inventory is called ______________________
2. A package used in BSNL to generate PSTN bills from the meter reading of the individual exchanges is ______________________________
3. The package designed for management of the vehicles in BSNL is called _________________________
4. The package used in BSNL to avoid the delay in provisioning of leased lines, all over the country is ………………………………………..
5. The management information of BSNL is maintained as a separate database using the package called as _____________ .
KEY
1. package used in BSNL IMP (Inventory Management Package)
2. Trichur Billing Package
3. Fleet Management system
4. TVARIT
5. MIS (management Information System)
1. One of the software which is used for customer relationship management in BSNL are --------------------
(a) SSANET (b) DOTSOFT (c) Both (d) None of the choices
The software which deals with the management of redressal of public complaints is called ---------------------
(a) HR Package (b) PGRMS (c) BSNLRMS (d) MIS
Project estimates can be prepared and sanctioned using the software called --------
(a) PGRMS (b) BSNLRMS (c) ATOMS (d) None
------------- software deals with the service records of the staff.
(a) BSNLRMS (b) PGRMS (c) HR Package (d) SSANET
Management decisions on the free phone services, ITC cards are taken on the basis of date maintained by -------------- software.
(a) MIS (b) INMIS (c) Both (d) None of the above
KEY
1. c
2. b
3. b
4. c
5. b
Additional questions
---------------- is the software package developed for management of vehicle inventry.
Write any four features of HR Package?
Mention any four features of DoTSoft?
------------------- is the package used for the management of leased lines.
Name three System tools available in windows
Name four functions used in MS Excel with suitable syntax?
What are the various types of Cell reference?
What are the steps involved in making a Chart in MS Excel?
How do you set margins on a page?
In MS Excel----------- operator is having the highest priority?
Only one data series can be plotted in -----------Chart?
What is the shortcut keystroke to allow you to quickly toggle text case from UPPERCASE to lowercase to TitleCase?
A filename can contain a maximum of -----------Characters?
How do you see the extensions of all files?
------------------- function adds the cells specified by a given criteria
Mention four important items in Control panel.
Write the steps to include headers ,footers,page-numbers in your document.
Mention the steps to setup the spelling Checker.
--------is used in linux to run commands at scheduled times .
Mention four advantages of oracle?
Mention four advantages of DBMS?
---------------used in oracle for defining structures such as staring and shutting down database
Mention any four Codd Rules.?
------- allows to load data stored in a variety of formats into an oracle database.
UPSC sylabus
General Science.
Current events of national and international importanceHistory of India and
Indian National MovementIndian and
World GeographyIndian Polity and EconomyGeneral
Mental Ability
Scheme of CS (Preliminary) Examination
The Preliminary Examination consists of two papers of objective type (multiple-choice questions) carrying a maximum of 450 marks. The Question Papers (Test Booklets) are set in English & Hindi
Paper - I General Studies 150 Marks Paper - II One of the optional subjects to be selected from the prescribed optional subjects 300 Marks
FPRIVATE "TYPE=PICT;ALT=Get More Specialise Information on IAS Exams conducted by UPSC. Syllabus, Question Papers and more ..."
:: Preliminary Examination Syllabus :: Main Examination Syllabus:: Upsc Syllabus - Other SubjectsHistory Syllabus for Preliminary Examination Section-A
1. Prehistoric cultures in India
2. Indus Civilization. Origins. The Mature Phase: extent, society, economy and culture. Contacts with other cultures.Problems of decline.
3. Geographical distribution and characteristics of pastoral and farming communities outside the Indus region, from the neolithic to early iron phases.
4. Vedic society. The Vedic texts; changefrom Rigvedic to later Vedic phases. Religion; Upanishadic thought. Political and social organisation; evolutuion of monarchy and varna system.
5. State formation and urbanization, from the mahajanapadas to the Nandas. Jainism and Buddhism. Factors for the spread of Buddhism.
6. The Mauryan Empire. Chandragupta; Megasthenes. Asoka and his inscriptions; his dhamma, administration, culture and art. The Arthasastra.
7. Post-Mauryan India, BC 200- AD 300. Society: Evolution of jatis. The Satavahanas and state formation in Peninsula. Sangam texts and society. Indo-Greeks, Sakas, Parthians, Kushanas; Kanishka. Contacts with the outside world. Religion : Saivism, Bhagavatism, Hinayana and Mahayana Buddhism; Jainism; Culture and art.
8. The Guptas and their successors (to c. 750 AD). Changes in political organisation of empire. Economy and society. Literature and science. Arts. Section-B
9. Early Medieval India. Major dynasties; the Chola Empire. Agrarian and political structures. The Rajaputras. Extent of social mobility. Postition of women. The Arabs in Sind and the Ghaznavides.
10. Cultural trends, 750-1200, Religious conditions : importance of temples and monastic institutions; Sankaracharya; Islam; Sufism. Literature and Science. Alberuni’s "India". Art and architecture.
11-12. Thirteenth and fourteenth Centuries: Ghorian invasions causes and consequences. Delhi Sultanate under the "Slave" Rulers. Alauddin Khalji : Conquests; administrative, agrarian and economic measures. Muhammad Tughlug's innovations. Firuz Tughluq and the decline of the Delhi Sultanate. Growth of commerce and urbanization. Mystic movements in Hinduism and Islam. Literature. Architecture, Technological changes.
13. The fifteenth and early 16th Century : major Provinicial dynasties; Vijaya-nagara Empire. The Lodis, First phase of the Mughal Empire: Babur, Humayun. The Sur empire and administration. The Portuguese. Montheistic movements: Kabir; Guru Nanak and Sikhism; Bhakti. Growth of regional literatures. Art and Culture.
14-15. The Mughal Empire , 1556-1707. Akbar: conquests, administrative measures, jagir and mansab systems; policy of sulh-i-kul. Jahangir, Shahjahan and Aurangzeb : expansion in the Deccan; religious policies. Shivaji. Culture: Persian and regional literatures. Religious thought: Abul Fazl; Maharashtra dharma. Painting. Architecture. Economy: conditions of peasants and artisans, growth in trade; commerce with Europe. Social stratification and status of women.
16. Decline of Mughal Empire, 1707-61. Causes behind decline. Maratha power under the Peshwas. Regional states. The Afghans. Major elements of composite culture. Sawai Jai Singh, astronomer. Rise of Urdu language. Section-C
17. British expansion : The Carnatic Wars, Conquest of Bengal. Mysore and its resitance to British expansion: The three Anglo-Maratha Wars. Early structure of British raj: Regulating and Pitt's India Acts.
18. Economic Impact of the British Raj : Drain of Wealth (Tribute); land revenue settlements (zamindari, ryotwari, mahalwari); Deindustrialisation; Railways and commercialisation of agriculture; Growth of landless labour.
19. Cultural encounter and social changes: Introduction of western education and modern ideas. Indian Renaissance, social and religious reform movements; growth of Indian middle class; The press and its impact: rise of modern literature in Indian languages. Social reforms measures before 1857.
20. Resistance to British rule : Early uprisings; The 1857 Revolt- causes, nature, course and consequences. 21. Indian Freedom struggle-the first phase: Growth of national consciousness; Formation of Associations; Establishment of the Indian National Congress and its Moderate phase;- Economic Nationalism; Swadeshi Movement; The growth of "Extremism" and the 1907 split in Congress; The Act of 1909 - the policy of Divide and Rule; Congress-League Pact of 1916.
22. Gandhi and his thought; Gandhian techniques of mass mobilisation- Khilafat and Non Cooperation Movement, Civil Disobedience and Quit India Movement; Other strands in the National Movement-Revolutionaries, the Left, Subhas Chandra Bose and the Indian National Army.
23. Separatist Trends in Indian nationalist politics- the Muslim League and the Hindu Mahasabha; The post -1945 developments; Partition and Independence.
24. India independent to 1964. A parliamentary, secular, democratic (republic the 1950 Constitution). Jawaharlal Nehru's vision of a developed, socialist society. Planning and state-controlled industrialization. Agrarian reforms. Foreign policy of Non-alignment. Border conflict with China and Chinese aggression.
History Syllabus for Main Examination Paper-ISection-A
1. Sources and approaches to study of early Indian history.
2. Early pastoral and agricultural communities. The archaeological evidence.
3. The Indus Civilization: its origins, nature and decline.
4. Patterns of settlement, economy, social organization and religion in India (c. 2000 to 500 B.C.) : archaeological perspectives.
5. Evolution of north Indian society and culture: evidence of Vedic texts (Samhitas to Sutras).
6. Teachings of Mahavira and Buddha. Contemporary society. Early phase of state formation and urbanization.
7. Rise of Magadha; the Mauryan empire. Ashoka's inscriptions; his dhamma. Nature of the Mauryan state.
8-9 Post-Mauryan period in northern and peninsular India: Political and administrative history,. Society, economy, culture and religion. Tamilaham and its society: the Sangam texts.
10-11 India in the Gupta and post-Gupta period (to c. 750) : Political histroy of northern and peninsular India; Samanta system and changes in political structure; economy; social structure; culture; religion.
12. Themes in early Indian cultural history: languages and texts; major stages in the evolution of art and architecture; major philosphical thinkers and schools; ideas in science and mathematics. Section-B
13. India, 750-1200 : Polity, society and economy. Major dynasties and political structurs in North India. Agrarian structures. " Indian feudalism". Rise of Rajputs. The Imperial Cholas and their contemporaries in Peninsular India. Villagle communities in the South. Conditions fof women. Commerce mercantile groups and guilds; towns. Problem of coinage. Arab conquest of Sind; the Ghaznavide empire.
14. India, 750-1200: Culture, Literature, Kalhana, historian. Styles of temple architecture; sculpture. Religious thought and institutions: Sankaracharya's vedanta. Ramanuja. Growth of Bhakti, Islam and its arrival in India. Sufism. Indian science. Alberuni and his study of Indian science and civilization.
15. The 13th Century. The Ghorian invasions. Factors behind Ghorian success. Economic, social and cultural consequences. Foundation of Delhi Sultanate. The "slave" Dynasty. IItutmish; Balban. "The Khalji Revolution". Early Sultanate architecture.
16. The 14th Century. Alauddin Khalji's conquests, agrarian and economic measures. Muhammad Tughluq's major "projects". Firuz Tughluq's concessions and public works. Decline of the Sultante. Foreing contacts: Ibn Battuta.
17. Economy societyand culture in the 13th and 14th centureis. Caste and slavery under sultanate. Tehnological changes. Sultanate architecture. [persian literature: Amir Khusrau, Historiography; Ziya Barani. Evolution of a composite culture. Sufism in North India. Lingayats. Bhakti schools in the south. 18. The 15th and early16th Century (Political History). Rise of Provincial Dynasties: Bengal, Kashmir (Zainul Abedin), Gujarat, Malwa, Bahmanids. The Vijayanagra Empire. Lodis. Mughal Empire, First phase : Babur, Humayun. The Sur Empire : Sher Shah's administration. The Portuguese colonial enterprise.
19. The 15th and early 16th Century (society, economy and culture). Regional cultures and literatures. provincial architectural styles. Society, culture, literature and the arts in Vijayanagara Empire. Monotheistic movements: Kabir and Guru Nank. Bhakti Movements: Chaitanya. Sufism in its pantheistic phase.
20. Akbar: His conquests and consolidation of empire. Establishment of jagir and mansab systems. His Rajput policy. Evolution of religious and social outlook. Theory of Sulh-i-kul and religious policy. Abul Fazl, thinker and historian. Court patronage of art and technology.
21. Mughal empire in the 17th Century. Major policies (administrative and religious) of Jahangir, Shahjahan and Aurangzeb. The Empire and the Zamindars. Nature of the Mughal state. Late 17th Century crisis: Revolts. The Ahom kingdom, Shivaji and the early maratha kingdom.
CIVIL-PAPER
- Which of the following is not correct about sabha and samithi in the Vedic age? women continued to take part in the assemblies during later Vedic period
- Which of the following is false? royal coronation Ashvamedha
- With regard to the position of women during the Vedic age, which one of the following statements is not true? the practice of sati was unknown during the later Vedic period
- In the Vedic age - widow could remarry
- Which of the following factors was not responsible for encouraging the practice of caste system during the later Vedic period? social inequalities
- The Painted Grey Ware (PGW) belong to the Vedic age
- Which of the following statements is false? Hiranyagarbha - a title given to varuna
- Identify the metal which was not mentioned in the Rig-Veda Lead
- Match the following
A. kshattri 1.Chamberlain
B. Bhagdugha 2.Collector of Taxes
C. samgrahitri 3.Treasurer
D. senani 4. Provincial governor
E. sthapati 5. Commander-in-Chief
A-1, B-2, C-3, D-5, E-4
- Match the following.
A. Rigveda 1.Aitareya Brahmana
B. Samaveda 2. Jaminiya Brahmana
C. Yajurveda 3. Gopatha Brahmana
D. Atharvaveda 4. Taittiriya Brahmana
A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
- Match the following
A. Patanjali 1. Niyaya Philosophy
B. Gautama 2. Sankhya Philosophy
C. Kapila 3. Yoga Philosophy
D. Kanda 4. Uttara Mimamsa Philosophy
E. Vyasa 5. Vaisheshika Philosophy
A-3, B-1, C-2, D-5, E-4
- Which of the following kingdoms is not mentioned in the Ramayana and the Mahabharata? - kausambi
- Which of the following is/are matched correctly?
I. Samaveda – melody
II. Atharvaveda – mainly magic spells
III. Aranyakas – forest books
IV. Srauta Sutra – ceremonies of domestic life
1, 2, 3
- Which of the following are manuals of instruction in the form of brief rules?
Sutras
- Which of the following is/are associated with Dharma sutras?
1. Gautama 2. Apasthamba 3.Vasishtha 4. Baudhyana
- Which of the following wrote the Smritis pertaining to the Dharmasashtra?
Yajnavalkya
- Which of the Vedangas gave rise to Dharmasutra?
Kalpa
- Who does the ‘Gayatri mantra’ in the Rigveda address?
Savitri
- The mediator between man and gods according to the Vedic people was Agni
- Which of the following is/are correctly matched?
1. Mitra – Sun’s beneficent energy
2. Parjanya – god of cloud and rain
3. Maruts – storm gods
4. Varuna – sky and water
- Which of the following changes took place in the later Vedic period vis-à-vis the Rig Vedic period?
The king’s rule became territorial.
Tribe pastoralists became peasants
- What was the nishka? –A gold coin
- Why was a guest in the Vedic period known as goghna?
He was fed on cattle
- the battle which is the story of Mahabharata most probably took place around 1000 BC
- The Bhagavad-Gita and Santiparva are part of the Mahabharata
- Iron came to be used by the Vedic people in around 1000BC
- Which of the following gives the correct chronological order of the Vedas? R S Y A
- The ashrama system gained importance in the post Vedic period of the Dharmasashtras. The four ashramas in right order are
Brahmachari, Grihastha, Vanaprastha, and Sanyasi.
- The ‘Battle of Ten Kings’ was fought on the banks of Parushni
- The learned lady who is said to have debated with famous law – giver Yajnavalkya was Gargi
- Which of the Vedas was divided into ‘White’ and ‘Black’ parts Yajurveda
- Which of the following is not matched correctly? Ayuveda – Magic
- What was the main cause for the rise of large states during and after the sixth century BC? wide spread use of iron in parts of and Bihar
- The modern location of some old states are given below which is/are correctly matched?
1. Anga : Bhagalpur and Monghyr
2. Magadha : Patna and Gaya
3. Kosala : Avadh
4. Panchala : Badaun, Bareilly
5. Matsya : Allahabad
1,2,3,4
- Which of the following old states and their capitals is/are correctly matched?
1. Anga : Champa
2. Vatsa : Saket
3. Panchala : Kanyakubha
4. Magadha : Girivraja
1, 4
- Tradition has it that Ajatasatru was instigated to muder his father by Devadatta
- the founder of the Nanda Dynasty was Mahapadma
- Who is often described as the second ‘Parasurama’ or ‘the exterminator of the entire Kshatriya race’? Mahapadma
- Which of the following caused the success of Magadha?
Magadha enjoyed an advantageous geographical position in the Iron Age, as
the most of the deposits were located there
II. The ruler of this state had very good weapons
III. No other power at that time had the courage to attack it
- The first foreigner to invade India was Darius I
- The founder of the Achaemenian dynasty was Cyrus
- “Of all the nations that we have known, it is India which has the largest population”. Who said these lines? Herodotus
- Which of the following was not a result of the Iranian contact? Indian grammar was influenced to a large extent
- In which battle did Alexander defeat Porus? Hydaspes
- On the banks of which river were Alexander and Porus involved in a grim battle? Jhelum
- Alexander died at Babylon
- Which of the following was not a result of Alexander’s invasion he made India a province of Greece
- Which of the following factors was responsible le for the rise of different religious sects during the 6th century BC?
The domineering attitude of the brahmanas towards the common people
Growth of untouchability and rigidity of the caste system
The indiscriminate killing of cattle was ruining the concept of new agriculture
- the original names of the sect which later came to be know as ‘Jaina’ was Trithankaras
100. Which of the following statements are correct with regard to Mahavira’s?
views? Rituals had nothing to do with the purification of souls
119. Match the following events in the life of Buddha and the places
A. Birthplace 1.Kusinagar
B. Attained enlightenment at 2.Sarnath
C. Delivered first sermon at 3. Bodhgaya
D. Attained nirvana at 4. Pataliputra
A-4, B-3,C-2, D-1
120. Match the following
A. Birth place of Mahavira 1.Pava
B. Enlightenment of Mahavira 2.Jrimbhikagrama
C. Mahavira’s nirvana 3.Kundapura
D. Place of first Jain Council 4. Pataliputra
A-, B-,C-,D-.
121. Identify the wrong statement
Sthaviravada is an orthodox school of Jainism
122. Milinda – Panho explains the disputed points of Buddhism in the form of a dialogue between the Indo - Greek king Menander and the Buddhist priest,
Nagasena
123. Parsvantha’s teachings were enlarged by Mahavira with the principle of
Chastity
124. Which of the following is not a correct match?
(a) Lingayata : Bijjala
(b) Lokayata : Ajita Kesakambalin
(c) Ajivika : Gosala Maskariputra
(d) Shumyavada : Nagarjuna
125. Of the following which one is not Bodhisattva?
Avichi
126. Which of the following is/are associated with Nagarjuna?
Madhyamika school of Buddhism
Shunyavada – the world is a mere illusion
127. Jataka stories are included in the Nikaya – Khuddaka
128. Which of the following places is not connected with the important events in the Buddha’s life? – Pavapuri
129. Which of the following schools of philosophy was the main offshoot of Bhagavatism? – Isipatana
130. The practice of image worship began among the followers of Brahmanism with the emergence of - Bhagavatism
131. Which of the following ideas is not shared by Bhagavatism and Buddhism? Stress upon devotion or Bhakti
132. the earliest known Greek follower of Bhagavatism was – Heliodorus
133. Buddhist tradition considers Chandragupta to have belonged to a Moriya tribe of – kshatriyas
134. Which of the following Books describes the revolt of Chandragupta Maurya’s with the help of Kautilya against the Nanda king? Visakhadatta’s Mudrarakshasa
135. Which one of the following factors was not responsible for Chandragupta Maurya’s success against the Nanda kings? Military assistance provided by Greek rulers
136. Which of the following kings made a request to a foreign king for figs, wine and sophists to be sent to India? Bindusara
137. What does the word ‘Asoka’ literally means? – Bereft of sadness
138. In which of the following books does the statement “In the happiness of the subjects lay his happiness and in their troubles lay his troubles” appear? Arthashastra
139. What is the importance of the Kalinga war in Indian history? It brought about a marked change in the foreign policy of Asoka.
140. Which of the following statements are true with regard to the Arthashastra?
I. It is a treatise on kingship, statecraft and diplomacy.
II. It lays down several rules for the management of the king’s farms based on developed agricultural techniques like the use of manure
III. It suggested the appointment of a superintendent
141. Which one of the following is not a contribution of Asoka to Indian polity and culture? – Reform in criminal justice and revolutionary change in the social system
142. The inscriptions of Asoka are written in 1.Greek 2. Kharosthi 3. Aramic
143. ‘Dharma’ or ‘Law of Piety’ had the essence of all religions
144. The ‘Dhamma’ is a Prakrit word
145. Which of the following is not correct with regard to social life during the Mauryan period? – Slavery was not in vogue
146. Which of the following are true with regard to art and architecture during the Mauryan period?
Mauryan art was influenced by Persian and Greek art
The most striking feature with regard to the pillars was its polish
It was influenced by Buddhism to a great extent.
147. What was the most likely cause which led to the dismemberment of the Mauryan Empire? Successors of Asoka were weaklings
148. Which of the following regions was/were not in Asoka’s kingdom? – Tanjore
149. Match the following
A. Rajuka 1. Provincial revenue collector
B. Sthanik 2. Collector – general of revenue
C. Vrajabhumik 3. Gatekeeper
D. Pratihara 4. Public works
E. Samaharta 5.District officer
A-1, B-5, C-4, D-3, E-2.
150. Which of the following Asokan inscriptions mention the Kalinga war?
13th Rock Edict
151. Which of the following is false
Envoy to Bindusara’s court - Dionysios
152. With which one of the following did Asoka not maintain diplomatic relations
Antiochus I soter of Syria
153. The edicts of Asoka emphasis
Pronouncements of policy
154. The oldest surviving Indian written record of historical significance belongs to the time of – Asoka
155. The king of the mauryan times was called Dharmapravartaka by Kautilya
156. The mauryan punch – marked silver coins did not carry the symbol of - cow
157. Which of the following sites, where the Asokan pillars exits, has the bull capital? - Ramapurva
158. The term not mentioned in the Asokan inscriptions is Cheras
159. Which of the following is not one of the animals carved on the Sarnath pillar? Deer
160. Which of the following was not one of the main purposes for which money was used in the Mauryan times? Taxes
161. With which of the following castes do we associate the Shungas - Brahmanas
162. Pushyamitra sunga – was a persecutor of Buddhism according to the Divyavadana
163. With which of the following regions can the Satavahanas be identified? Andhra
164. Which of the following is true regarding the Satavahanas?
165. Which of the following inscriptions describes the achievements of Kharavela, king of Kalinga? Hathigumpha inscription
civil services preliminary examination PROJECT
- HOW TO improving your memory
- 1.PERSONALITY DEVELOPMENT
- 2.ASSOCIATION
- 3.TIME MANAGEMENT
- 4.MOTIVATION
- 5.MEDITATION
- 6.TECHNICS TO ADOPT
- 7.NEWS
- 8.CURRENT AFFAIRS JOURNALS & MAGAZINES
- 9.SUBJECT
civil services preliminary examination - GENERAL STUDIES
- civil services preliminary examination - GENERAL STUDIES
- GENERAL MENTAL ABILITY - 30 M
- INDIAN NATIONAL MOVEMENT 20 M
- INDIAN POLITY and ECONOMY 20 M
- GEOGRAPHY - 20 M
- INDIAN HISTORY - 20 M
- CURRENT EVENTS - 25 M
- GEN SCIENCE-15 M
- TOTAL=150
Indian History - Optionalof Part A - Preliminary Examination of Civil Services Exam
Indian History - Optionalof Part A - Preliminary Examination of Civil Services Exam
Back to Section III
Section-A
1. Prehistoric cultures in India
2. Indus Civilization. Origins. The Mature Phase: extent, society, economy and culture. Contacts with other cultures.Problems of decline.
3. Geographical distribution and characteristics of pastoral and farming communities outside the Indus region, from the neolithic to early iron phases.
4. Vedic society. The Vedic texts; changefrom Rigvedic to later Vedic phases. Religion; Upanishadic thought. Political and social organisation; evolutuion of monarchy and varna system.
5. State formation and urbanization, from the mahajanapadas to the Nandas. Jainism and Buddhism. Factors for the spread of Buddhism.
6. The Mauryan Empire. Chandragupta; Megasthenes. Asoka and his inscriptions; his dhamma, administration, culture and art. The Arthasastra.
7. Post-Mauryan India, BC 200- AD 300. Society: Evolution of jatis. The Satavahanas and state formation in Peninsula. Sangam texts and society. Indo-Greeks, Sakas, Parthians, Kushanas; Kanishka. Contacts with the outside world. Religion : Saivism, Bhagavatism, Hinayana and Mahayana Buddhism; Jainism; Culture and art.
8. The Guptas and their successors (to c. 750 AD). Changes in political organisation of empire. Economy and society. Literature and science. Arts.
Section-B
9. Early Medieval India. Major dynasties; the Chola Empire. Agrarian and political structures. The Rajaputras. Extent of social mobility. Postition of women. The Arabs in Sind and the Ghaznavides.
10. Cultural trends, 750-1200, Religious conditions : importance of temples and monastic institutions; Sankaracharya; Islam; Sufism. Literature and Science. Alberuni’s "India". Art and architecture.
11-12. Thirteenth and fourteenth Centuries: Ghorian invasions causes and consequences. Delhi Sultanate under the "Slave" Rulers. Alauddin Khalji : Conquests; administrative, agrarian and economic measures. Muhammad Tughlug's innovations. Firuz Tughluq and the decline of the Delhi Sultanate. Growth of commerce and urbanization. Mystic movements in Hinduism and Islam. Literature. Architecture, Technological changes.
13. The fifteenth and early 16th Century : major Provinicial dynasties; Vijaya-nagara Empire. The Lodis, First phase of the Mughal Empire: Babur, Humayun. The Sur empire and administration. The Portuguese.
Montheistic movements: Kabir; Guru Nanak and Sikhism; Bhakti. Growth of regional literatures. Art and Culture.
14-15. The Mughal Empire , 1556-1707. Akbar: conquests, administrative measures, jagir and mansab systems; policy of sulh-i-kul. Jahangir, Shahjahan and Aurangzeb : expansion in the Deccan; religious policies. Shivaji.
Culture: Persian and regional literatures. Religious thought: Abul Fazl; Maharashtra dharma. Painting. Architecture.
Economy: conditions of peasants and artisans, growth in trade; commerce with Europe. Social stratification and status of women.
16. Decline of Mughal Empire, 1707-61. Causes behind decline. Maratha power under the Peshwas. Regional states. The Afghans. Major elements of composite culture. Sawai Jai Singh, astronomer. Rise of Urdu language.
Section-C
17. British expansion : The Carnatic Wars, Conquest of Bengal. Mysore and its resitance to British expansion: The three Anglo-Maratha Wars. Early structure of British raj: Regulating and Pitt's India Acts.
18. Economic Impact of the British Raj : Drain of Wealth (Tribute); land revenue settlements (zamindari, ryotwari, mahalwari); Deindustrialisation; Railways and commercialisation of agriculture; Growth of landless labour.
19. Cultural encounter and social changes: Introduction of western education and modern ideas. Indian Renaissance, social and religious reform movements; growth of Indian middle class; The press and its impact: rise of modern literature in Indian languages. Social reforms measures before 1857.
20. Resistance to British rule : Early uprisings; The 1857 Revolt- causes, nature, course and consequences.
21. Indian Freedom struggle-the first phase: Growth of national consciousness; Formation of Associations; Establishment of the Indian National Congress and its Moderate phase;- Economic Nationalism; Swadeshi Movement; The growth of "Extremism" and the 1907 split in Congress; The Act of 1909 - the policy of Divide and Rule; Congress-League Pact of 1916.
22. Gandhi and his thought; Gandhian techniques of mass mobilisation- Khilafat and Non Cooperation Movement, Civil Disobedience and Quit India Movement; Other strands in the National Movement-Revolutionaries, the Left, Subhas Chandra Bose and the Indian National Army.
23. Separatist Trends in Indian nationalist politics- the Muslim League and the Hindu Mahasabha; The post -1945 developments; Partition and Independence.
24. India independent to 1964. A parliamentary, secular, democratic (republic the 1950 Constitution). Jawaharlal Nehru's vision of a developed, socialist society. Planning and state-controlled industrialization. Agrarian reforms. Foreign policy of Non-alignment. Border conflict with China and Chinese aggression.
GK HISTORY
1. Which of the following year is associated with the outbreak of World War II?
a) 1935 b) 1937 c) 1638 d) 1939
2. Who was the author of the American Declaration of Independence?
a) George Washington b) Thomas Paine c) Lafayette d) Thomas Jefferson
3. The Russian city where a tank of radio active waste exploded in April 1993 is
a) Chernobyl b) Serov c) Tomsk-7 d) Cerepovec
4. The Hijra era is counted from
a) 1526 AD b) 712 AD c) 632 AD d) 622 AD
5. The Gulf war of 1991 was precipitated by the Iraqi annexation of
a) Bahrain b) Kuwait c) Saudi Arabia d) South Yemen
6. Who among the following were known as ‘Physiocrats’ at the time of French Revolution?
a) The clergy b) economists c) the nobility d) medical professionals
7. The parleys between the Prime Ministers Zulfikar Ali Bhutto and Indira Gandhi, so much referred to in world politics, were held at
a) Manali b) Rawalpindi c) Shimla d) Islamabad
8. Which of the following was strongly advocated by Fascism?
a) disarmament b) federalism c) secularism d) war
9. Fabian socialism emerged first in
a) India b) Great Britain c) Germany d) Russia
10. Which of the following is not associated with socialism?
a) Fabianism b) Syndicalism c) Communism d) Fascism
11. Russian revolution took place in
a) 1789 b) 1776 c) 1688 d) 1917
12. In America, the Bill of Rights was added to the Federal Constitution largely at the instance of
a) Thomas Jefferson b) George Washington c) Thomas Paine d) Benjamin Franklin
13. Who wrote ‘Das Capital’?
a) Engel b) Lenin c) Karl Marx d) Adam Smith
14. Civil Disobedience is associated with
a) Voltaire b) Thomas Paine c) HD Thoreau d) Thomas Hobbes
15. French Revolution took place in
a) 1789 b) 1776 c) 1688 d) 1917
16. Who among the following is associated with the philosophy of ‘the social contract’?
a) Voltaire b) Thomas Paine c) HD Thoreau d) Thomas Hobbes
17. American War of Independence took place in
a) 1776 b) 1789 c) 1801 d) 1919
18. Which of the following was built between 3000 BC and 1800 BC?
a) The tomb of Alexander b) The Collosus of Rhodes c) The Palace of Diana at Ephesis d) The Pyramids of Egypt
19. Which of the following parties is associated with former Pakistan cricket team captain Imran Khan?
a) Pakistan People’s Party b) Jamhurie Islam c) Tehreek e-Insaf d) Awami League
20. Who among the following is associated with the philosophy of ‘Rights of Man’?
a) Thomas Paine b) Rousseau c) Emerson d) Abraham Lincoln
21. The Cairo Summit held in March 1996 was concerned with which of the following?
a) peace in West Asia b) terrorism c) oil crisis d) economic aid to African countries
22. No taxation without representation is a well-known slogan associated with which of the following?
a) French revolution b) British civil war c) Indian National Movement d) American War of Independence
23. Which one of the following is not related to the continuing turmoil in Bosnia?
a) Serbs b) Muslims c) Jews d) Croats
24. The fall of the prison at Bastille is associated with which of the following?
a) Russian revolution b) French revolution c) American War of Independence d) none of those
25. Who among the following faced a devastating defeat in the battle of Waterloo?
a) Duke of Wellington b) Napoleon c) Alexander the Great d) Hitler
Answers
1. 19392. Thomas Jefferson3. Chernobyl4. 622 AD5. Kuwait6. economists7. Shimla8. war9. Great Britain10. Fascism11. 191712. Thomas Jefferson13. Karl Marx14. HD Thoreau15. 178916. Voltaire17. 177618. The Pyramids of Egypt19. Tehreeq-e-Insaf20. Thomas Paine21. terrorism22. American War of Independence23. Jews24. French revolution25. Napoleon
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GK History 2
1. In which edict did Asoka express regret over the bloodshed in his conquest of Kalinga?
a) Pillar Edict VII b) Minor Rock Edict I c) Lumbini Pillar Edict d) Rock Edict XIII
2. Who was the first Delhi Sultan to introduce gold and silver coinage?
a) Iltumish b) Balban c) Muhammad bin Tughlaq d) Ibrahim Lodhi
3. Where is Ibadat Khana situated?
a) Lahore b) Delhi c) Agra d) Fatehpur Sikri
4. During whose reign was Ramacharitamanas composed by Tulsidas?
a) Harsha b) Akbar c) Babur d) Alauddin Khilji
5. Who amongst the Vijayanagar rulers is considered to be the greatest patron of literature?
a) Davaraya I b) Rama Raja c) Devaraya II d) Krishnadevaraya
6. Who among the following made the ‘August offer’ of 1940 rejected by the Congress?
a) Lord Wavell b) Lord Linlithgow c) Sir George Stanley d) Lord Willington
7. Who among the following pioneered the movement leading to the Widow Remarriage Act?
a) Raja Ram Mohan Roy b) Dayananda Saraswathi c) Vivekananda d) Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar
8. Which of the following was the designation of the principal governors in the Vijayanagar Empire?
a) Nayaks b) Ranaks c) Rayas d) Senapathis
9. Which Sikh guru compiled the ‘Adi Granth’?
a) Gura Nanak b) Ramdas c) Arjun Dev d) Tegh Bahadur
10. Which of the following terms is not related to Buddhism?
a) Sangha b) Mahayana c) Ashwamedha d) Nirvana
Answers
1. Rock Edict XIII2. Iltumish3. Fatehpur Sikri4. Akbar5. Devaraya II6. Lord Linlithgow7. Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar8. Nayaks9. Arjun Dev10. Ashwamedha
-------------
GK History 3
1. What did Ramanuja preach?
a) Satya b) Ahimsa c) Gyana d) Bhakti
2. Who among the Governor Generals of India is called the ‘Maker of Modern India’?
a) Cornwallis b) Warren Hastings c) Lord Ripon d) Lord Dalhousie
3. From where did Gandhiji develop the technique of Satyagraha?
a) South Africa b) Chauri Chaura c)Bardoli d) Sabarmati
4. Who organized the ‘Khudai Khidmatgars’?
a) Abdul Ghaffar Khan b) Abul Kalam Azad c) Maulana Mohammad Ali d) Sir Sayyid Ahmed Khan
5. Who among the following estimated Indian National Income and criticized the constant drain of wealth from India to England?
a) Gandhiji b) Gokhale c) Dadabhai Naoroji d) Bal Gangadhar Tilak
6. Who introduced the principle of the ‘Doctrine of Lapse’?
a) Clive b) Cornwallis c) Warren Hastings d) Dalhousie
7. Which of the following Vedic sacrifices was a royal consecration ceremony?
a) Agnishtoma b) Rajasuya c) Vajapeya d) Asvamedha
8. Which of the following dynasties was ruling at the time of the invasion of Alexander?
a) Nandas b) Mauryas c) Guptas d) Sungas
9. In which one of the following do we come across a detailed account of the municipal administration of the Mauryas?
a) Arthashastra b) Indica b) Mudrarakshasa d) Mauryan inscriptions
10. The Moplah rebellion broke out in
b) Uttarakhand b) Chauri Chaura c) Malabar d) Telengana
11. To which period does the Mehrauli Pillar inscription belong?
a) Mauryas b) Sungas c) Kushanas d) Guptas
12. Which of the following works deals with the history of Kashmir?
a) Gaudavaha b) Harshacharita c) Arthashastra d) Rajatarangini
13. Who built the famous Moti Masjid in the Red Fort?
a) Sher Shah b) Shahjahan c) Aurangzeb d) Akbar
14. During whose reign did Delhi become the capital of Hindustan for the first time?
a) Iltumish b) Raziya c) Balban d) Qutub-ud-din Aibak
15. Which one of the following was one of the effects of the Sepoy Mutiny (1857)?
a) Reorganization of the East India company b) Establishment of princely states c) abolition of East India company d) none of these
Answers
1. Bhakti2. Lord Dalhousie3. South Africa4. Abdul Ghaffar Khan5. Dadabhai Naoroji6. Dalhousie7. Rajasuya8. Nandas9. Indica10. Malabar11. Guptas12. Rajatarangini13. Shahjahan14. Iltumish15. abolition of East India company
--------------------
GK Indian History Quiz 4
1. Who was the first Indian to be elected to the House of Commons?
a) Gokhale b) Dadabhai Naoroji c) Badr-ud-din-Tyabji d) Romesh Chander Dutt
2. Which one of the following literature was patronized by the Pandya kings?
a) sacred literature b) secular literature c) Sangam literature d) Sanskrit literature
3. At which of the following places did Vasco-da-Gama land on 20th May, 1498?
a) Calicut b) Masulipatanam c) Goa d) Cannanore
4. Why did the Communists in India decide to support the Government of India during the World War II?
a) Gandhiji’s call to the nation b) Lord Linlithgow’s statement c) Activities of the Azad Hind Fauj d) Hitler’s attack on Russia
5. The architectural features of Taj Mahal have resemblance to which of the following?
a) Jama Masjid at Delhi b) Mecca Masjid at Hyderabad c) Humayun’s tomb at Delhi d) Gol Gombaz
6. Which of the following was the capital of the Hoysalas?
a) Warangal b) Madurai c) Dwarasamudram d) Badami
7. Who was the first to describe the great mutiny of 1857 as the first War of Independence?
a) Nehru b) Tilak c) VD Savarkar d) Lajpat Rai
8. Who among the following is referred to as the ‘Father of Local self-government in India’?
a) Lord Curzon b) Lord Rippon c) Lord Harding d) Lord Dalhousie
9. With which of the following incidents did Mahatma Gandhi’s entry into national politics start?
a) Champaran movement b) Dandi March c) Non-cooperation movement d) civil disobedience movement
10. In its session held at which place did Indian National Congress declare ‘Complete Independence’ as its goal?
a) Madras in 1927 b) Calcutta in 1928 c) Lahore in 1929 d) Allahabad in 1930
11. Which of the following works state that the society was divided into seven classes in the Mauryan period?
a) Arthashastra b) Edicts of Asoka c) Puranas d) Indica
12. In which language were the Sangam classics written?
a) Tamil b) Telugu c) Kannada d) Malayalam
13. Which of the following dynasties of early medieval India was justly famous for its system of village administration?
a) Cholas b) Pandyas c) Rashtrakutas d) Palas
14. Who popularized Ganesh festival during the freedom struggle?
a) Mahadev Govinda Ranade b) Gokhale c) Bal Gangadhar Tilak d) VD Savarkar
15. Which of the following was the greatest achievement of Allauddin Khilji?
a) invasion of South India b) contribution to art c) measures to improve the standards of living d) revenue system and control of inflation
Answers
1. Dadabhai Naoroji2. Sangam literature3. Calicut4. Hitler’s attack on Russia5. Humayun’s tomb at Delhi6. Dwarasamudram7. VD Savarkar8. Lord Rippon9. Champaran movement10. Lahore in 192911. Indica12. Tamil13. Cholas14. Bal Gangadhar Tilak15. revenue system and control of inflation
-------------------
GK - Indian History Quiz 5
1. Which Chalukya King had the title of Sri Prithvi-Vallabha and Parameswara?
a) Pulakesin Ib) Maharaja Kirtivarmanc) Mangalesad) Pulakesin II
2. Which dynasty built the Meenakshi temple at Madurai?
a) Pandyasb) Pallavasc) Cholasd) Palas
3. Who amongst the following is regarded as the historical founder of Jainism?
a) Mahavirab) Sisunagac) Rishabhad) Gautama
4. During the Indus Valley period what was the dominant number used for weights and measures?
a) sixb) eightc) twelved) sixteen
5. During whose reign was India’s first currency note printed?
a) Ashokab) Samudra Guptac) Akbard) Vikramaditya
6. In which of the following kingdom was the Hoysala kingdom finally dissolved?
a) Bahmanib) Pallavasc) Vijayanagard) Chalukyas
7. Which of the following was the capital city of Tipu Sultan?
a) Dwarasamudrab) Srirangamc) Belurd) Srirangapatanam
8. Which of the following was the most commonly used coin during the Mauryan period?
a) Nishkab) Suvarnac) Kakinid) Karshapana
9. Who among the following did not accept the Subsidiary Alliance?
a) the Nizam of Hyderabadb) The Scindia of Gwaliorc) The Rajput States of Jodhpur, Jaipur and Bharatpurd) The Holkar state of Indore
10. To which dynasty did the famous king of legends Bhoja belong?
a) Rashtrakutasb) Pratiharasc) Pallavasd) Palas
11. Akbar built Ibadat Khana at Fatehpur Sikri to
a) conduct mass prayerb) hold darbarc) hold religious discussionsd) hear public grievances
12. Which one of the given Mughal buildings bears the inscription ‘If on earth be an Eden of Bliss it is this, it is this, none but this’?
a) Diwan-i-Amb) Diwan-i-Khasc) Taj Mahald) Buland Darwaza
13. Who is the British Viceroy who took a number of measures to preserve ancient buildings and monuments of India?
a) Lord Irwinb) Lord Cornwallisc) Lord Ripond) Lord Lytton
14. Who presided over the Lahore session of the Indian National Congress when Swaraj was interpreted as complete independence?
a) WC Bannerjib) Jawahar Lal Nehruc) Gandhijid) Motilal Nehru
15. During whose reign did the Mughal painting achieve fulsome development?
a) Akbarb) Jahangirc) Shah Jahand) Aurangzeb
16. Where did Buddha give his first Sermon?
a) Lumbinib) Bodh Gayac) Sarnathd) Sanchi
17. Buddha attained enlightenment at
a) Bodh Gayab) Sarnathc) Sanchid) Lumbini
18. Satavahanas minted their coins predominantly in
a) goldb) silverc) copperd) lead
19. Which of the following was the first permanent home of Aryans in India?
a) Baluchistanb) Sindhc) Uttar Pradeshd) Punjab
20. Which of the following scholars accompanied Mahmood of Ghazni to India?
a) Ibn Batutab) Al-Birunic) Al-Firdausid) Al-Razi
21. Who were the first people to introduce Islam in India?
a) Arab merchantsb) Arab travelersc) Turkish warriorsd) Persian Scholars
22. Who introduced the Iqtadari system?
a) Akbarb) Ala-ud-din Khiljic) Iltumishd) Muhammad bin Tughlaq
23. Who among the following composed the popular devotional song ‘Bhaja Govindam’?
a) Thyagarajab) Shyama Shastric) Sankaracharyad) Shad Kala Govinda Marar
24. In which of the following ancient towns was the great council held soon after the ‘nirvana’ of Buddha to codify his doctrines?
a) Kusinagarab) Girivrajac) Bodh Gayad) Sarnath
25. Who was the finance minister of Akbar?
a) Raja Man Singhb) Raja Todar Malc) Faijid) Bahadur Singh
Answers
1. Pulakesin II2. Pandyas3. Mahavira4. sixteen5. Samudra Gupta6. Bahmani7. Srirangapatanam8. Kakini9. The Holkar state of Indore10. Pratiharas11. conduct mass prayer12. Diwan-i-Khas13. Lord Ripon14. Jawahar Lal Nehru15. Jahangir16. Sarnath17. Bodh Gaya18. lead19. Punjab20. Al-Biruni21. Arab travelers22. Iltumish23. Sankaracharya24. Girivraja25. Raja Todar Mal
------------------
GK - Indian History 6
1. Who founded the famous Pala dynasty which ruled over Bengal?
a) Dharmapalab) Devapalac) Gopala Id) Jayapala
2. From where did the Sakas come to India?
a) Europeb) Western Chinac) Central Asiad) Arabia
3. Who gave the famous ‘Girnar inscription’?
a) Rudramanb) Ashokac) Samudraguptad) Kanishka
4. By what name is Purushapura, the capital of Kushanas known today?
a) Purushapurab) Peshavarc) Patnad) Patliputra
5. Who is the author of the famous literary work Tahqiq-i-Hind?
a) Alberunib) Badamic) Zia-ud-din Barnid) Khafi Khan
6. During whose reign did the famous Buddhist pundits Aswagosha, Vasumitra and Nagarjuna live?
a) Ashokab) Kanishkac) Harshavardhanad) Samudragupta
7. Which of the following is the correct chronological order of the Slave dynasty rulers?
a) Qutub-ud-din Aibak, Balban, Iltumish, Raziyab) Qutub-ud-din Aibak, Iltumish, Raziya, Balbanc) Balban, Qutub-ud-din Aibak, Raziya, Iltumishd) Qutub-ud-din-Aibak, Balban, Raziya, Iltumish
8. Who among the following forbade intoxicating drinks?
a) Akbarb) Sher Shahc) Allauddin Khiljid) Aurangazeb
9. Who is the author of ‘Buddha Charita’?
a) Asvagoshab) Nagarjunac) Banabhattad) Vasumitra
10. Between the Hinayana and Mahayana schools of Buddhism, which one was patronized by Kanishka?
a) Hinayanab) Mahayanac) Bothd) Neither
11. The reign of which dynasty is known as the golden period of Hinduism and Sanskrit literature?
a) Guptab) Mauryac) Kushanad) Saka
12. Who is the author of the famous ‘Panchatantra’ stories?
a) Amarasimhanb) Vishnusharmac) Nagarjunad) Bilhana
13. Who among the following issued edicts regulating the prices pf all articles and goods?
a) Ala-ud-din Khiljib) Baburc) Muhammad bin-Tughlaqd) Sher Shah Suri
14. Ala-ud-din Khilji became the Sultan of Delhi in 1296 AD after treacherously murdering his uncle and patron. Who was this patron?
a) Jalal-ud-din Khiljib) Nasir-ud-din Khusrauc) Ghias-ud-din-Balband) Qutub-ud-din Mubarak
15. Who among the following is believed to have been the destroyer of the Khilji dynasty?
a) Nasir-ud-din Khusrau Shahb) Malik Kafurc) Ghazni Malikd) Qutub-ud-din Mubarak Shah
16. Who among the following required that all grains should be stored in the royal granaries in Delhi?
a) Sher Shahb) Akbarc) Ala-ud-din Khiljid) Balban
17. Who among the following was the founder of the Tughlaq dynasty?
a) Firuz Shah Tughlaqb) Muhammad-bin-Tughlaqc) Ghias-ud-din Tughlaqd) Balban
18. Who amongst the following brothers of Aurangazeb was condemned to death and his body paraded in Delhi?
a) Dara Shikohb) Murad Bakshc) Shujad) None of these
19. Which of the following was a maritime power?
a) Bahmanisb) Chalukyasc) Cholasd) Rashtrakutas
20. During whose reign did Ibn-Batutah, the famous traveler visit India?
a) Ala-ud-din Khiljib) Ghias-ud-din Tughlaqc) Sher Shah Surid) Muhammad bin Tughlaq
21. The rulers of which of the following dynasty established the largest dominion in southern India?
a) Chalukyasb) Cholasc) Pallavasd) Pandyas
22. Two of the great Mughal emperors wrote their own memoirs. Who are they?
a) Babur and Humayunb) Humayun and Jahangirc) Babur and Jahangird) Babur and Akbar
23. Who among the following wrote the famous Sanskrit plays ‘Ratnavali’, ‘Priyadarsika’ and ‘Naganandam’?
a) Harshavardhanab) Kalidasac) Bhasad) Asoka
24. Whose court did Banabhatta adorn?
a) Harshavardhanab) Chandragupta IIc) Kanishkad) Asoka
25. Who authored ‘Harshacharita’ and ‘Kadambari’?
a) Banabhattab) Bilhanac) Visakhadattad) Aryabatta
Answers
1. Gopala I2. Western China3. Rudraman4. Peshavar5. Alberuni6. Kanishka7. Qutub-ud-din Aibak, Iltumish, Raziya, Balban8. Allauddin Khilji9. Asvagosha10. Mahayana11. Gupta12. Vishnusharma13. Ala-ud-din Khilji14. Jalal-ud-din Khilji15. Malik Kafur16. Ala-ud-din Khilji17. Ghias-ud-din Tughlaq18. Dara Shikoh19. Cholas20. Muhammad bin Tughlaq21. Cholas22. Babur and Jahangir23. Harshavardhana24. Harshavardhana25. Banabhatta
---------------
GK - Indian History 7
1. Who among the following was a great musician in the court of Akbar?
a) Amir Khusro b) Tansen c) Ramdasd) Abul Fazl
2. Who is the author of Mrchchhakatika?
a) Varahamihira b) Visakhadatta c) Sudraka d) Bilhana
3. The Butler Committee Report enquired into which of the following?
a) Jallianwala Bagh Massacre b) The growth of education in British India c) Working of Diarchy as mentioned in the Montague Chelmsford reforms d) Relationship between Indian states and the paramount power
4. Which of the following committee reports enquired into the growth of education in British India and potentialities of its further progress?
a) Butler Committee Report b) The Hurtog Committee Report c) Muddiman Committee Reportd) Hunter Commision
5. Who among the following is associated with Kakori Conspiracy?
a) Ram Prasad Bismalb) Jatin Das c) Surya Sen d) Vasudeo Phadke
6. Which dynasty built the rock-cut temples at Khajuraho?
a) Chandellas b) Cholas c) Rashtrakudas d) Chalukyas
7. Who among the following has been the President of Indian National Congress thrice?
a) Dadabhai Naoroji b) Annie Besant c) Gokhale d) Aurobindo
8. Who were the first to call the river Sindhu, ‘Hindu’?
a) Persians b) Greeks c) Turks d) Egyptians
9. Which of the following committee report enquired into the working of diarchy as laid down in the Montague Chelmsford reforms?
a) Muddiman Committee report b) The Hurtog Committee Report c) Butler Committee Report d) none of these
10. The most important feature of which civilization was well planned and well built towns?
a) Vedic civilization b) Indus Valley civilization c) Egyptian civilization d) Persian civilization
11. The Indus Valley people are believed to have been the worshippers of
a) Mother Goddess b) Indra b) Agni d) Vishnu
12. From where did Aryans, the nomadic pastoral people come to India?
a) Western Asia b) Central Asia c) Europe d) Africa
13. The Aryans reached the frontiers of the Indian subcontinent by 2000 BC. In India where did they settle down first?
a) Rajasthan b) Gujarat c) Punjab d) Kashmir
14. Among whom were the worship of trees, animals and stones quite present?
a) The Aryansb) The Dravidas c) The Huns d) The Bactrians
15. Who among the following was worshiped by Aryans?
a) Mother Goddess b) Lord Shiva c) Varuna d) Trees
16. During which period were the Ramayana and Mahabharata composed?
a) Indus Valley Civilization b) Early Vedic period c) During the reign of Guptas d) Later Vedic period
17. Which one of the following was an important republic that existed during the 7th and early 6th centuries?
a) Vaishali b) Magadha c) Kosala d) Avanti
18. Alexander invaded India in
a) 326 BC b) 420 BC c) 322 BC d) 360 BC
19. Between whom were the battle of Karri fought?
a) Alexander and Porus b) Tipu Sultan and the British c) Muhammd Ghori and Prithviraj d) The British and the French
20. On the bank of which river was the battle of Karri fought?
a) Indus b) Chenad c) Ravi d) Jhelum
21. ‘As a King treats a King’, that was how the loser replied when the conqueror asked him what treatment he should be meted out. Who are the winner and the loser here?
a) Alexander and Porus b) Babur and Ibrahim Lodhi c) Akbar and Hemu d) Prithviraj Chauhan and Mohammad Ghori
22. Which dynasty was ruling over the Gangetic planes at the time of the invasion of Alexander?
a) Nandas b) Mauryas c) Guptas c) Hunas
23. Which of the following was the capital of Nandas?
a) Magadha b) Purushapura c) Vatsa d) Kosala
24. In which year was the Mauryan Empire founded by Chandragupta Maurya?
a) 322 BC b) 326 BC c) 320 BC d) 341 BC
25. Which of the following was the capital city of the Mauryans?
a) Pataliputra b) Purushapura c) Magadha d) Badami
Answers
1. Tansen2. Visakhadatta3. working of diarchy as laid down in the Montague Chemlsford reforms4. The Hurtog Committee Report5. Ram Prasad Bismal6. Chandellas7. Dadabhai Naoroji8. Persians9. Muddiman Committee report10. Indus Valley civilization11. Mother Goddess12. Central Asia13. Punjab14. The Dravidas15. Varuna16. Later Vedic period17. Vaishali18. 326 BC19. Alexander and Porus20. Jhelum21. Alexander and Porus22. Nandas23. Magadha24. 322 BC25. Pataliputra
------------
GK - Indian History 8
1. Which one of the following books gives a vivid description about the Mauryan administration?
a) Arthashashtrab) Rajtarangini c) Mrichchhatika d) Kadambari
2. Who among the following succeeded Chandra Gupta Maurya to the throne?
a) Ashoka b) Bindusara c) Bimbisarad) Samudragupta
3. To which dynasty did the Great Emperor Ashoka belong?
a) Maurya b) Gupta c) Kushana d) Nanda
4. Who was the first Indian ruler to rule over almost the whole of India?
a) Ashokab) Chandra Gupta Maurya c) Samudragupta d) Kanishka
5. Which of the following is the birth place of Vardhamana Mahavira?
a) Vaishali b) Gaya c) Pavapuri d) Sarnath
6. With which religion is ‘Digambaras’ and ‘Swethambaras’ associated?
a) Jainism b) Buddhism c) Hinduism d) Islam
7. Who was the founder of the Sunga dynasty?
a) Pushymitra b) Brihadratha c) Vasudevad) Ajathasatru
8. Brihadrata, the last Mauryan king was murdered by his own Brahman Commander-in-Chief who later found a new empire. Who was he?
a) Brihadratha b) Mihirajul c) Toramana d) Pushymitra
9. Which one of the following is the death place of Vardhamana Mahavira?
a) Pavapuri b) Kushinarac) Vaishalid) Gaya
10. Who was the founder of the Kanva dynasty which overthrew the Sungas in 73 BC?
a) Vasudeva b) Bimbisara c) Ajathasathru d) Ashoka
11. Who was the first Persian king to attack India?
a) Nadir Shah b) Sultan Mahmud c) Muhammad bin Kasim d) Darius
12. Who among the following was the contemporary of Gautam Buddha?
a) Bimbisara b) Ashoka c) Chandragupta Maurya d) Vasudeva
13. After defeating whom did the Nandas succeed into power?
a) Sisunagas b) Mauryas c) Satavahanasd) Kushanas
14. At which of the following places was Gautam Buddha born?
a) Vaishali b) Lumbini c) Sarnath d) Gaya
15. During the reign of which dynasty was Patanjali’s ‘Mahabhashya’ composed?
a) Mauryas b) Sungas c) Nandas d) Guptas
16. Which dynasty was the first to issue gold coins in India?
a) Kushanas b) Bactrians c) Mauryas d) Guptas
17. Minander, who embraced Buddhism under the influence of monk Nagarjuna, belonged to which dynasty?
a) Bactrians b) Hunas c) Kushanas d) Sishunagas
18. The victory won by Chandra Gupta Maurya over which dynasty is commemorated by the Vikram era?
a) Parthians b) Sakas c) Bactrians d) Hunas
19. Whose coming into power marks the beginning of Saka era?
a) Ashoka b) Kanishka c) Vasudeva d) Pushyamitra
20. Gautam Buddha died at
a) Kushinara b) Pavapuri c) Pataliputra d) Sarnath
21. During the reign of which dynasty did the great scientists Charaka and Surutha live?
a) Kushanas b) Guptas c) Sakas d) Mauryas
22. Which of the following was the capital of Kushanas?
a) Pataliputra b) Magadha c) Purushapura d) Vaishali
23. During the reign of which dynasty were the historical monuments at Nagarjunakonta, Nasik and Amaravathi built?
a) Satavahanas b) Kushanas c) Hunas d) Sungas
24. Who among the following rulers styled himself as ‘Maharajadhiraja’?
a) Ashoka b) Chandra Gupta c) Chandra Gupta Mauraya d) Chandra Gupta II
25. Who among the Gupta rulers is known as ‘Vikramaditya’?
a) Chandra Gupta b) Chandra Gupta II c) Samudra Gupta d) Kumara Gupta
Answers
1. Arthashashtra2. Bindusara3. Maurya4. Ashoka5. Vaishali6. Jainism7. Pushymitra8. Pushymitra9. Pavapuri10. Vasudeva11. Darius12. Bimbisara13. Sisunagas14. Lumbini15. Sungas16. Bactrians17. Bactrians18. Sakas19. Kanishka20. Kushinara21. Kushanas22. Purushapura23. Satavahanas24. Chandra Gupta25. Chandra Gupta II
------------
GK - Indian History Quiz 9
1. Which of the following was introduced by the Government of India Act, 1935?
a) Diarchyb) Bi-cameral legislaturec) Indian councilsd) Provincial Autonomy
2. With which of the following was the Hunter Commission constituted during Lord Ripon’s administration concerned?
a) Public healthb) Educationc) Administrative reformsd) Upliftment of women
3. Who introduced the system of Local boards or Local Bodies in India?
a) Lord Lyttonb) Lord Riponc) Lord Curzond) Lord Mayo
4. Who among the following is associated with Subsidiary Alliance?
a) Robert Cliveb) Hastingsc) Wellesleyd) Dalhousie
5. At which of the following places was the Provisional Government of Independent India (Azad Hind) formed?
a) Singaporeb) Tokyoc) Kuala Lumpurd) Jakarta
6. During which of the following did Mahatma Gandhi give the slogan ‘Do or Die’?
a) Quit India Movementb) Non-cooperation Movementc) Khilafat Movementd) Civil Disobedience Movement
7. Who set up the Indian Independence League?
a) Aruna Asaf Alib) Rash Behari Bosec) Jayaprakash Narayand) SM Joshi
8. Who founded the Ghadar Party in the USA?
a) Jayaprakash Narayanb) Motilal Nehruc) Lala Hardayald) Sir Syed Ahmad Khan
9. Who was the first woman President of the Indian National Congress?
a) Sarojini Naidub) Annie Besantc) Vijayalakshmi Panditd) Madam Bikaji Cama
10. The term Satyagraha was coined by Gandhiji when he was in
a) Englandb) Sabarmati Ashramc) Agha Khan Palaced) South Africa
11. Who among the following did not participate in the 1857 mutiny?
a) Nana Sahibb) Rani Lakshmi Bhaic) Tipu Sultand) Tantia Tope
12. By the Act passed in which year was the demand for separate electorate for Muslims in India conceded?
a) 1904b) 1909c) 1892d) 1919
13. The British East India Company established its first factory in India at
a) Madrasb) Suratc) Calcuttad) Bombay
14. Who among the following freedom fighters died due to a hunger strike in jail?
a) Bhagat Singhb) BG Tilakc) Jatin Dasd) Bipin Chandra Pal
15. At which of the following places was the first session of Indian National Congress held?
a) Lahoreb) Mumbaic) Barodad) Madras
16. Azad Hind Fauj was formed in
a) 1937b) 1942c) 1943d) 1945
17. Where was the first Congress Session held in 1907 at which the first split in Congress took place?
a) Calcuttab) Meerutc) Allahabadd) Surat
18. From which of the following places was the Civil Disobedience Movement started by Gandhiji in 1930?
a) Sevagramb) Dandic) Sabarmatid) Wardha
19. Who among the following used Hughly as the base for piracy in the Bay of Bengal?
a) The Portuguese b) The Frenchc) The Danishd) The British
20. Who was the first to use the term Harijan for tribal people?
a) Mahatma Gandhib) Swami Vivekanandac) Jyotiba Phuled) BR Ambedkar
21. Who founded the Satyagraha Ashram at Wardha?
a) Gandhijib) Jamanlal Bajajc) Jawahar Lal Nehrud) JB Kripalani
22. Who was the founder of the National School at Lahore?
a) Naoroji b) Madan Mohan Malaviac) Lala Lajpat Raid) Annie Besant
23. Who among the following was a social reformer belonging to the Mali Community of Pune?
a) Thakkar Bhappab) BR Ambedkarc) Jyotiba Phuled) None of these
24. In opposition to which of the following was the ‘Independence for India League’ founded by the radical wing of the Congress party?
a) The Gandhi-Irwin Pactb) The Home-rule Movementc) The Nehru reportd) The Montford reforms
25. Which of the following battles was fought by the allied forces of Shuja-ud-Daulah, Mir Kasim and Shah Alam against Robert Clive?
a) Battle of Buxarb) Battle of Wandiwashc) Battle of Chelianwalad) Battle of Tarrain
Answers 1. Provincial Autonomy2. Education3. Lord Ripon4. Wellesley5. Singapore6. Quit India Movement7. Rash Behari Bose8. Lala Hardayal9. Annie Besant10. South Africa11. Tipu Sultan12. 190913. Surat14. Jatin Das15. Mumbai16. 194317. Surat18. Sabarmati19. The Portuguese20. Mahatma Gandhi21. Jamanlal Bajaj22. Lala Lajpat Rai23. Jyotiba Phule24. The Gandhi-Irwin Pact25. Battle of Buxar
----------------
GK - Indian History Quiz 10
1. Who is the founder of Indian Association which was a precursor of the Indian National Movement?
a) Satyendra Nath Boseb) WC Bannerjic) Surendra Nath Bannerjid) Gopal Krishna Gokhale
2. Which of the following was the seat of power of the Rajput clan of Solankis?
a) Kanaujb) Kathiavarc) Malwad) Kashmir
3. Who led the Civil Disobedience Movement in the North West Frontier Province?
a) Sir Sayyid Ahmed Khanb) Sardar Patelc) Khan Abdul Gaffar Khand) Badruddin Tyabji
4. Who was the first President of the Indian National Congress?
a) Annie Besantb) WC Bannerjic) Gopal Krishna Gokhaled) Subash Chandra Bose
5. Which of the following battles laid the foundations of Muslim rule in India?
a) First Battle of Tarrainb) Second Battle of Tarrainc) First Battle of Panipatd) Second Battle of Panipat
6. Who was the first Muslim King of India?
a) Muhammad Ghorib) Qutub-ud-in Aibakc) Balband) Babur
7. Who among the following rulers of Delhi Sultanate is known as the Darvesh King?
a) Muhammad bin Tughlaqb) Nasir-ud-din Mahmudc) Ala-ud-din Khiljid) Firoz Shah Tughlaq
8. Ala-ud-din Khilji was poisoned by his Prime Minister thus bringing an end to the Khilji dynasty. Who was this Prime Minister?
a) Mir Jafarb) Mir Qasimc) Malik Kafurd) Mir Jumla
9. Who is the founder of the Tughlaq dynasty?
a) Ghias –ud-din Tughlaqb) Muhammad bin Tughlaqc) Feroz Shah Tughlaqd) Mahmud Tughlaq
10. Who among the rulers of Tughlaq dynasty built the city of Tughlaqabad near Delhi?
a) Ghias –ud-din Tughlaqb) Muhammad bin Tughlaqc) Feroz Shah Tughlaqd) Mahmud Tughlaq
11. The invasion of Delhi by Timur in 1398 marked the end of which dynasty?
a) Khilji Dynastyb) Tughlaq Dynastyc) Lodhi Dynastyd) Sayyid Dynasty
12. Who was the ruler of Delhi Sultanate when Timur invaded India in 1398 AD?
a) Mahmud Tughlaqb) Muhammad bin Tughlaqc) Feroz Shah Tughlaqd) Ghias-ud-din Tughlaq
13. Who founded the City of Agra?
a) Muhammad bin Tughlaqb) Sikandar Lodhic) Ibrahim Lodhid) Akbar
14. Whom did Daulat Khan, the Governor of Punjab, invite to defeat Ibrahim Lodhi?
a) Timur the Lameb) Nadir Shahc) Baburd) Khizar Khan
15. Who was the Delhi Sultanate ruler when the Vijayanagara and the Bahmani Kingdoms emerged in South India?
a) Sikandar Lodhib) Ibrahim Lodhic) Baburd) Muhammad bin Tughlaq
16. Who among the following rulers was killed when a wooden pandal erected to welcome him collapsed suddenly?
a) Feroz Shah Tughlaqb) Ghias-ud-din Tughlaqc) Sikandar Lodhid) Muhammad bin Tughlaq
17. Whom did Timur appoint as the king of Delhi in 1414?
a) Daulat Khanb) Khizar Khanc) Nadir Shahd) Malik Kafur
18. The Hindu Kingdom of Vijayanagara was founded by two brothers Harihara and Bukka under the inspiration of their guru. Who was he?
a) Ramanujab) Madhav Vidhyaranyac) Chaitanyad) Sankaracharya
19. Who was the most famous king of the Vijayanagar Empire?
a) Deva Rayab) Krishnadeva Rayac) Achyuta Rayad) Rama Raya
20. Who was the leader of the Hindu revivalist movement known as Bhakti Movement?
a) Ramanujab) Ramanandac) Kabird) Shankaracharya
21. Whose court did the Persian poet Amir Khusru adorn?
a) Ala-ud-din Khiljib) Jalal-ud-din Khiljic) Akbard) Balban
22. Whose court did the famous ‘vidhushaka’ Thenali Raman adorn?
a) Rama Rayab) Krishna Deva Rayac) Deva Raya IId) Achyuta Raya
23. Who is the founder of the philosophy of Vishishtadvaita or qualified monism?
a) Ramanujab) Ramanandac) Kabird) Chaitanya
24. At which of the following places is the tomb of Khwaja-Mouin-ud-din Chisti?
a) Jai Salmerb) Jaipurc) Ajmerd) Lahore
25. Who was the ruler of Bengal who drove Humayun out of Hindustan and crowned himself as the emperor?
a) Sher Shah Surib) Daulat Khanc) Khizar Khand) Ziraj-ud-daulah
Answers
1. Surendra Nath Bannerji2. Malwa3. Khan Abdul Gaffar Khan4. WC Bannerji5. Second Battle of Tarrain6. Qutub-ud-in Aibak7. Nasir-ud-din Mahmud8. Malik Kafur9. Ghias –ud-din Tughlaq10. Ghias –ud-din Tughlaq11. Tughlaq Dynasty12. Mahmud Tughlaq13. Sikandar Lodhi14. Babur15. Muhammad bin Tughlaq16. Ghias-ud-din Tughlaq17. Khizar Khan18. Madhav Vidhyaranya19. Krishnadeva Raya20. Shankaracharya21. Ala-ud-din Khilji22. Krishna Deva Raya23. Ramanuja24. Ajmer25. Sher Shah Suri
---------------
GK - Indian History Quiz 11
1. In the battle of Plassey fought in 1757, Nawab Siraj-ud-daulah of Bengal was defeated by the British forces. Who led the British forces in this battle?
a) Lord Dalhousieb) Lord Clivec) Lord Wellesleyd) Cornwallis
2. East India Company was granted the Diwani of Bengal, Bihar and Orissa after the battle of Buxar in 1764. Who was then the Governor of Bengal?
a) Lord Cliveb) Lord Mintoc) Lord Wellesleyd) Cornwallis
3. The Treaty of Sreerangapatanam was signed after the defeat of Tipu sultan in the Third Anglo-Mysore war. Between whom were this treaty signed?
a) Tipu Sultan and Cornwallisb) Tipu Sultan and Lord Mintoc) Tipu Sultan and Lord Wellesleyd) Tipu Sultan and Lord Canning
4. Who was the first Indian to the elected to the House of Commons?
a) Rash Behari Boseb) Dadabhai Navrojic) Satyendranath Bannerjid) Gopal Krishna Gokhale
5. Who was the first British Governor General of India?
a) Warren Hastingsb) Dalhousiec) Canningd) Clive
6).Which British Governor-General is associated with ‘subsidiary alliance’?
a) Warren Hastingsb) Lord Wellesleyc) Lord Clived) Cornwallis
7. Who was the British Governor –General during the period in which the British Navy conquered Java, Sumatra and Malay Peninsula?
a) Lord Mintob) Lord Wellesleyc) Lord Dalhousied) Warren Hastings
8. The third Anglo-Maratha war, which proved a total disaster for the Marathas, was fought in?
a) 1817 ADb) 1857 ADc) 1912 ADc) 1805 AD
9. During whose tenure was the British supremacy over India established?
a) Lord Wellesleyb) Lord Dalhousiec) Lord Clived) Lord Warren Hastings
10. Who was the British Governor-General of India when Punjab was annexed to the British Empire?
a) Lord Wellesleyb) Lord Dalhousiec) Lord Clived) Lord Warren Hastings
11. Which were the three states annexed to the British Empire under the Doctrine of Lapse?
a) The states of Mumbai, Madras and Calcuttab) The states of Jhansi, Nagpur and Satarac) The states of Mumbai, Thane and Puned) none of these
12. Who was the chief architect, of Prarthana Samaj?
a) Raja Ram Mohan Royb) Mahadev Govind Ranadec) D Savarkard) Surendranath Bannerjee
13. Who was the Governor-General of India when Sind was annexed to the British Empire?
a) Lord Wellesleyb) Ellenboroughc) Lord Clived) Lord Warren Hastings
14. The system of Dual Government is associated with?
a) Lord Wellesleyb) Lord Dalhousiec) Lord Clived) Lord Warren Hastings
15. In which year did most of the Rajput states accept British paramountcy?
a) 1818 ADb) 1827 ADc) 1835 ADd) 1820 AD
16. Who is associated with the institution of organized ‘Civil Services’ in India?
a) Lord Cliveb) Cornwallisc) Lord Dalhousied) Warren Hastings
17. Who abolished the system of Dual Government in Bengal?
a) Lord Cliveb) Cornwallisc) Lord Dalhousied) Warren Hastings
18. Who was the founder of a regular Postal system in British India?
a) Lord Cliveb) Cornwallisc) Lord Dalhousied) Warren Hastings
19. Who is associated with the vigorous application of the Doctrine of Lapse?
a) Lord Cliveb) Cornwallisc) Lord Dalhousied) Warren Hastings
20. In a sense, who was the political guru of Gandhiji?
a) Gopal Krishna Gokhaleb) Leo Tolstoyc) Rabindra Nath Tagored) Raja Ram Mohan Roy
21. Who were the first Europeans to trade with India?
a) The Frenchb) The Dutchc) The Britishd) The Portuguese
22. When was the title of ‘Viceroy’ added to the Governor General of India for the first time?
a) 1857 ADb) 1858 ADc) 1901 ADd) 1900 AD
23. When did the Government of the English East India Company come to an end?
a) 1857 ADb) 1858 ADc) 1901 ADd) 1900 AD
24. Who was the last Governor-General and the first India Viceroy of British India?
a) Lord Cliveb) Cornwallisc) Lord Canningd) Warren Hastings
25. Who was the Governor-General of India when the first war of India’s independence broke out in 1857?
a) Lord Cliveb) Cornwallisc) Lord Canningd) Warren Hastings
Answers
1. Lord Clive2. Lord Clive3. Tipu Sultan and Cornwallis4. Dadabhai Navroji5. Warren Hastings6. Lord Wellesley7. Lord Minto8. 1817 AD9. Lord Dalhousie10. Lord Dalhousie11. The states of Jhansi, Nagpur and Satara12. Mahadev Govind Ranade13. Ellenborough14. Lord Clive15. 1818 AD16. Cornwallis17. Warren Hastings18. Lord Clive19. Lord Dalhousie20. Gopal Krishna Gokhale21. The Portuguese22. 1858 AD23. 1858 AD24. Lord Canning25. Lord Canning
history bits
1. History is the carefully written record of the
(a) Present
(b) Past
(c) Future
2. Languages such as Pali and Prakrit which are no longer spoken are called
(a) Dead language
(b) Vintage language
(c) Classical language
3. The study of inscription is called
(a) Archaeology
(b) Epigraphy
(c) History
4. The Deccan is surrounded by
(a) Mountains on tree sides
(b) Sea on three sides
(c) Plains on three sides
5. In ancient India, the Indo- Gangetic Plain was referred to as
(a) Indus valley
(b) Aryavartha
(c) Dakshinapatha
6. The Palaeolithic Age refers to
(a) The Old Stone Age
(b) The New Stone Age
(c) The Bronze Age
7. Man discovered fire in the
(a) Neolithic Age
(b) Chalcolithic Age
(c) Palaeolithic Age
8. The Chalcolithic Age refers to the
(a) Iron Age
(b) Bronze Age
(c) Copper Age
9. The Indus Valley Civilization flourished
(a) 4,500 years ago
(b) 3,500 years ago
(c) 2,500 years ago
1.(b) 2.(a) 3.(b) 4.(b) 5.(b) 6.(a) 7.(c) 8.(c) 9.(a)
10. The Indus Valley Civilization is also know as the
(a) Vedic Civilization
(b) Harappan Civilization
(c) Classical Civilization
11. The Indus Valley Civilization is know for its
(a) Planned cities
(b) Pictographic script
(c) Code of law
12. Aryans are popularly believed to have come to India from
(a) Central Asia
(b) China
(c) Europe
13. The main source of information about the Early Vedic period is
(a) The Rig-Veda
(b) The Ramayana
(c) The Brahmins
14. The period from 1000 BC to 600 BC is know as the
(a) Early Vedic period
(b) Epic age
(c) Neolithic age
15. The Early Vedic society was divided into four Varnas on the basis of
(a) Occupation
(b) Heredity
(c) Age
16. By 600BC how many mahajanapadas were in northern India
(a) Ten
(b) Fourteen
(c) Sixteen
17. Among these Janapadas which was the most powerful?
(a) Avanthi
(b) Magadha
(c) Sakyas
18. Which of the cities was captured by Bimbisara?
(a) Champa
(b) Rajgriha
(c) Pataliputra
10.(b) 11.(a) 12.(a) 13.(a) 14.(b) 15.(a) 16.(c) 17.(b) 18.(b)-- praveen.yarasani








































